FISIKA Kelas 12 - Gaya Magnetik | GIA Academy
Summary
TLDRThis YouTube video from Gia Akademi explores the concept of magnetic force, also known as the Lorentz force. Discovered by Dutch physicist Hendrik Antoon Lorentz, it's the force exerted by a magnetic field on an electric current. The video explains how to determine the direction of the Lorentz force using the right-hand rule and discusses its applications in various scenarios, including a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field, a charged particle moving in a magnetic field, and parallel wires carrying current. It also covers the calculations for the force's magnitude and direction, providing examples and solving problems to deepen understanding.
Takeaways
- 🔊 The script introduces the concept of magnetic force, also known as Lorentz force, which is generated by a magnetic field on an electric current.
- 🧲 Lorentz force is named after the Dutch physicist Hendrik Antoon Lorentz, who defined it as the force exerted by a magnetic field on an electric current.
- ✋ The direction of the Lorentz force can be determined using the right-hand rule, where the thumb indicates the direction of the electric current, the index finger shows the direction of the magnetic field, and the middle finger points in the direction of the force.
- 💡 The Lorentz force can be generated by a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field, a charged particle moving in a magnetic field, or a current-carrying wire parallel to another current-carrying wire.
- 📐 The formula for Lorentz force on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field is \( F = B \cdot I \cdot L \cdot \sin(\theta) \), where \( F \) is the force, \( B \) is the magnetic field, \( I \) is the current, \( L \) is the length of the wire, and \( \theta \) is the angle between the field and the current.
- 🚫 If the magnetic field is parallel to the electric current, the Lorentz force is zero, indicating no force is exerted on the wire.
- 🌀 For a charged particle moving in a magnetic field, the Lorentz force can cause the particle to move in a circular path, with the force providing the centripetal force necessary for this motion.
- 🔗 The magnitude of the Lorentz force between two parallel current-carrying wires depends on the direction of the currents; parallel currents attract each other, while anti-parallel currents repel.
- 📚 The script provides several examples and problems to illustrate the calculation of Lorentz force in different scenarios, helping viewers to understand and apply the concept.
- 🎓 The video concludes with a summary and an invitation to watch more videos on the channel, emphasizing continuous learning and engagement.
Q & A
What is the Lorentz force?
-The Lorentz force, also known as the magnetic Lorentz force, is the combination of electric and magnetic force on a charged particle moving through a magnetic field. It is given by the equation F = q(E + v × B), where q is the charge, E is the electric field, v is the velocity of the particle, and B is the magnetic field.
Who discovered the Lorentz force?
-The Lorentz force was discovered by the Dutch physicist Hendrik Antoon Lorentz.
