14 September BE 2567
Summary
TLDRThe transcript discusses a control system lecture focusing on the Pi (Proportional-Integral) controller. It explains the need to determine the range of parameters for system stability using the R-array and R stability criteria. The lecture introduces disturbances and asks students to derive transfer functions, design proportional gains to minimize the effect of disturbances, and analyze system responses. It also touches on the physical concept of balancing, comparing the effectiveness of looking at the top versus the hand when balancing an object like an umbrella, and concludes with a bonus challenge related to a balancing pendulum.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The script discusses the concept of error in control systems and how it should ideally be zero.
- 📚 There's a mention of a PD (Proportional-Derivative) controller problem where the challenge is to compose the R array and find the parameter range for stability.
- 🧮 The Pi (Proportional-Integral) Controller is explained, emphasizing the need to satisfy R criteria for stability.
- 📉 The script simplifies the Pi Controller formula to an exam context, discussing the need to find conditions for system stability.
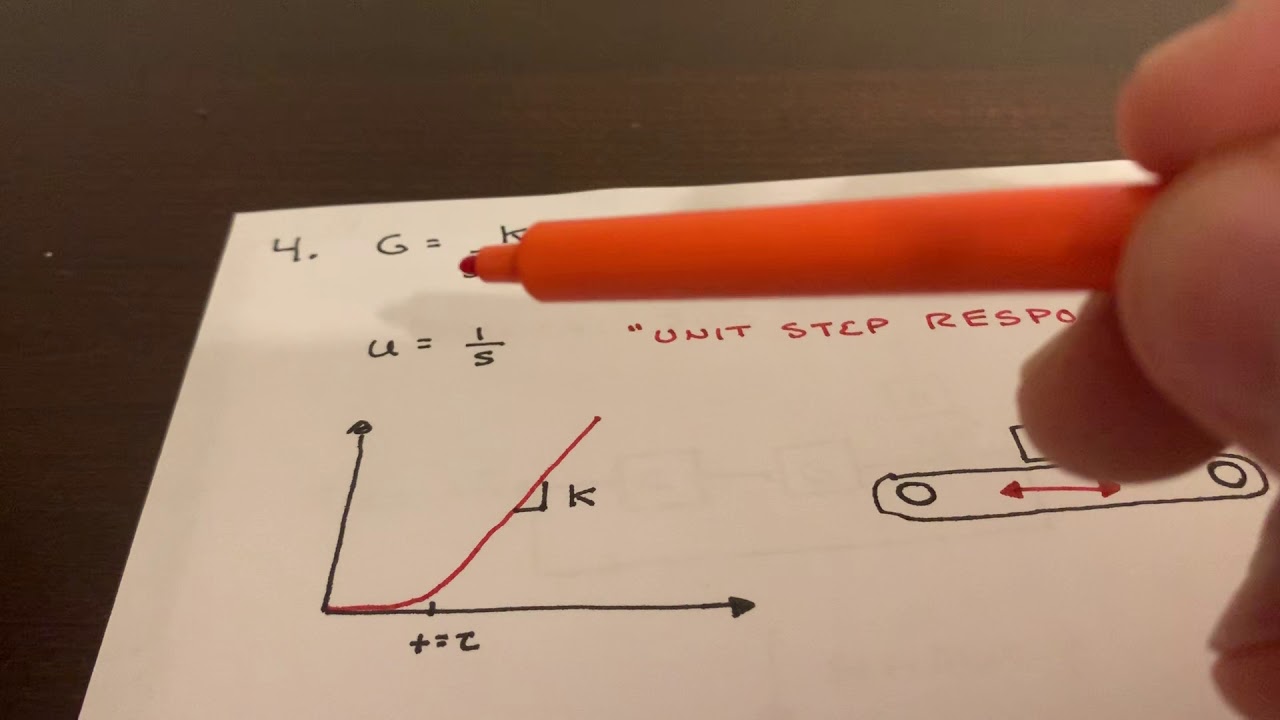
- 📘 Problem 5 introduces the concept of disturbance and asks to derive the transfer function of the output with respect to the disturbance.
- 🎓 The design of a proportional gain (KP) is discussed, with an emphasis on making the system's response to disturbance less than 10%.
- 📝 The script talks about the final value theorem and how it can be used to determine the steady-state response of a system.
- 📊 Question 6 involves obtaining a transfer function and analyzing its response in terms of peak time, setting time, and maximum overshoot.
- 🤔 The script ponders whether to keep certain information secret, suggesting a decision based on who should know the information.
- 🏋️♂️ A balancing challenge is introduced, comparing the strategy of looking at the top versus the hand when balancing a pendulum or an umbrella.
Q & A
What does the term 'PD controller' refer to in the context of the transcript?
-In the transcript, 'PD controller' likely refers to a Proportional-Derivative controller, which is a type of control system that uses the proportional and derivative terms to adjust the control input based on the error signal.
What is the significance of composing the 'R array' in the context of a PI controller?
-Composing the 'R array' in the context of a PI controller is significant for determining the range of the proportional gain (KP) that ensures the system remains stable according to the R stability criteria.
What is the general form of a PI controller as mentioned in the transcript?
-The general form of a PI controller mentioned in the transcript is a combination of a proportional term (KP * Error) and an integral term (KI * integral of Error), where KP and KI are constants.
What is the purpose of using the R stability criteria in the context of the transcript?
-The purpose of using the R stability criteria is to find the conditions, specifically the range of the proportional gain (KP), that keep the system stable when using a PI controller.
How does the introduction of disturbance affect the system as discussed in the transcript?
-The introduction of disturbance in the system, as discussed in the transcript, requires the derivation of the transfer function of the output with respect to the disturbance and the design of a proportional gain (KP) to minimize the effect of the disturbance on the system.
What is the ideal response of the system to disturbance as per the transcript?
-The ideal response of the system to disturbance, as per the transcript, is to have the output (x) divided by the disturbance approach zero, indicating minimal impact of the disturbance on the system's output.
What is the role of the proportional gain (KP) in minimizing the effect of disturbance on the system?
-The role of the proportional gain (KP) is to be designed in such a way that the ratio of the system's output (x) to the disturbance is less than a certain percentage (e.g., 10%), thus minimizing the effect of the disturbance.
What does 'x div by disturbance' refer to in the context of the transcript?
-In the context of the transcript, 'x div by disturbance' refers to the ratio of the system's output (x) to the disturbance, which should be minimized to ensure the system's stability and performance.
What is the significance of the final value theorem mentioned in the transcript?
-The final value theorem mentioned in the transcript is used to determine the steady-state value of the system's output (x) when the input is a step function, which is crucial for analyzing the system's long-term behavior.
What is the challenge presented in the transcript regarding balancing a pendulum?
-The challenge presented in the transcript is to balance a pendulum by looking at the top instead of the hand, which is suggested to be a more successful strategy due to the physical dynamics involved in balancing.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)