Cara Pintar | Memahami Hukum Kirchoff
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Nurul, an expert in physics, introduces viewers to the smart class and shares a quick method for solving Kirchhoff's Law problems. She explains the two laws: Kirchhoff's Current Law and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law, which describe the relationships between current and voltage in electrical circuits. Nurul demonstrates how to apply these laws to analyze a circuit with given voltage sources and resistances, guiding through the process of setting up equations and solving for the unknown currents. The video concludes with a clever shortcut for solving such problems efficiently, encouraging viewers to share, subscribe, and stay tuned for more informative content.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script is a tutorial on Kirchhoff's Laws, presented by Nurul, a physics expert.
- 🔬 Kirchhoff's Laws were first stated by German physicist Gustav Robert Kirchhoff.
- 📚 There are two laws: Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL).
- 💡 KCL states that the sum of currents entering a junction equals the sum of currents leaving the junction.
- 🔋 KVL states that the sum of electromotive forces (EMFs) and voltage drops around a closed loop equals zero.
- 📐 An example circuit is used to demonstrate how to apply KCL and KVL to solve for currents in a network.
- 🔄 The tutorial explains how to determine the direction of loops and currents to apply the laws correctly.
- 🧮 A step-by-step approach is provided to solve a sample problem using traditional methods.
- 🚀 A shortcut method is introduced to quickly solve Kirchhoff's Law problems using a single formula.
- 📉 The shortcut involves calculating the current through a resistor by using the difference in EMF and voltage drops across resistors.
- 📝 The tutorial concludes with a reminder to share, subscribe, and turn on notifications for more informative content.
Q & A
Who introduced Kirchhoff's laws?
-Kirchhoff's laws were introduced by the German physicist Gustav Robert Kirchhoff.
What do Kirchhoff's laws explain?
-Kirchhoff's laws explain how to analyze the relationship between current and voltage in an electrical circuit.
What is Kirchhoff's first law?
-Kirchhoff's first law states that the sum of currents entering a junction is equal to the sum of currents leaving the junction.
How is Kirchhoff's first law mathematically represented?
-Mathematically, Kirchhoff's first law can be represented as ΣI_in = ΣI_out, where I_in represents the currents entering a junction and I_out represents the currents leaving the junction.
What is Kirchhoff's second law?
-Kirchhoff's second law states that the sum of the potential rises and drops around a closed loop in a network is zero.
How is Kirchhoff's second law mathematically expressed?
-Mathematically, Kirchhoff's second law can be expressed as ΣE - ΣI*R = 0, where E represents the electromotive force (emf), I is the current, and R is the resistance.
What are the steps to solve a problem using Kirchhoff's laws?
-The steps include determining the direction of loops and currents, applying Kirchhoff's first law at junctions to get equations, and applying Kirchhoff's second law around loops to get additional equations, then solving the system of equations.
Why is it recommended to choose the direction of loops in a consistent manner?
-It is recommended to choose the direction of loops consistently, preferably in the same direction, to simplify the calculations and avoid confusion when applying Kirchhoff's laws.
What is the significance of the direction of current relative to the loop direction in Kirchhoff's laws?
-The direction of current relative to the loop direction affects the sign of the voltage drops and rises in the equations. If they are in the same direction, the voltage is positive; if they are opposite, it is negative.
How can one quickly solve a problem involving Kirchhoff's laws as demonstrated in the script?
-A quick method demonstrated in the script involves directly applying a formula derived from Kirchhoff's laws to find the current through a specific resistance without going through multiple steps.
What is the shortcut formula mentioned in the script for solving problems related to Kirchhoff's laws?
-The shortcut formula mentioned in the script is I3 = (E3 - E2*R1 + E3*R2) / (R1 + R2 + R3), which is used to quickly find the current through a 5Ω resistor in a given circuit.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

FISIKA KELAS XI | TEORI KINETIK GAS (PART 2) - Persamaan Gas Ideal
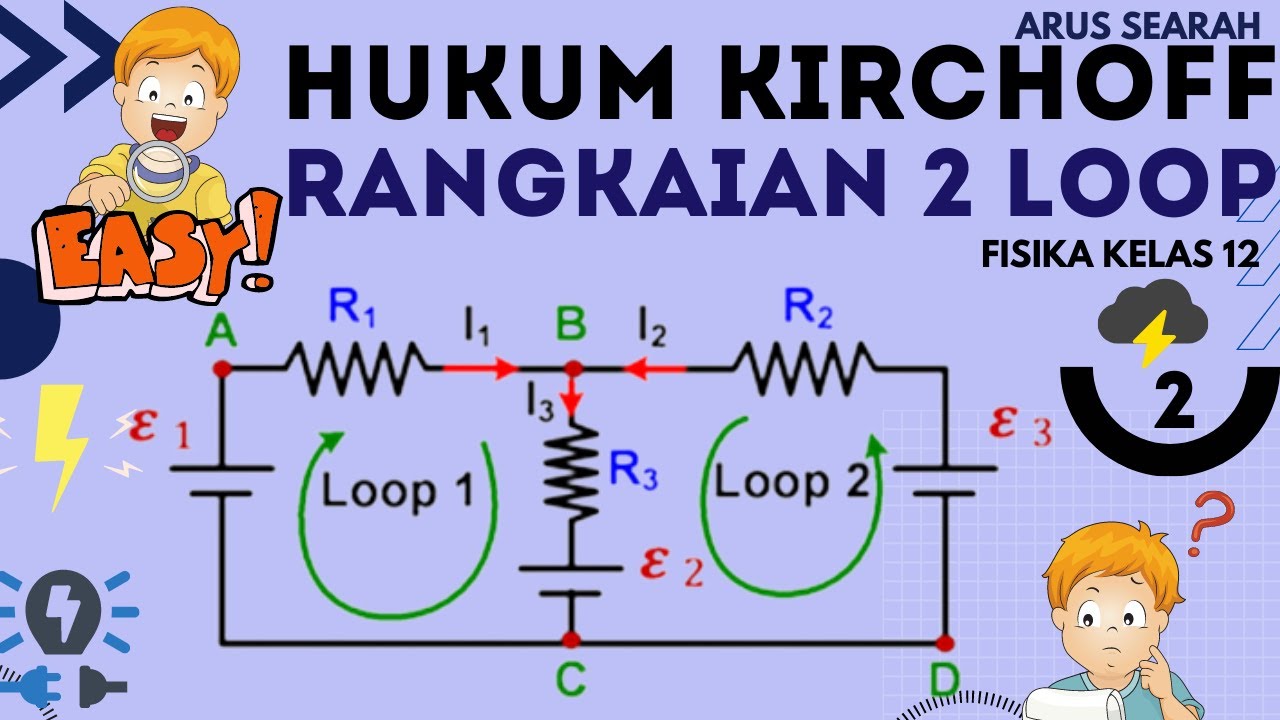
Hukum Kirchhoff Rangkaian 2 Loop : [CARA CEPAT] - Listrik Dinamis Fisika Kelas 12 Part 2

Cara Pintar | Persoalan Cahaya dan Alat Optik
HUKUM II KIRCHHOFF

Basic Circuits Math - Using Substitution and Matrices to Solve Circuits Equations
Nodal Analysis EP.16 (Tagalog/English Electronics)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)