Embryology | Mesoderm
Summary
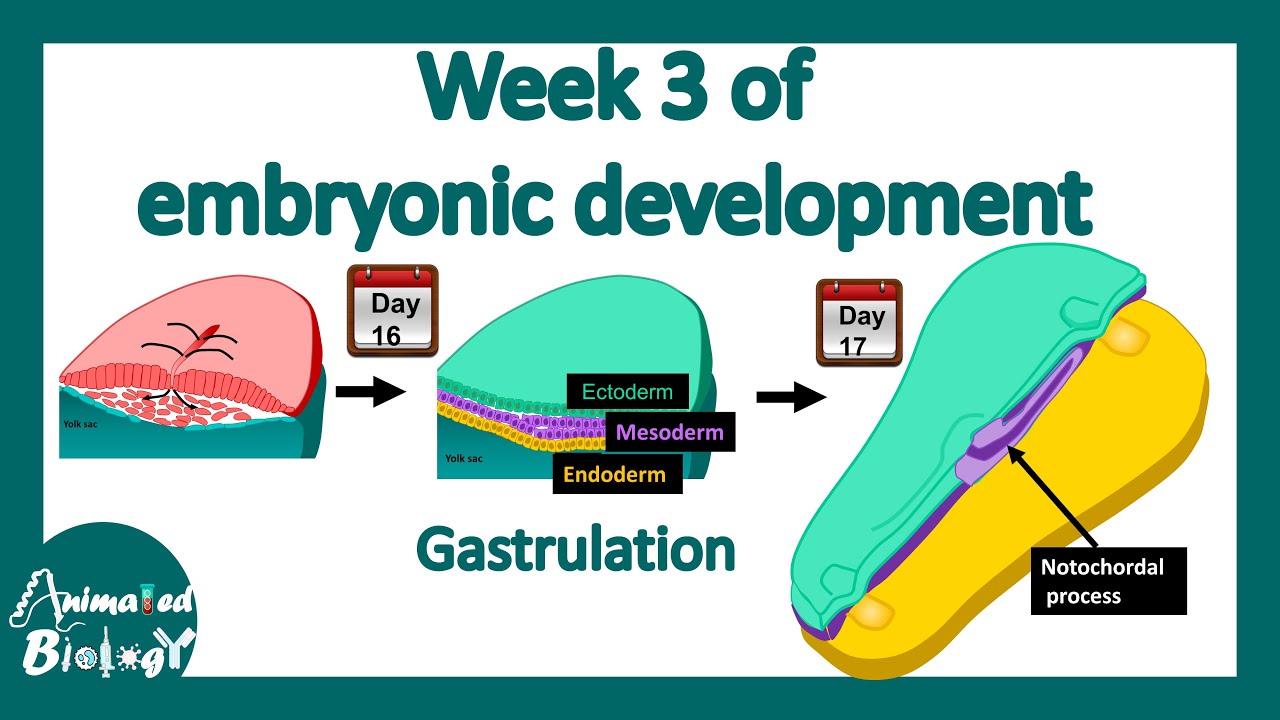
TLDRIn this educational video, the focus is on the development of the mesoderm, a critical layer in embryonic growth. The script explains the gastrulation process, transitioning from a bilaminar to a tri-laminar disc, and the formation of the mesoderm between the epiblast and endoderm layers. It details the分化 of mesoderm into various structures including somites, which further develop into dermatome, myotome, and sclerotome, contributing to skin, muscle, and bone formation. The video also covers the roles of paraxial, intermediate, and lateral plate mesoderm in creating essential body components like the renal system, gonads, and cardiovascular system. A mnemonic 'ENGINEERS' is introduced to help remember the derivatives of mesoderm.
Takeaways
- 🌟 The video discusses the formation and differentiation of mesoderm, a middle layer in embryonic development.
- 🕵️♂️ Gastrulation is a key process that transforms a bilaminar disc into a tri-laminar disc, involving the epiblast and hypoblast layers.
- 🔍 The primitive streak and node are critical areas where epiblast cells migrate to form the mesoderm layer.
- 🌱 Growth factors like fibroblast growth factor 8 play a role in directing cell migration during gastrulation.
- 🐌 The mesoderm differentiates into three main regions: paraxial, intermediate, and lateral plate mesoderm, each with distinct developmental roles.
- 🦴 The paraxial mesoderm gives rise to structures like somites, which further develop into dermatome, myotome, and sclerotome.
- 💪 The dermatome develops into skin, spinal meninges, and subcutaneous tissue, while the myotome forms the skeletal muscles of the trunk and limbs.
- 🦴 The sclerotome contributes to the formation of the vertebrae, intervertebral discs, and ribs.
- 🧘♂️ The intermediate mesoderm is responsible for the development of the kidneys, ureters, gonads, and their associated ductal systems.
- 🔁 The lateral plate mesoderm differentiates into the somatic and splanchnic layers, contributing to body cavities, limbs, and the cardiovascular system.
Q & A
What is mesoderm and why is it significant in embryonic development?
-Mesoderm is one of the three primary germ layers in the developing embryo, derived from the epiblast during gastrulation. It is significant as it gives rise to various structures including muscles, bones, the cardiovascular system, and the urogenital system.
What are the three primary germ layers formed during gastrulation?
-The three primary germ layers formed during gastrulation are the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. These layers give rise to the majority of tissues and organs in the developing embryo.
How does the primitive streak contribute to the formation of mesoderm?
-The primitive streak is a formation in the epiblast layer during gastrulation. Epiblast cells migrate through the primitive streak, moving downwards and laterally, to form the mesoderm layer.
What are the different segments of mesoderm and their respective locations in relation to the notochord and neural tube?
