Electroporation
Summary
TLDRThis video lecture delves into electroporation, a technique that uses low voltage electricity to create temporary pores in the cell membrane, allowing for the delivery of genetic material or drugs directly into the cell's cytosol. The process involves the realignment of phospholipids in the cell membrane under an electric field, forming hydrophilic pores that facilitate the passage of foreign particles. Electroporation is crucial for genetic material delivery, cell transformation, and plant breeding, offering a cost-effective and labor-efficient method.
Takeaways
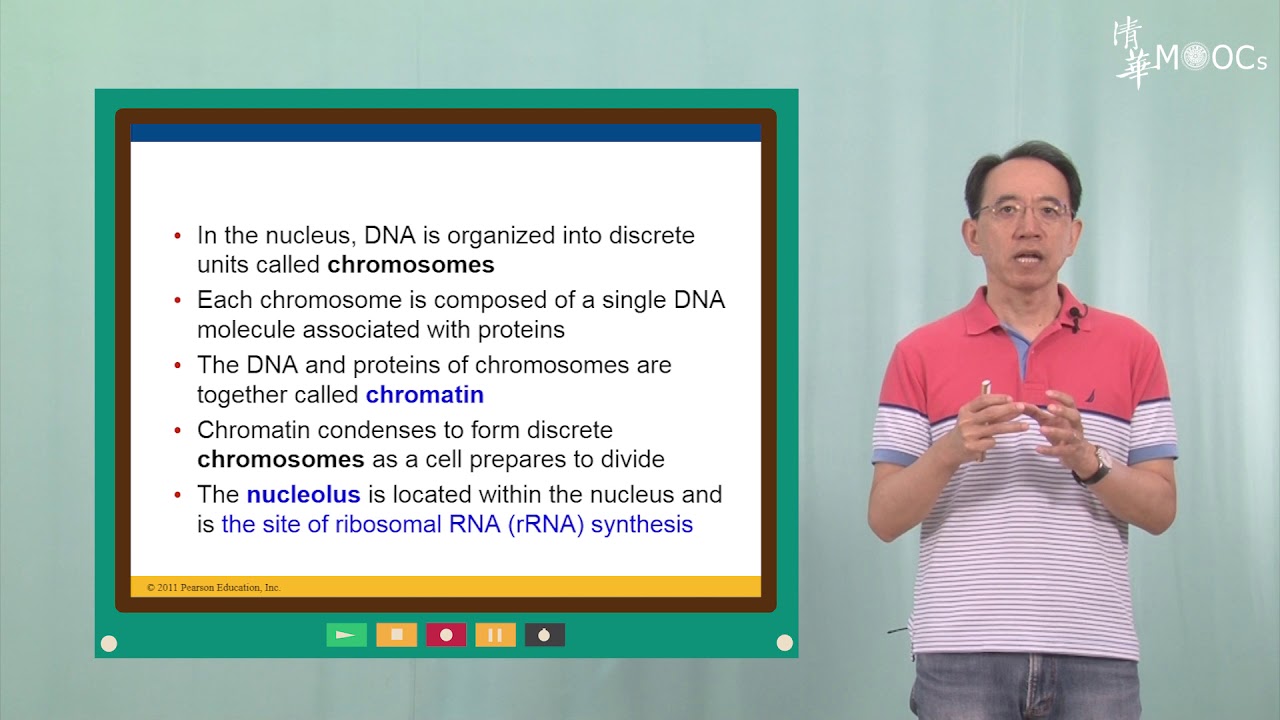
- 🔬 Electroporation, also known as electropermeabilization, is a technique that uses a small voltage to create pores in the cell membrane.
- 🔌 By applying a mild voltage (100-300 volts) across a short distance (e.g., 5 millimeters), the cell membrane's phospholipids realign to form temporary pores.
- 🧬 This process allows for the direct delivery of genetic material or drugs into the cell's cytosol or nucleus, bypassing the protective cell membrane.
- 🧠 The cell membrane's phospholipids normally align in a bilayer fashion, with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails, but voltage application causes a reorientation.
- 💧 The realignment of phospholipids creates a hydrophilic pathway through the membrane, enabling the passage of hydrophilic particles like DNA.
- 🌿 Electroporation is crucial for genetic engineering, cell transformation, plant breeding, and tissue culture, where genetic material needs to be introduced into cells.
- 📈 The technique is cost-effective and labor-efficient, as it requires only a brief application of voltage to achieve the desired effect.
- 🔗 The process is reversible, with the cell membrane's pores re-sealing after the voltage is removed, allowing cells to recover and integrate the introduced material.
- 🌐 For a more detailed visual understanding, 3D models of electroporation can be found on platforms like Wikipedia.
- 👍 The video encourages viewers to engage with the content by liking, sharing, and subscribing for more educational videos on similar topics.
Q & A
What is electroporation?
-Electroporation, also known as electropermeabilization, is a process that uses a small amount of electrical voltage to create pores in the cell membrane, allowing for the delivery of genetic material or drugs directly into the cell's cytosol.
Why is it necessary to evade the cell membrane during the delivery of genetic material or drugs?
-The cell membrane acts as a protective barrier, preventing foreign substances from entering the cell. To insert genetic material or drugs directly into the cell, this barrier must be temporarily breached.
How does the application of voltage lead to the formation of pores in the cell membrane?
-The application of voltage causes the phospholipids in the cell membrane to realign, creating a temporary pore. This rearrangement allows for the passage of hydrophilic particles, such as DNA or drugs, through the membrane.
What is the typical voltage range used in electroporation?
-The voltage applied in electroporation is typically in the range of 100 to 300 volts, depending on the specific requirements and the size of the cell.
How does the phospholipid bilayer normally align in a cell membrane?
-In a normal cell membrane, phospholipids align in a bilayer fashion with hydrophilic heads facing outward and hydrophobic tails facing inward, creating a barrier between the cell and its environment.
What happens to the phospholipids when voltage is applied during electroporation?
-Upon the application of voltage, the phospholipids realign, with the hydrophilic heads forming a temporary pore and the hydrophobic tails interacting with each other, creating a separation that allows particles to pass through.
Why is electroporation an important technique in genetic engineering?
-Electroporation is crucial in genetic engineering because it enables the efficient transfer of DNA into cells, which is essential for processes like genetic transformation and plant breeding.
What are some applications of electroporation in plant tissue culture?
-Electroporation is used in plant tissue culture for the transformation of cells and the introduction of genetic material, such as plasmids, which can lead to the development of genetically modified plants.
How does the process of electroporation compare to other methods of genetic material delivery in terms of cost and labor?
-Electroporation is often less expensive and requires less labor compared to other methods, as it only requires the application of a mild voltage across the cell membrane to facilitate the transfer of genetic material.
Can you provide an example of how DNA is introduced into a cell using electroporation?
-In electroporation, DNA fragments are placed in a surrounding mixture, and then a voltage is applied. This causes the DNA to pass through the temporary pore created in the cell membrane, effectively delivering the genetic material into the cell.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)