Why the Supreme Court Endorsed, Then Limited Affirmative Action | Retro Report
Summary
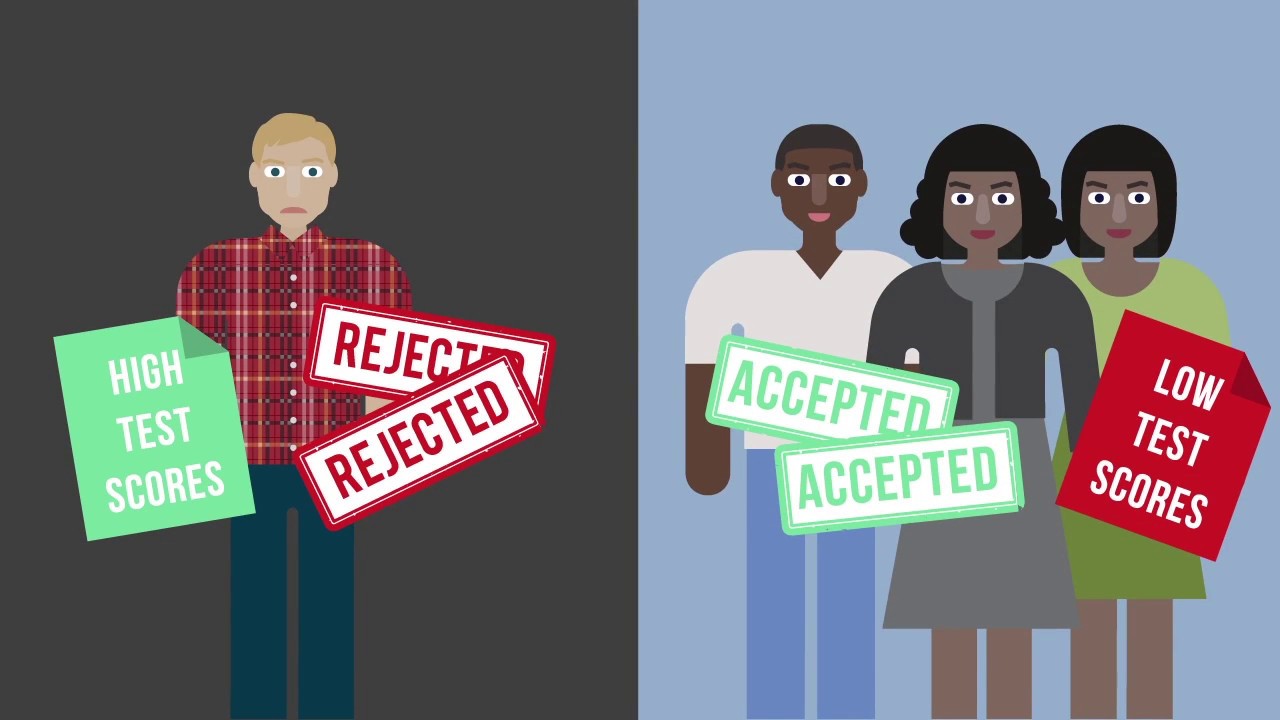
TLDRThe video script discusses the contentious issue of affirmative action in US college admissions, focusing on the Supreme Court's 2023 decision to strike down race-based admissions at Harvard and the University of North Carolina. It features Muskaan Arshad, an Asian American activist from Arkansas, who shares her experiences of racial discrimination and the importance of considering race in college applications for a diverse student body. The script also covers the legal challenges led by Edward Blum, who argues that affirmative action is unconstitutional and discriminatory, particularly against Asian Americans. The debate is set against the backdrop of historical Supreme Court cases and the ongoing struggle for racial equity in education.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Muskaan Arshad, an Asian American activist from Arkansas, played a role in the removal of a Confederate statue in Bentonville Square and faced racial challenges growing up.
- 📚 Muskaan's college application to Harvard highlighted how her race defined her experiences, emphasizing the importance of diversity in admissions.
- 🏛 The Supreme Court's 2023 decision struck down race-based admissions programs at Harvard and the University of North Carolina, viewing such efforts as unconstitutional.
- 📖 Edward Blum, behind the Supreme Court cases, has a history of challenging affirmative action, arguing it is unfair and unconstitutional.
- 📉 The ruling could potentially impact the diversity of student bodies in universities, as seen in California's experience post-affirmative action ban where African American representation dropped.
- 🤔 The debate over affirmative action is complex, with some arguing it's necessary for minority opportunities, while others see it as discriminatory.
- 👨🎓 Michael Wang, an Asian American student, filed complaints against Harvard for alleged discrimination, sparking a broader conversation within the Asian American community.
- 🏢 The case against Harvard also brought attention to the potential for elite universities to discriminate against Asian Americans, despite the policy's intent to promote diversity.
- 🤝 The Supreme Court's decision has been divisive, with some seeing it as a step towards colorblind admissions, while others argue it undermines efforts to address systemic inequalities.
- 🌈 Muskaan Arshad and others argue for the importance of maintaining diversity in higher education, believing that race-conscious admissions are crucial for equal opportunity.
Q & A
What was previously located at Bentonville Square before the sunflower bed?
-There used to be a Confederate statue housed at Bentonville Square.
Why did Muskaan Arshad become a social activist?
-Muskaan Arshad became a social activist due to her own challenges growing up as an Asian American in Arkansas, where she experienced racial discrimination.
How did Muskaan Arshad's race impact her childhood experiences?
-Muskaan Arshad's race defined her experiences growing up, and she felt that being brown, Indian, and Asian American was not accepted, as evidenced by an incident in class where no one would hold her hand due to her skin color.
What was the significance of Muskaan Arshad's college application essay?
