What If a Simple Blood Test Could Detect Cancer? | Hani Goodarzi | TED
Summary
TLDRScientists have identified 'orphan non-coding RNAs' or oncRNAs, a new class of small RNAs not coding for proteins, which are unique to cancer cells. These oncRNAs can be detected in blood samples, forming a molecular barcode for each cancer type. Leveraging AI, partial oncRNA barcodes in blood can be used to reconstruct the full barcode, aiding in early cancer detection and identification. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize cancer screening, making it more precise, sensitive, and accessible.
Takeaways
- 🔍 **Early Cancer Detection**: Identifying cancer in its earliest stages is crucial for treatment and saving lives.
- 🧬 **RNA's Role**: RNA, particularly non-coding RNAs, plays a significant role in cancer detection.
- 🌟 **Discovery of oncRNAs**: A new class of non-coding RNAs, termed oncRNAs, has been discovered that is specific to cancer cells.
- 🔬 **Transformation in Detection**: The discovery of oncRNAs has revolutionized the approach to non-invasive cancer detection from blood samples.
- 🧐 **Cancer Cell Biology**: oncRNAs provide insights into the biology of cancer cells, offering a window into tumor behavior.
- 🧬 **Genomic Reprogramming**: Cancer cells reprogram their genomic machinery, leading to the activation of silent parts of the genome and the creation of oncRNAs.
- 📖 **Digital Molecular Barcode**: oncRNAs act as a unique digital molecular barcode for different types or subtypes of cancer.
- 🩸 **Blood Sample Detection**: oncRNAs can be detected in blood samples, indicating the presence of cancer.
- 🤖 **AI and Machine Learning**: Machine learning and AI are used to reconstruct the full oncRNA barcode from partial information in blood samples.
- 🏥 **Clinical Application**: Preliminary studies have shown the potential of using oncRNAs to detect residual disease in breast cancer patients post-treatment.
- 🌐 **Future of Cancer Screening**: The speaker envisions a future where blood detection of cancers is precise, sensitive, and accessible.
Q & A
What is the significance of detecting cancer at its earliest stages?
-Detecting cancer early is crucial because it is when it is most treatable, potentially saving countless lives by allowing for more effective interventions.
How does RNA relate to the detection of cancer?
-RNA, particularly messenger RNA, is transcribed from DNA and serves as a template for protein synthesis. The discovery of a new class of non-coding RNAs, called oncRNAs, has transformed cancer detection approaches.
What are oncRNAs and why are they significant in cancer research?
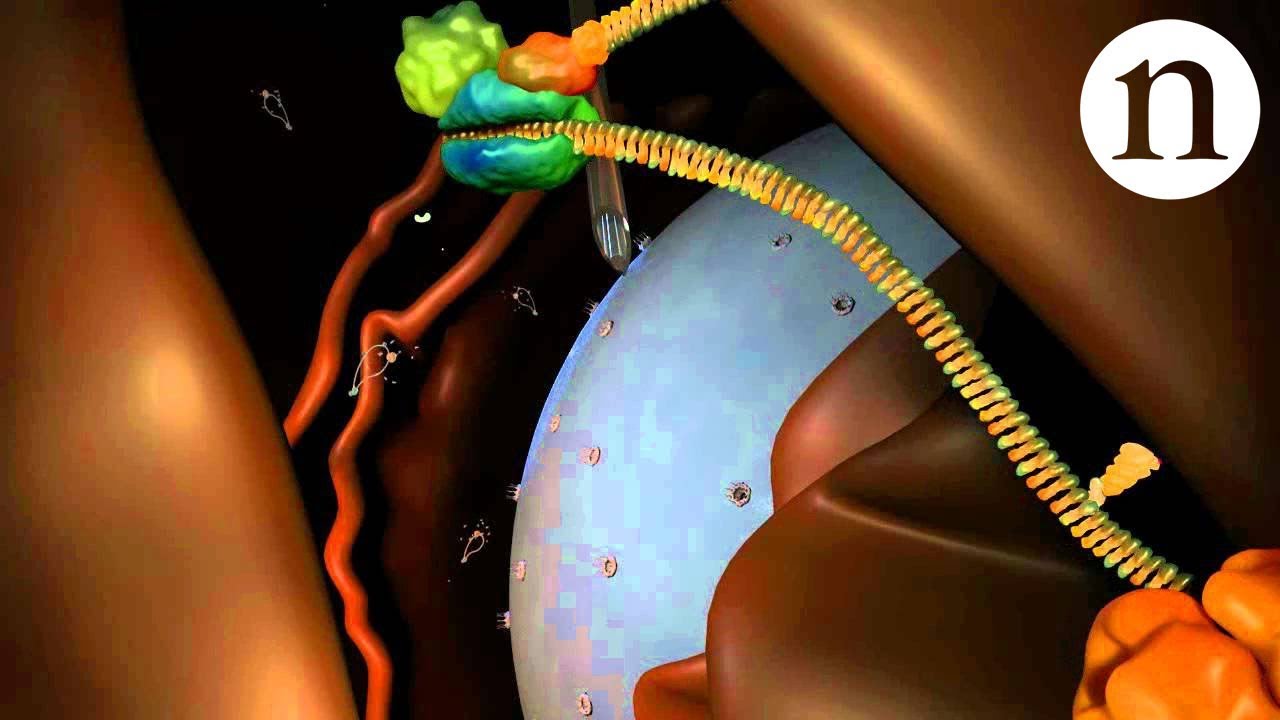
