ДС ИНО, часть 1
Summary
TLDRThis lecture delves into the intricacies of dispersed systems and colloidal solutions, explaining their role in biological and medical contexts. The script covers the classification of these systems based on particle size, aggregate state, and interactions between dispersed phase and dispersion medium. It also examines their stability, preparation methods, and purification techniques, such as dialysis and electrodialysis. Furthermore, the lecture touches on the physical properties of colloidal solutions, including optical and electrokinetic properties, and how these systems behave under various conditions, emphasizing their importance in both research and clinical practices.
Takeaways
- 😀 Dispersed systems are micro heterogeneous systems where particles are distributed in another material, known as the dispersion medium.
- 😀 Colloidal systems are a type of dispersed system, characterized by particles that range in size from 10^-7 to 10^-9 cm.
- 😀 Dispersed systems can be classified by particle size, aggregate state, interaction between dispersed phase and medium, and structural/mechanical properties.
- 😀 Lyophobic colloidal systems are unstable, with weak interactions between dispersed particles and the dispersion medium, whereas lyophilic systems are stable with strong interactions.
- 😀 Dispersed systems can be classified based on the aggregate state of the dispersed phase (e.g., aerosols, liquids, solids).
- 😀 In medical practice, colloidal systems, particularly those with a liquid dispersion medium, play an essential role.
- 😀 Colloidal particles are formed through dispersion and condensation methods, with mechanical dispersion methods involving fragmentation, and condensation methods forming particles from smaller molecules.
- 😀 Micelles are structural units in colloidal solutions, formed through the aggregation of particles, and their stability is affected by zeta potential.
- 😀 The stability of colloidal solutions relies on the zeta potential, where a higher value indicates greater stability.
- 😀 Colloidal solutions can be purified using methods like filtration, dialysis, and electrodialysis to remove impurities and stabilize the system.
Q & A
What are dispersed systems and how do they relate to biological systems?
-Dispersed systems are micro-heterogeneous systems where particles of one material (dispersed phase) are distributed within another material (dispersion medium). In biological systems, substances like blood, lymphocytes, and extracellular fluids are examples of dispersed systems or colloidal solutions.
How are dispersed systems classified based on particle size?
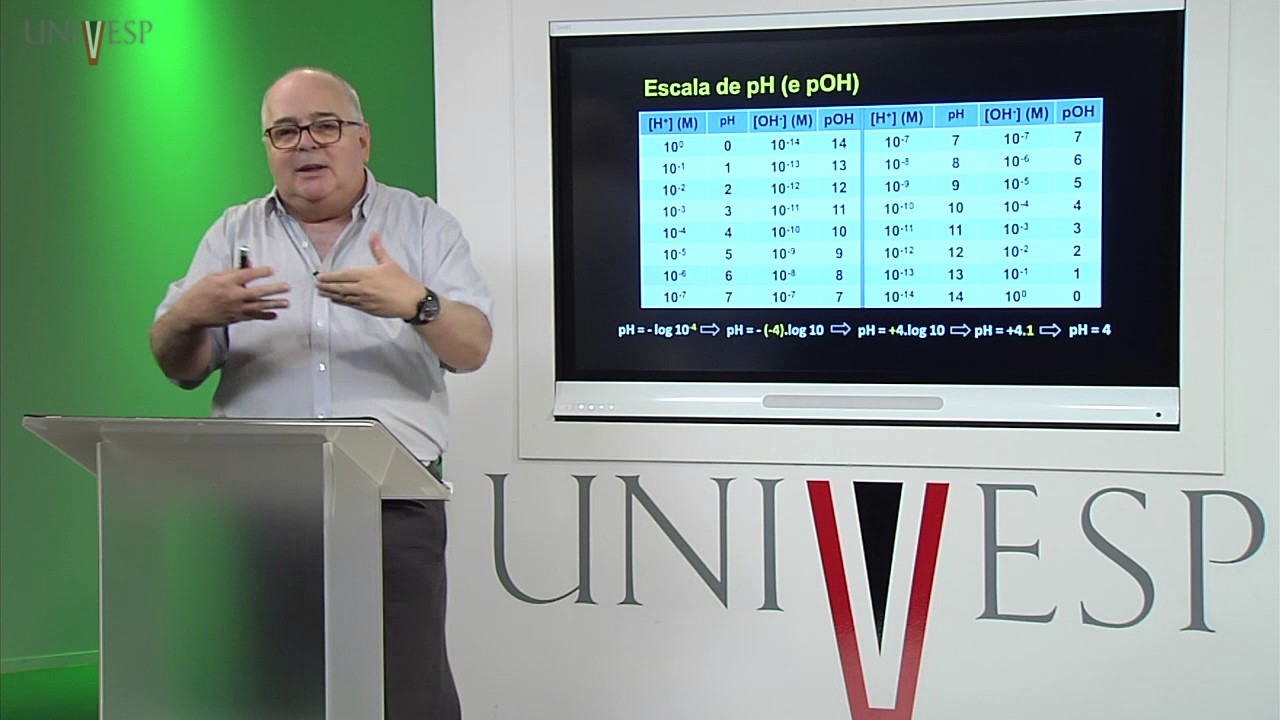
-Dispersed systems are classified into three categories based on particle size: 1) Coarse systems (particles larger than 10^-7 cm, which do not pass through paper filters), 2) Ultra-micro heterogeneous or colloidal systems (particles between 10^-7 and 10^-9 cm, which pass through filters but not membranes), and 3) True solutions (particles smaller than 10^-9 cm, which are clear).
What are the differences between lyophobic and lyophilic colloids?