-Muskaan Arshad's college application essay was significant because it highlighted how race was an essential part of her identity and experiences, which she believed was crucial for painting a full picture of who she was.
What Supreme Court decision in 2023 affected affirmative action policies?
-In June 2023, the Supreme Court delivered a decision that struck down race-based admissions programs at Harvard and the University of North Carolina, ruling that their efforts to create racially diverse campuses were unconstitutional.
Who is Edward Blum and what is his stance on affirmative action?
-Edward Blum is the man behind the Supreme Court cases challenging affirmative action. He has spent decades seeding lawsuits to challenge affirmative action practices, arguing that they are inherently unfair, polarizing, and unconstitutional.
What was the argument in the lawsuit against Harvard and the University of North Carolina Chapel Hill?
-The argument in the lawsuit against Harvard and the University of North Carolina Chapel Hill was that elite universities were using affirmative action policies to discriminate against Asian Americans.
What was Michael Wang's experience with Harvard's admissions process?
-Michael Wang was rejected by Harvard despite having an impressive resume, including singing at Obama's inauguration and winning multiple speech and debate awards. He suspected that being Asian American might have disadvantaged him in the admissions process.
How did the Supreme Court's decision in Grutter v. Bollinger in 2003 impact affirmative action?
-The Supreme Court's decision in Grutter v. Bollinger upheld the use of affirmative action to racially diversify universities, stating that student body diversity is a compelling state interest that can justify the narrowly tailored use of race in admissions.
What was Sandra Day O'Connor's position on affirmative action, and what did she include in her ruling that was considered a 'ticking time bomb'?
-Sandra Day O'Connor supported a limited kind of affirmative action in higher education that didn't have a fixed quota and considered each applicant as an individual. In her ruling, she included a statement that anticipated the end of the need for affirmative action in 25 years, which was seen as a 'ticking time bomb' because it set an expiration date for the policy.
What concerns do universities have following the Supreme Court's ruling on affirmative action?
-Universities are concerned that the ruling may hamper their efforts to diversify their student bodies and may face an increase in litigation over their implementation of admissions policies.
How does Muskaan Arshad view the role of race-conscious admissions in higher education?
-Muskaan Arshad believes that race-conscious admissions are necessary to account for the disparities in opportunities and to address systemic issues that still exist, even if society tries to pretend that race doesn't matter.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Regents of University of California v. Bakke Case Brief Summary | Law Case Explained

Affirmative action in college admissions

How Asian Americans Became The Center Of The Affirmative Action Debate

Affirmative Action vs. Race-Neutral Admissions: A Case Study | WSJ

DeFunis v. Odegaard Case Brief Summary | Law Case Explained

Kl university Vijayawada | how to join in college & university | #telugu #nikasnikki
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)