HUKUM II KIRCHHOFF
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into Kirchhoff's Laws, specifically focusing on Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL). It explains how the sum of potential differences in a closed circuit equals zero, indicating no energy loss within the circuit. The script guides viewers through applying KVL to analyze circuits, using illustrations to clarify concepts. It also outlines rules for determining the direction of loops and the sign of voltage drops, crucial for solving electrical circuit problems. The tutorial aims to simplify the understanding and application of KVL, encouraging viewers to engage with the material and seek further clarification if needed.
Takeaways
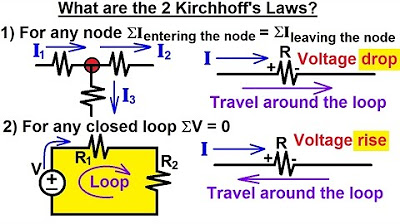
- 😀 The video discusses the second law of Kirchhoff, also known as Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL), which states that the sum of the voltages in a closed circuit is equal to zero.
- 🔌 The law applies to non-branching circuits, as opposed to the first law of Kirchhoff, which deals with current in branching circuits.
- 🔋 Kirchhoff's second law is fundamental in analyzing the potential difference in a closed electrical circuit, ensuring that the total energy in the circuit is conserved with no energy being lost.
- 📚 The mathematical representation of KVL is given by the equation ΣV = 0, where V represents the voltage drops and sources in the circuit.
- 👉 The direction of the loop in the circuit can be chosen arbitrarily, but it's recommended to align it with the direction of the current for ease of calculation.
- ⚡ When the direction of the loop is the same as the direction of the current, the voltage drop is considered positive; if opposite, it is negative.
- 🔄 If the loop encounters a positive terminal first, the electric current direction should also be positive; conversely, if a negative terminal is encountered first, the current direction should be negative.
- 📉 The law helps in solving for unknown currents and voltages in electrical circuits by setting up equations based on the conservation of energy.
- 📝 An example problem is solved in the script, demonstrating how to apply KVL to find the current flowing through a circuit with given resistors and voltage sources.
- 🤔 The video encourages viewers to ask questions if they have difficulties understanding the material, offering multiple communication channels for clarification.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the script?
-The main topic discussed in the script is Kirchhoff's laws, specifically focusing on Kirchhoff's second law, also known as Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL).
What is Kirchhoff's first law about?
-Kirchhoff's first law, also known as Kirchhoff's current law (KCL), states that the total current entering a junction in a circuit is equal to the total current leaving the junction.
What does Kirchhoff's second law (KVL) imply about the sum of the voltages in a closed circuit?
-Kirchhoff's second law (KVL) implies that the sum of the voltages (potential differences) in a closed circuit is equal to zero, indicating that there is no loss of energy in the circuit.
What is the mathematical expression for Kirchhoff's second law in terms of voltages?
-The mathematical expression for Kirchhoff's second law is ΣV = 0, where the sum of all the voltages (potential differences) around a closed loop is zero.
How does the script differentiate between the application of Kirchhoff's first and second laws?
-The script differentiates by stating that Kirchhoff's first law is applied to circuits with branches (junctions), while the second law is applied to analyze the potential differences in a closed circuit without branches.
What is the significance of the direction of the loop in applying Kirchhoff's second law?
-The direction of the loop is significant because it determines the sign of the potential difference when applying Kirchhoff's second law. If the loop direction is the same as the current flow, the potential difference is positive; if opposite, it is negative.
What is the practical application of Kirchhoff's laws in solving electrical circuit problems?
-Kirchhoff's laws are used to analyze and solve complex electrical circuits by providing a systematic method to calculate unknown currents and voltages in the circuit.
How does the script suggest determining the direction of the current flow for easier calculations?
-The script suggests that for easier calculations, the direction of the loop should preferably be the same as the direction of the current flow, although it can be chosen freely.
What is the importance of understanding the sign of the potential difference in a circuit?
-Understanding the sign of the potential difference is important because it indicates whether the energy is being absorbed or supplied in a part of the circuit, which is crucial for correctly applying Kirchhoff's second law.
Can you provide an example from the script where Kirchhoff's second law is applied to calculate the current in a circuit?
-Yes, the script provides an example with three resistors (R1=2Ω, R2=6Ω, R3=4Ω) and two voltage sources (6V and 12V). It uses Kirchhoff's second law to set up an equation and solve for the current, which is found to be 0.5 amperes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

KVL and KCL (Circuits for Beginners #11)
Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (8 of 31) What Are Kirchhoff's Laws?
Chapter 2 - Fundamentals of Electric Circuits

Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (11 of 31) Kirchhoff's Laws: A Medium Example 2

Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) - How to Solve Complicated Circuits | Basic Circuits | Electronics

Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) Explained
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)