-Lyophobic colloids are colloidal systems with weak forces of attraction between the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium, making them thermodynamically unstable. Lyophilic colloids, on the other hand, have strong attraction forces between the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium, making them thermodynamically stable.
How are colloidal solutions prepared using dispersion methods?
-Dispersion methods involve fragmenting larger particles into smaller ones that match the size of colloidal particles. Techniques include mechanical dispersion (using colloidal or ball mills), ultrasonic dispersion, electrical dispersion, and chemical dispersion, which uses a stabilizer to prepare colloidal solutions of metals.
What is the structure of micelles in lyophobic colloidal solutions?
-In lyophobic colloidal solutions, micelles are formed when particles, such as AgI, aggregate into larger structures. These micelles consist of a core of potential-determining ions (e.g., Ag+) surrounded by a diffuse layer of counter-ions. The micelle's stability is influenced by the zeta potential, which measures the electrostatic potential between the core and the diffuse layer.
What is the significance of the zeta potential in colloidal solutions?
-The zeta potential is crucial for determining the stability of colloidal solutions. A higher zeta potential indicates greater stability because it reflects the electrostatic repulsion between particles, preventing them from aggregating and settling.
What are some methods for purifying colloidal solutions?
-Colloidal solutions can be purified through several methods, including filtration, ultrafiltration, dialysis, electrodialysis, and compensation dialysis. These methods remove impurities like low molecular weight substances and ions that could destabilize the colloidal system.
What is Brownian motion, and how does it relate to colloidal solutions?
-Brownian motion is the random movement of particles in a colloidal solution caused by collisions with molecules of the dispersion medium. It is a characteristic property of colloidal systems, although the movement is less pronounced than in true solutions due to the larger particle size.
What optical properties are associated with colloidal solutions?
-Colloidal solutions exhibit optical properties like light scattering (opalescent effect), where light diffracts off the larger particles, and the Tyndall effect, which produces a visible cone of light when viewed against a dark background.
How does electrophoresis work in colloidal systems?
-Electrophoresis is the movement of dispersed phase particles relative to the dispersion medium under the influence of an electric field. The charged particles move towards oppositely charged electrodes, and this property is essential for characterizing and separating colloidal substances in research and clinical practices.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Sistem Koloid • Part 1: Perbedaan Larutan, Koloid, dan Suspensi; Jenis-Jenis Koloid
Bioquímica - Aula 03 - Alguns conceitos químicos importantes - 2

LECTURE 1/4 : MFRS 141/ IAS 41 AGRICULTURE (BIOLOGICAL ASSETS) : FAR320 TOPIC 2 - PART 1

Biologi Part 2 : Biological Molecul

Week 1-Lecture 1

Buffers (A-level IB Chemistry)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)