How Things Are Made | An Animated Introduction to Manufacturing Processes
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful overview of key manufacturing processes, breaking them down into six main categories: forming, casting, molding, machining, joining, and additive manufacturing. It explains the various techniques within each category, such as forging, die casting, injection molding, and 3D printing, highlighting their applications, benefits, and limitations. The video emphasizes the factors influencing the selection of manufacturing processes, such as material type, object geometry, and production scale. Whether you're curious about how everyday products are made or seeking to understand industrial processes, this video offers a comprehensive look into the world of manufacturing.
Takeaways
- 😀 Manufacturing processes can be divided into six main categories: forming, casting, moulding, joining, machining, and additive manufacturing.
- 😀 Factors like material type, object geometry, production quantity, and cost play a key role in selecting the right manufacturing process.
- 😀 Forming involves applying force to deform material, often used with metals, and can be done either hot (easier to deform) or cold (increases strength).
- 😀 Common forming processes include forging, rolling, and extrusion, with each having specific advantages like improved mechanical properties or tight tolerances.
- 😀 Casting is a primary shaping process where molten metal is poured into a mold and solidified, with types like die casting, sand casting, and investment casting.
- 😀 Die casting is great for high-volume production with excellent surface finish but has high start-up costs.
- 😀 Sand casting is cost-effective for small production runs but results in a poorer surface finish and less accuracy.
- 😀 Investment casting is good for complex geometries and tight tolerances but is slow and expensive.
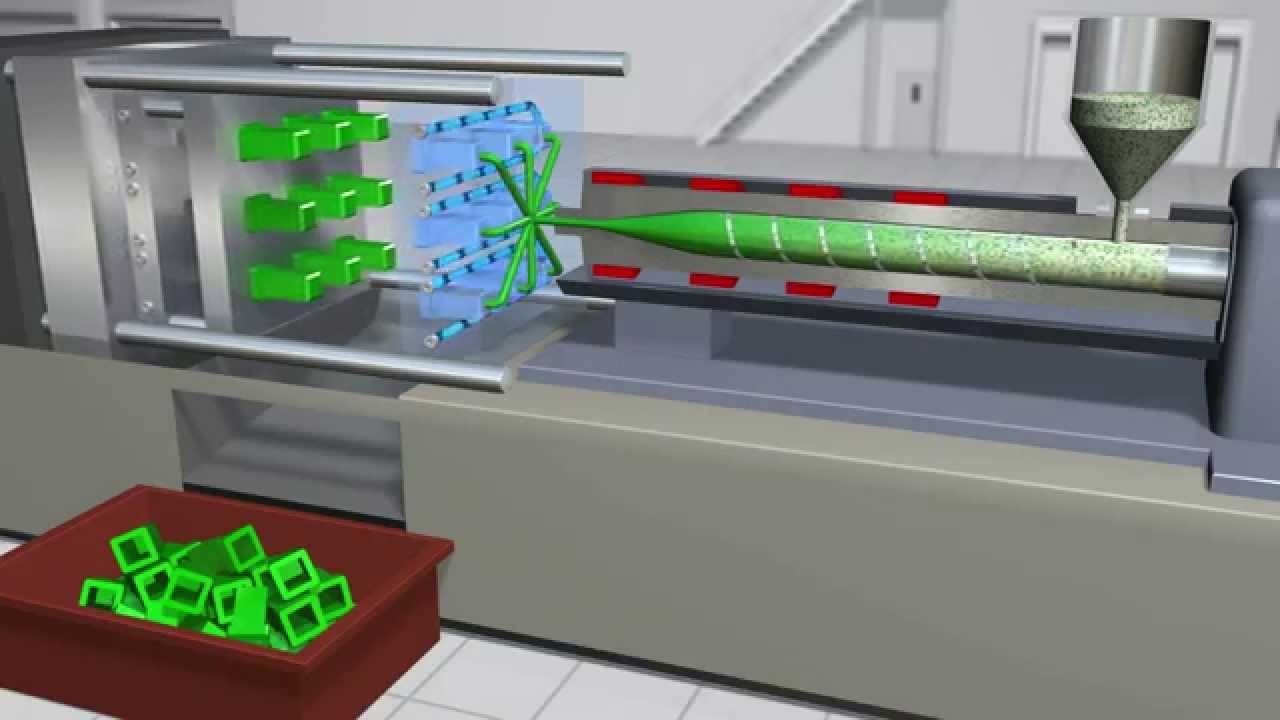
- 😀 Molding, primarily used for plastics, involves shaping liquid or pliable material using molds, with injection molding and compression molding being the most common.
- 😀 Additive manufacturing (like 3D printing) builds objects layer by layer and is ideal for prototyping, though it’s slow and limited in material options.
Q & A
What are the six main categories of manufacturing processes?
-The six main categories of manufacturing processes are forming, casting, moulding, joining, machining, and additive manufacturing.
What factors should be considered when selecting a manufacturing process?
-Factors to consider when selecting a manufacturing process include the material being used, the geometry of the object, the number of parts being produced, tool and material costs, and required levels of automation.
What is the difference between hot working and cold working in forming processes?
-Hot working involves deforming metal above its recrystallization temperature, making it easier to shape. Cold working is done below the recrystallization temperature and results in strain hardening, which increases the strength of the material.
What are three common forming processes, and what is unique about each?
-The three common forming processes are forging, rolling, and extrusion. Forging involves using hammers to shape metal, rolling reduces thickness by passing metal through rollers, and extrusion forces hot metal through a die to create long objects with a constant cross-section.
What is the key advantage of extrusion in manufacturing?
-Extrusion provides an excellent surface finish and can achieve very tight tolerances. It is ideal for producing long objects with a constant cross-section.
What is die casting, and when is it used?
-Die casting involves forcing molten metal into reusable metal dies at high pressure. It is primarily used for non-ferrous metals like aluminum and zinc and is suitable for large production runs due to its high initial costs.
What is the main difference between sand casting and investment casting?
-Sand casting uses a damp sand mold for one-time use, while investment casting creates a ceramic mold around wax patterns, which are melted out before pouring molten metal. Investment casting offers tight tolerances and is good for complex geometries, but it is more expensive and time-consuming.
How does injection molding differ from compression molding?
-Injection molding involves forcing thermoplastic polymer granules into a mold under pressure, while compression molding places a specific amount of thermoset material into a mold and applies pressure and heat. Injection molding is faster and more automated, whereas compression molding is slower but better for small production runs.
What is the purpose of machining in manufacturing processes?
-Machining is a material removal process used to shape an object by removing material from a larger piece. It is often used as a secondary shaping method after a primary process like casting.
What are the types of joining processes, and what distinguishes welding from brazing and soldering?
-Joining processes include welding, riveting, brazing, soldering, and fastening. Welding involves melting the base metal to fuse parts together, whereas brazing and soldering use lower temperatures and do not melt the base metal.
How does additive manufacturing work, and when is it typically used?
-Additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer by adding material. It is a slower process with limited material options and is typically used for prototyping rather than mass production.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Process Equipment

INJECTION MOLDING - DEFINISI, CARA KERJA, DAN BAGIAN-BAGIAN MESIN INJECTION MOLDING

8. VÍDEO - Processos Físicos Industriais

How 3D printing is enabling the ‘4th Industrial Revolution’ | Dr. Tim Minshall | TEDxOxBridge
Plastic Processing Overview

Materiais e Processos de Fabricação para Engenharia de Produção - Propriedades do Materiais
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)