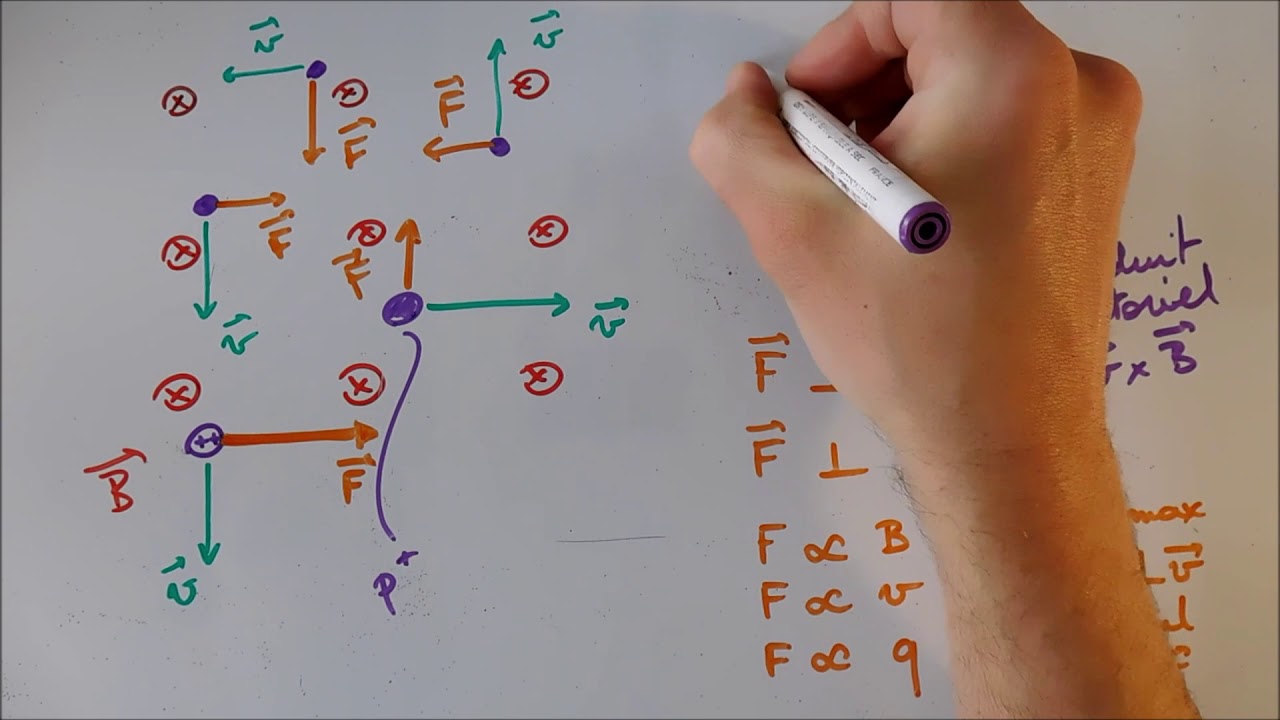
How can you determine the direction of the Lorentz force using the right-hand rule?
-Using the right-hand rule, if you point your thumb in the direction of the electric current (I), your index finger in the direction of the magnetic field (B), then your middle finger will point in the direction of the Lorentz force (F).
What is the formula for calculating the Lorentz force on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field?
-The formula for calculating the Lorentz force (F) on a current-carrying wire of length (l) in a magnetic field (B) with current (I) is F = B * I * l * sin(θ), where θ is the angle between the direction of the current and the magnetic field.
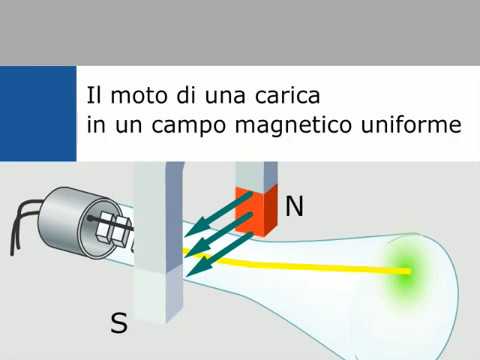
What happens when a charged particle moves through a uniform magnetic field?
-When a charged particle with charge (Q) moves with velocity (V) through a uniform magnetic field (B), it experiences a Lorentz force that is perpendicular to both the velocity and the magnetic field, causing the particle to move in a circular path.
What is the relationship between the radius of the path of a charged particle in a magnetic field and the Lorentz force?
-The radius (r) of the path of a charged particle in a magnetic field is related to the Lorentz force by the equation r = m * v / (q * B), where m is the mass of the particle, v is its velocity, q is its charge, and B is the magnetic field strength.
How can you calculate the force between two parallel current-carrying wires in a magnetic field?
-The force (F) between two parallel current-carrying wires carrying currents I1 and I2, separated by a distance a in a magnetic field, can be calculated using the formula F = (μ0 * I1 * I2 * l) / (2π * a), where μ0 is the permeability of free space.
What is the significance of the angle between the direction of the current and the magnetic field in the Lorentz force?
-The angle between the direction of the current (I) and the magnetic field (B) is significant because the Lorentz force is maximized when this angle is 90 degrees (sin(90) = 1) and is zero when the current and magnetic field are parallel (sin(0) = 0).
How does the sign of the charge affect the direction of the Lorentz force?
-The sign of the charge affects the direction of the Lorentz force. For a positive charge, the force is in the direction of the cross product of the velocity and magnetic field, while for a negative charge, the force is in the opposite direction.
What is the formula for calculating the magnetic field strength if the Lorentz force, charge, velocity, and angle are known?
-If the Lorentz force (F), charge (Q), velocity (V), and angle (θ) are known, the magnetic field strength (B) can be calculated using the formula B = F / (Q * V * sin(θ)).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

GAYA LORENTZ KELAS 9 (MEMBUKTIKAN ADANYA GAYA LORENTZ)

Gaya Lorentz

Materi Kemagnetan Kelas 9 (Part-3) Induksi Magnet dan Gaya Lorentz
TEORIA Moto di una carica in un campo magnetico uniforme AMALDI ZANICHELLI
Force électromagnétique - 1: Force de Lorentz

FISIKA Kelas 12 - Induksi Elektromagnetik: Induktansi Diri | GIA Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)