What is a resistor?
Summary
TLDRThis script defines a resistor as a passive electrical component that limits electric current. It uses the water flow analogy to explain its function, comparing water pressure to voltage and the narrowing of a tube to a resistor's effect on current. Ohm's law, discovered by Georg Simon Ohm in 1827, is introduced to describe the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance. The script also covers various types of resistors, including fixed, variable, and those with resistance dependent on physical quantities, and touches on their applications and construction materials. It concludes with a brief explanation of how to read resistor color bands to determine their value and tolerance.
Takeaways
- 🔌 A resistor is a passive electrical component that limits the flow of electric current.
- ⚡ The standard symbols for resistors are a zigzag line, with the American standard on the left and the IEC standard on the right.
- 💧 The script uses the analogy of water flow through a tube to explain how resistors work in an electrical circuit.
- 📉 Resistors cause a voltage drop across them, similar to a pressure drop in a water pipe when it narrows.
- ⚖️ Ohm's law, discovered by Georg Simon Ohm in 1827, states that resistance is equal to voltage divided by current (R = V/I).
- 🔋 A simple circuit with a battery and a resistor can demonstrate Ohm's law, where the resistor limits the current to a desired level.
- 💡 An example application is a basic LED circuit, where a resistor is used to prevent the LED from burning out by limiting the current.
- 🔩 There are various types of resistors, including fixed, variable, and those with resistance that varies with physical quantities like light or temperature.
- 📏 Fixed resistors are the most common and come in through-hole and surface-mount device (SMD) packages.
- 🔄 Variable resistors can adjust resistance mechanically and are known as potentiometers or rheostats depending on their application.
- 🌐 Resistors can be categorized by material and construction, such as wirewound, carbon composition, carbon film, metal film, and metal oxide film.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a resistor?
-A resistor's primary function is to limit the flow of electric current in an electrical circuit.
What are the standard symbols for resistors according to the American and International standards?
-The standard symbol for resistors in the American Standard is a zigzag line, while the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) uses a similar zigzag symbol but with a different shape.
How does a resistor create a voltage drop in a circuit?
-A resistor creates a voltage drop by having a higher resistance than the connecting leads, which causes a reduction in electrical current, similar to how a narrow part in a water pipe creates a pressure drop.
Who discovered Ohm's law and what does it state?