-The mesoderm segments, from medial to lateral, are the paraxial mesoderm (closest to the notochord and neural tube), intermediate mesoderm, and lateral plate mesoderm (furthest lateral).
What is the function of the notochord in relation to mesoderm differentiation?
-The notochord is a rod-like structure that extends along the dorsal side of the neural tube. It secretes proteins and growth factors, such as sonic hedgehog, which trigger the differentiation of the mesoderm into various specialized structures.
What structures does the paraxial mesoderm give rise to during embryonic development?
-The paraxial mesoderm gives rise to somites, which further differentiate into the dermatome, myotome, and sclerotome. These structures contribute to the formation of skin, muscles, and vertebrae, respectively.
How does the intermediate mesoderm contribute to the urogenital system?
-The intermediate mesoderm contributes to the formation of the kidneys, ureters, gonads (testes or ovaries), and the associated ductal systems, such as the epididymis, vas deferens, fallopian tubes, and uterus.
What are the two main parts of the lateral plate mesoderm and their respective contributions to body structures?
-The lateral plate mesoderm is divided into the somatic layer (also known as the somatopleure), which contributes to the linings of body cavities and structures like the sternum and limbs, and the splanchnic layer (also known as the splanchnopleure), which forms the smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal tract, parts of the cardiovascular system, and red bone marrow.
What mnemonic is provided in the script to help remember the derivatives of mesoderm?
-The mnemonic provided is 'ENGINEERS', which stands for Myeloid stem cells, Erythroid stem cells, Spleen, O (for Gonads), D for Dermis, E for Entire trunk, R for Renal system, M for Meninges, A for Adrenal cortex, L for Lymphoid stem cells, C for Cardiovascular system, L for Linings of body cavities, L for Limbs, and S for Smooth muscle of the GIT.
What is the role of the lateral folding process in the formation of body cavities and the positioning of mesoderm?
-Lateral folding is a process where the ectoderm comes around and 'hugs' the mesoderm and endoderm, leading to the formation of body cavities. This process also positions the somatic and splanchnic layers of the lateral plate mesoderm to contribute to the linings of these cavities and other structures.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Gastrulação: Ectoderma, Mesoderma e Endoderma - Terceira Semana do Desenvolvimento (Embriologia)

How is the primitive streak formed | Best 3D Medical Learning App | MediMagic

Fase embrionik pertumbuhan dan perkembangan pada hewan - materi biologi sma kelas 12

Período Embrionario y Período Fetal | Biología | Desarrollo Embrionario | V4 | Egg Educación

Gastrulation - Embryology
Week 3 of embryonic development | Gastrulation | Neural induction
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)