Heart Failure
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how the heart functions, focusing on the blood flow through its chambers and the impact of heart failure. It describes how oxygen-poor and oxygen-rich blood move through the heart and body. The script also covers the causes and effects of heart failure, such as weakened or stiff ventricular walls, and highlights symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, and fluid buildup. Various treatments, including medications, lifestyle changes, and surgeries, are discussed to manage heart failure and improve overall heart function.
Takeaways
- 💓 The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood containing oxygen and nutrients throughout the body.
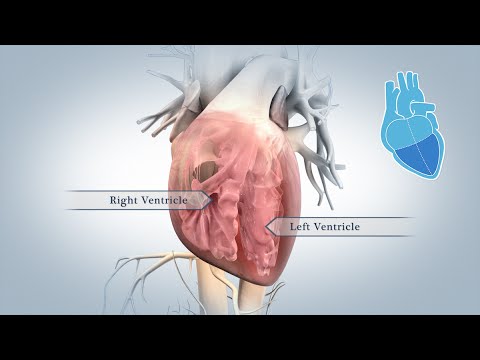
- 🫀 The heart has four pumping sections: right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
- 💨 Oxygen-poor blood flows from the body into the right atrium and ventricle, where it is sent to the lungs to pick up oxygen.
- 🩸 Oxygen-rich blood flows from the lungs to the left atrium and ventricle, then is pumped to the body.
- 😮💨 Left-sided heart failure results in tiredness and shortness of breath due to the left ventricle's inability to pump enough oxygen-rich blood.
- 🌬️ Right-sided heart failure causes fluid buildup (edema) in the body due to the right ventricle’s inability to pump blood to the lungs.
- 📉 Heart failure leads to weakened, enlarged ventricles that pump less blood to the body, worsening over time due to stress hormones.
- 🩺 Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and damaged heart valves or muscles.
- 💊 Treatment for heart failure involves medications (diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta blockers), lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery.
- ⚕️ Advanced treatments include surgeries like coronary artery bypass, valve reconstruction, and even heart transplant for extreme cases.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the heart?
-The heart's primary function is to pump blood, which carries oxygen and nutrients to the body.
What are the main pumping sections of the heart?
-The main pumping sections of the heart are the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
How does oxygen-poor blood travel through the heart?
-Oxygen-poor blood flows from the body into the right atrium, then moves into the right ventricle, which contracts to send blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen.
How does oxygen-rich blood travel through the heart?
-Oxygen-rich blood moves from the lungs into the left atrium, then into the left ventricle, which contracts to send the blood out to the body.
What happens when you have left-sided heart failure?
-In left-sided heart failure, the left ventricle cannot pump enough oxygen-rich blood to the body, causing fatigue, shortness of breath, and fluid buildup in the lungs.
What are the consequences of right-sided heart failure?
-Right-sided heart failure prevents the right ventricle from pushing blood to the lungs, leading to blood buildup in the veins and fluid retention in the body, known as edema.
How does the body try to compensate for heart failure, and why can it worsen the condition?
-The body releases stress hormones to increase heart rate and contraction force, but over time, these hormones damage heart muscle cells, worsening heart failure.
What are some common causes of heart failure?
-Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, damaged heart valves, heart muscle disease, arrhythmias, lung diseases, and sleep apnea.
What are some medical treatments for heart failure?
-Treatments for heart failure include medications such as diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and beta blockers, as well as lifestyle changes, heart-assisting devices, or surgery.
What lifestyle changes are recommended for heart failure patients?
-Heart failure patients are advised to exercise regularly, maintain a healthy weight, quit smoking, limit salt and alcohol, and follow a heart-healthy diet.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)