Kuliah Kimia Fisika - Larutan part 1
Summary
TLDRThis lecture focuses on the thermodynamics of non-electrolyte solutions, delving into their classification, properties, and equilibrium states. It distinguishes between mixtures, colloids, and true solutions, highlighting the importance of concentration in determining solution behavior. The discussion covers partial properties, activity coefficients, and how they relate to Gibbs free energy changes. The lecture aims to provide a foundation for understanding solution thermodynamics and its applications in chemical processes and design.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lecture discusses non-electrolyte solutions, building upon previous material on equilibrium.
- 📚 It covers the classification of mixtures into coarse mixtures, colloids, and homogeneous solutions.
- 🔬 The properties of solutions are explored, including thermodynamics and the balance between solute and other phases.
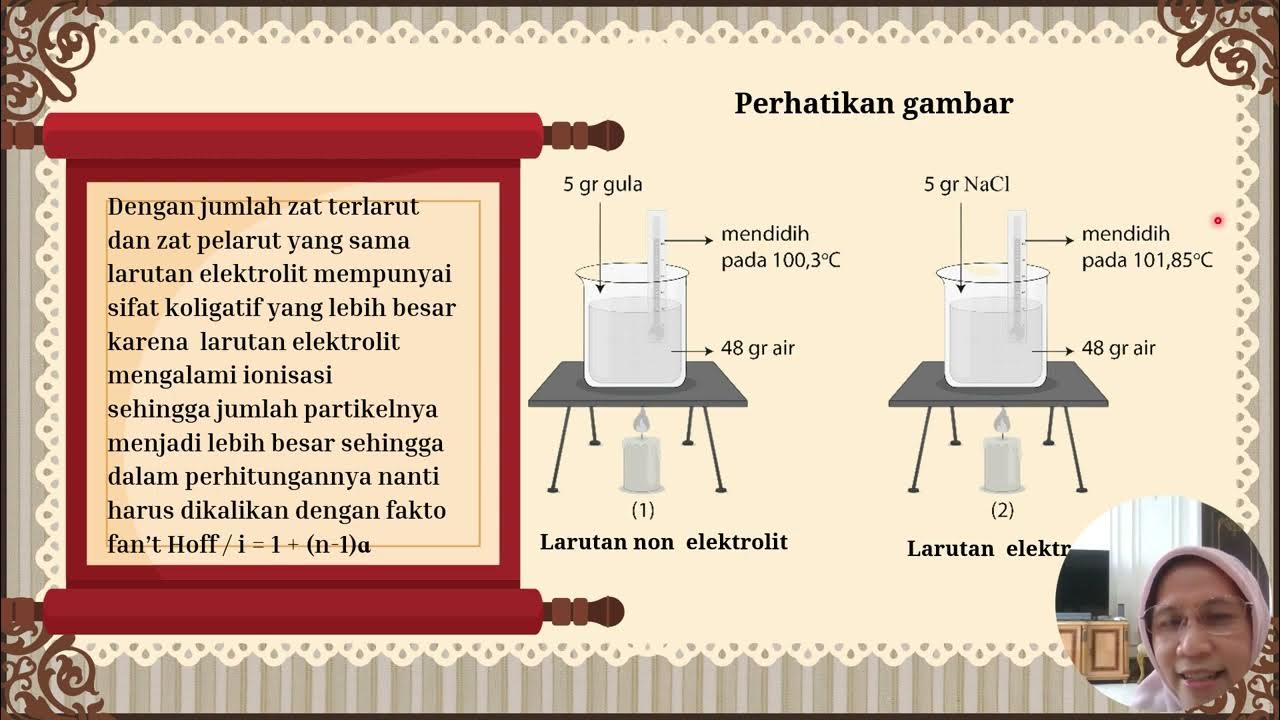
- 💧 The lecture explains the concept of vapor pressure in solutions and the colligative properties of solutions.
- 🌐 It introduces the terms 'solute' and 'solvent', and how they relate to the composition of a solution.
- 📊 Concentration in solutions is described using terms like mass fraction, molality, and molarity.
- 🔍 The thermodynamic properties of solutions are detailed, including partial properties and how they differ from single-component properties.
- ⚖️ The relationship between Gibbs free energy, enthalpy, entropy, and the effects of temperature and pressure on these properties is discussed.
- 🔄 The concept of activity in solutions is introduced, which is influenced by concentration and impacts thermodynamic properties.
- 🔬 The importance of understanding thermodynamics for designing processes and selecting appropriate equipment is highlighted.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lecture?
-The main topic of the lecture is the study of non-electrolyte solutions, which is a continuation of previous materials related to equilibrium.
What are the three types of mixtures discussed in the lecture?
-The three types of mixtures discussed are: 1) Mechanical mixtures, where components do not dissolve but are mixed physically, like sugar and salt. 2) Colloidal dispersions, where one substance is trapped within another, such as oil in water. 3) True solutions, where one substance is dissolved in another to form a homogeneous mixture, like sugar in water.
What is the difference between a solution and a liquid?
-A solution is a homogeneous mixture where one substance (solute) is dissolved in another (solvent), while a liquid is a state of matter that is not necessarily a solution and can exist as a pure substance.
What are the units used to express concentration in a solution?
-Concentration in a solution can be expressed in terms of mass, such as mass fraction or molality, or in terms of volume, such as molarity.
What is meant by the term 'partial properties' in the context of thermodynamics?
-Partial properties refer to the properties of a component within a mixture or solution, as opposed to the total properties of the entire system.
How are the partial properties of a substance in a solution related to its total properties?
-The partial properties of a substance in a solution are related to its total properties by being multiplied by the mole fraction of that substance in the solution.
What is the significance of Gibbs free energy in the context of the lecture?
-Gibbs free energy is significant as it is used to determine the spontaneity of a process in thermodynamics. It is also used to calculate the changes in energy during mixing processes in solutions.
What is activity in the context of solutions, and how does it relate to concentration?
-Activity in the context of solutions is a measure that accounts for the effective concentration of a solute in a solution, which is influenced by the actual concentration and interactions within the solution.
How does the mixing of two substances affect the Gibbs free energy of the resulting solution?
-The Gibbs free energy change of mixing is the sum of the product of the mole numbers of each component and the natural logarithm of their respective activities.
What is the relationship between the change in Gibbs free energy and the thermodynamic properties of a solution?
-The change in Gibbs free energy is related to the thermodynamic properties of a solution through the equations that connect changes in Gibbs free energy with changes in enthalpy, entropy, and volume at constant temperature and pressure.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)