-Ohm's law was discovered by the German scientist Georg Simon Ohm in 1827. It states that electrical resistance is equal to voltage divided by current.
How can Ohm's law be used to calculate the resistance needed for a circuit with a specific current and voltage?
-Ohm's law can be used to calculate the resistance needed by using the formula Resistance = Voltage / Current. For example, if you want a current of 4 amps with a voltage source of 2 volts, the resistance needed would be 0.5 ohms.
What is the purpose of using a resistor in an LED circuit?
-In an LED circuit, a resistor is used to limit the current to a safe level to prevent the LED from burning out due to excessive current.
How can you calculate the resistance needed to limit the current to a specific value using Ohm's law?
-To calculate the resistance needed to limit the current to a specific value, use Ohm's law: Resistance = Voltage / Current. For instance, to limit the current to 30 milliamps with a 9-volt battery, the resistance would be 300 ohms.
What are the different types of resistors mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions fixed resistors, variable resistors, and resistors with varying resistance dependent on physical quantities. Fixed resistors include carbon composition, carbon film, metal film, and metal oxide film types. Variable resistors include potentiometers and rheostats.
What is the difference between a potentiometer and a rheostat?
-A potentiometer is a variable resistor used as a voltage control device, while a rheostat is a variable resistor used to control the current in a circuit.
What is the significance of the color bands on a resistor, and how can you read them?
-The color bands on a resistor indicate its resistance value and tolerance. The first and second bands represent the first two digits of the resistance value, the third band is the multiplication factor, and the fourth band indicates the tolerance. For example, a resistor with red, blue, gray, and gold bands has a value of 2.6 megaohms with a 5% tolerance.
Where can one find more information about resistor types, properties, and color codes?
-More information about resistor types, properties, and color codes can be found at websites like resistorguide.com, which also offers a color code chart and an automatic calculator to decode resistor values.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Basic Electricity - Resistance and Ohm's law
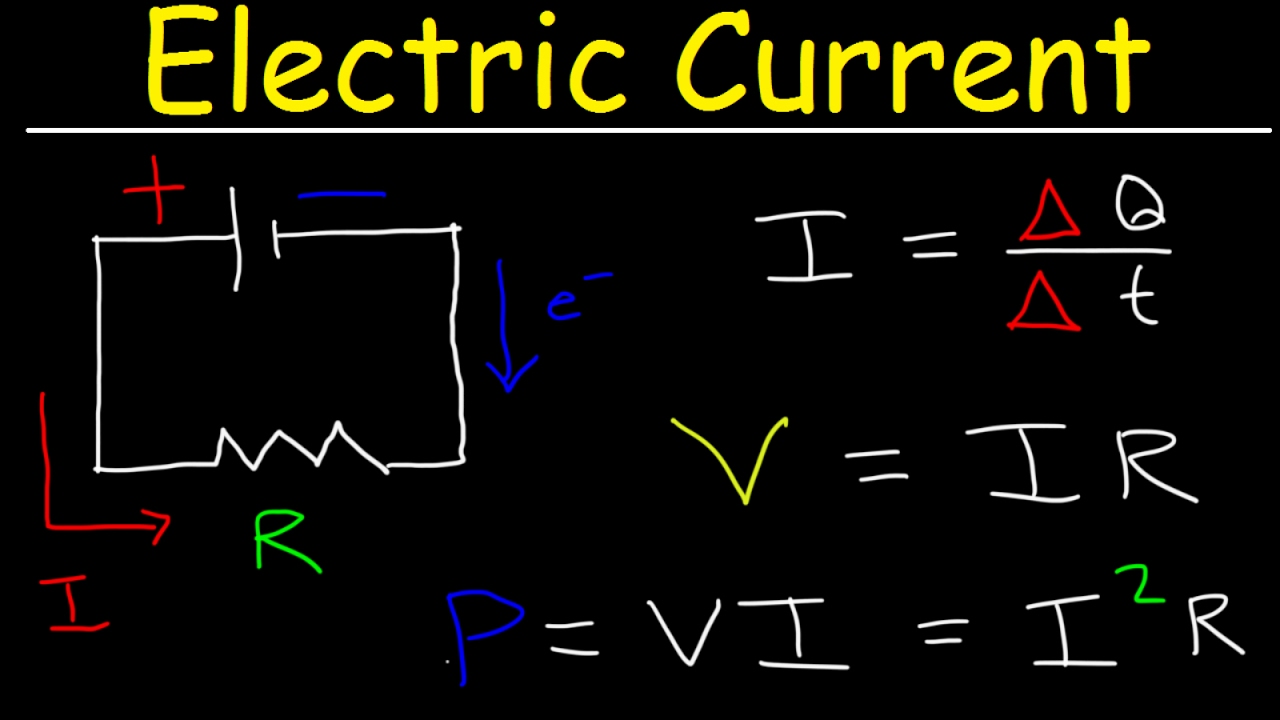
Electric Current & Circuits Explained, Ohm's Law, Charge, Power, Physics Problems, Basic Electricity

Arus, Tegangan, dan Hambatan | Rangkaian DC | Part 1 | Fisika Dasar

How Does Electric Current Flow in a Circuit?

What is Earthing Transformer or Grounding Transformer? #interviewquestions #electricalengineering
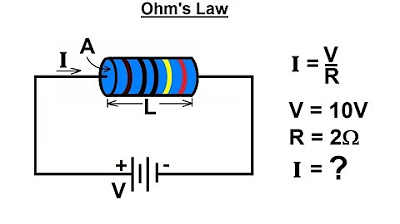
Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (2 of 31) Ohm's Law
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)