-OncRNAs, short for orphan non-coding RNAs, are small RNAs that do not code for proteins. They are significant because they are uniquely expressed in cancer cells and can serve as molecular barcodes for identifying the type or subtype of cancer.
How do oncRNAs change the approach to cancer detection?
-OncRNAs allow for non-invasive detection of cancer through blood samples. They provide a digital molecular barcode that captures the identity of cancer cells, which can be detected and analyzed to identify the presence and type of cancer.
How do cancer cells hijack the cell's machinery to their advantage?
-Cancer cells hijack the cell's machinery by increasing the expression of genes that promote tumor growth and spread, while silencing or down-regulating genes that normally keep cancer in check.
What is the role of genomic reprogramming in cancer cells?
-Genomic reprogramming in cancer cells involves the activation of parts of the genome that are normally silent in healthy cells, leading to the production of oncRNAs, which are unique to cancer.
How can oncRNAs found in blood samples be used for cancer detection?
-Although only a subset of oncRNAs are secreted into the blood, their presence can be detected in blood samples. Machine learning and AI can use this partial information to reconstruct the full oncRNA barcode and identify the type of cancer.
What is the potential impact of oncRNA-based cancer detection on clinical practice?
-OncRNA-based detection can help identify residual disease in patients post-treatment, guiding clinicians on who needs additional treatment or monitoring. This can lead to more targeted and effective cancer care.
How does the speaker envision the future of cancer screening with oncRNAs?
-The speaker envisions a future where blood detection of cancers becomes a reality, leveraging AI and oncRNA molecular barcodes to create a precise, sensitive, and accessible cancer screening method.
What is the significance of the preliminary study conducted on breast cancer patients?
-The preliminary study on breast cancer patients demonstrated the potential of using oncRNAs to detect residual disease post-treatment, which is a significant step towards bringing this technology to clinical use.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

ncRNAs - all types of non-coding RNA (lncRNA, tRNA, rRNA, snRNA, snoRNA, siRNA, miRNA, piRNA)

Gene Silencing by Micro RNA - Medical Animation

Non coding RNA types, features and function. miRNA, siRNA, lncRNA, piRNA, snRNA, snoRNA, rRNA, tRNA.

Generation and action of siRNAs and miRNAs

Epigenética
RNA interference (RNAi): by Nature Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)