Transactional Communication
Summary
TLDRThis presentation delves into the transactional communication model, illustrating how communication occurs in various settings. It emphasizes the encoding and decoding process, the importance of the channel, and the impact of context on communication. The speaker discusses the challenges of perfect communication due to individual differences and introduces the concept of noise, which includes physiological, psychological, physical, and semantic interferences. The transactional model is highlighted as a dynamic, simultaneous process involving feedback and the interplay between the source and receiver.
Takeaways
- 🗣️ Communication is a process involving a sender and receiver, with the aim to influence or be influenced.
- 👤 Harold Lasswell's definition of communication emphasizes who is communicating, the message, the channel, and the effect on the audience.
- 📚 The study of communication as an academic field gained prominence after World War II, particularly due to the need for propaganda and persuasion.
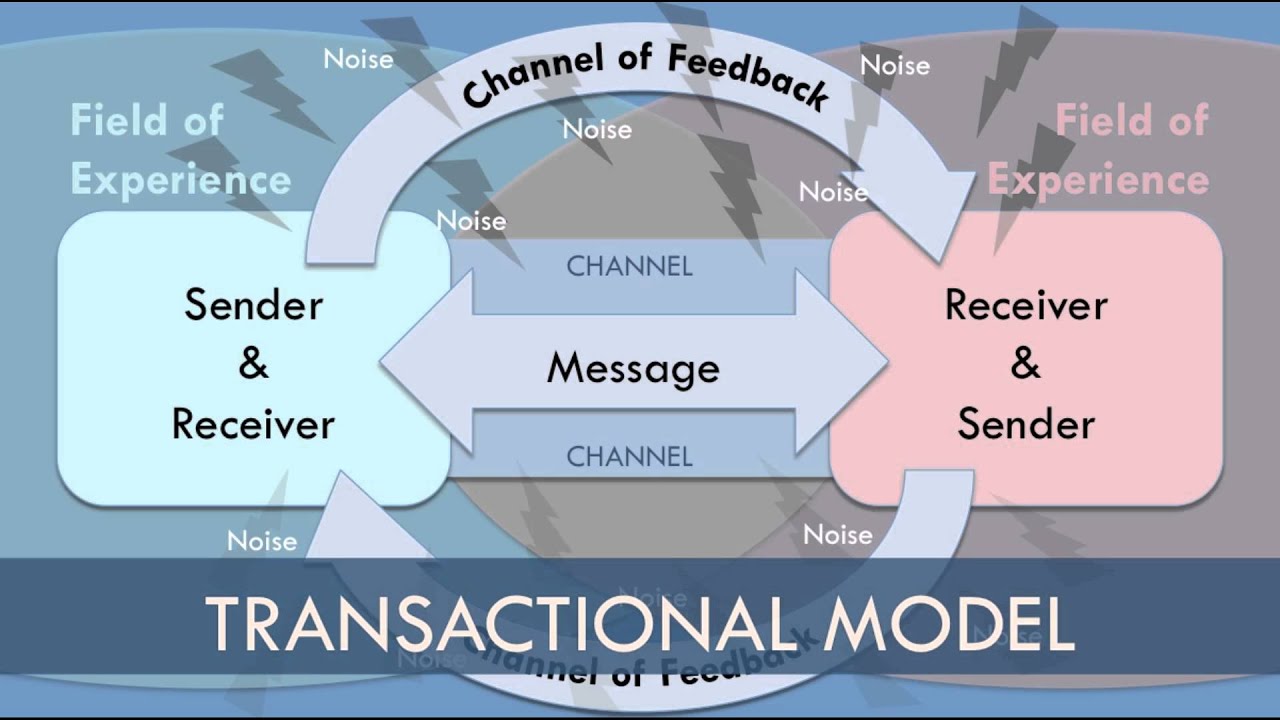
- 🔄 The transactional model of communication is distinct from other models like the action or linear models, focusing on the interactive nature of communication.
- 💡 The source's role in communication is to encode the message, which is the act of translating thoughts into a transmittable form that the receiver can understand.
- 🌐 The message can be verbal or nonverbal, and the channel, or medium, through which it is sent can greatly affect how it is perceived.
- 👂 The receiver's task is to decode the message, interpreting the meaning from the encoded message sent by the source.
- 🔕 Noise can interfere with the communication process and comes in four types: physiological, psychological, physical, and semantic.
- 🔁 Feedback in the transactional model is simultaneous with the message, as the receiver also acts as a source by responding to the initial message.
- 🌐 The context, including the setting and the relationship between individuals, plays a crucial role in shaping the communication process.
Q & A
What is the definition of communication according to Harold Lasswell?
-Harold Lasswell's definition of communication is 'Who, says what, to whom, in what channel, with what effect.'
How did the field of communication become prominent in modern academia?
-The field of communication became prominent in modern academia after World War II when various academic disciplines came together to create propaganda and persuasion campaigns, leading to the creation of a new discipline.
What are the different models of communication mentioned in the script?
-The different models of communication mentioned are the action model, the linear model, and the transactional model.
What is the role of the source in the communication process?
-The source is the sender of the message and has the job of encoding meaning into the message to ensure it is understood as intended by the receiver.
Why is perfect communication considered impossible?
-Perfect communication is considered impossible because individuals have unique life experiences and perspectives, making it difficult to perfectly translate one's thoughts from one brain to another.
What is the difference between verbal and nonverbal messages?
-Verbal messages are spoken or written words, while nonverbal messages are communicated through body language, facial expressions, and other non-linguistic cues.
How does the channel of communication affect the message?
-The channel of communication, or the medium used, affects how the message is perceived and understood. Different channels can alter the impact and interpretation of the message.
What is the role of the receiver in the communication process?
-The receiver is responsible for decoding the message sent by the source, interpreting its meaning, and providing feedback.
What are the four types of noise that can interfere with communication?
-The four types of noise are physiological noise, psychological noise, physical noise, and semantic noise, which can all interfere with the clarity of message transmission.
How is feedback incorporated in the transactional model of communication?
-In the transactional model, feedback is the message sent back from the receiver to the source, indicating that the source and receiver are simultaneously communicating with each other.
What is the significance of context in the communication process?
-Context is significant as it includes the setting and the relationship between individuals, which can greatly influence the communication process and the type of conversation that occurs.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)