生命科學(一) Ch7-3 A Tour of the Cell
Summary
TLDRThis lecture focuses on the structure and function of the cell nucleus and ribosomes. It explains how DNA, stored in the nucleus, contains genetic information, while ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis. The nucleus, enclosed by a double membrane, communicates with the cytoplasm through nuclear pores. The distinction between chromatin and chromosomes is also discussed, with chromatin condensing into chromosomes during cell division. Ribosomes, either free in the cytosol or attached to the rough ER, synthesize proteins using messenger RNA. The lecture further elaborates on the structure and role of ribosomes in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Takeaways
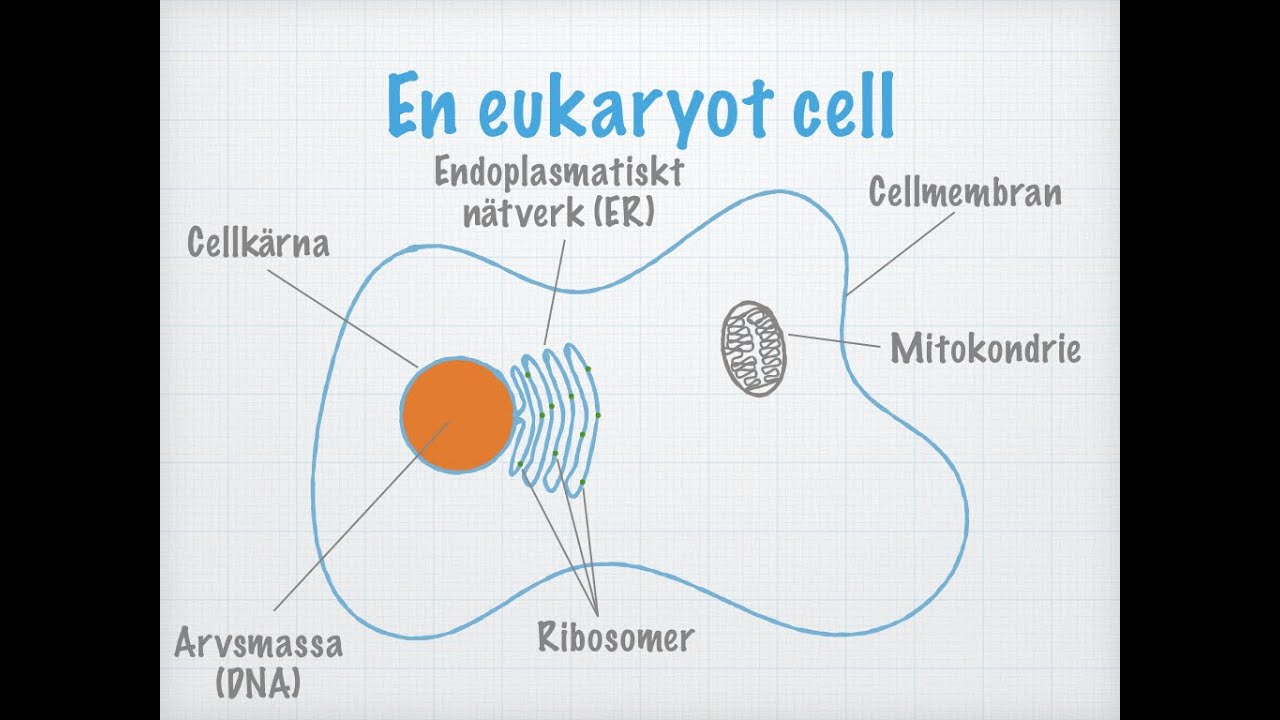
- 🔬 The nucleus (細胞核) contains the genetic material of the cell, mainly DNA, and is the most visible cell structure under a microscope.
- 🛡️ The nucleus is enclosed by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which consists of two layers of lipid bilayers.
- 🌀 The nucleolus (核仁) is a dense region within the nucleus that produces ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
- 🔗 The nuclear envelope has nuclear pores, which allow for communication and movement of materials between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
- 🧱 Chromatin (染色質) is a combination of DNA and proteins found in the nucleus, which condenses into chromosomes during cell division.
- 📡 The nuclear lamina supports the structure of the nucleus and maintains its shape.
- 🔄 Messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized in the nucleus and passes through nuclear pores to the cytoplasm for protein synthesis.
- 🧬 Ribosomes (核醣體) are involved in protein synthesis and can be either free in the cytosol or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- 🌐 Ribosomes consist of a large and a small subunit, and they are present in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
- 💡 The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is connected to the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope and plays a role in protein synthesis, especially in the rough ER with ribosomes attached.
Q & A
What is the main function of the nucleus in a cell?
-The main function of the nucleus is to store genetic information in the form of DNA. It also plays a crucial role in regulating the activities of the cell, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
What is the nuclear envelope, and what is its structure?
-The nuclear envelope is the membrane that surrounds the nucleus. It is a double membrane structure composed of two lipid bilayers: an inner membrane and an outer membrane. It protects the nucleus and regulates the exchange of materials between the nucleus and the cytoplasm through nuclear pores.
What is the function of the nuclear pore complex?
-The nuclear pore complex regulates the transport of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. It allows the passage of materials such as messenger RNA (mRNA) and other essential molecules in and out of the nucleus while controlling what can enter or leave.
What is the difference between chromatin and chromosomes?
-Chromatin refers to the loosely packed form of DNA and protein found in the nucleus when the cell is not dividing. During cell division, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, which are more compact and easily visible under a microscope.
What is the nucleolus, and what is its primary function?
-The nucleolus is a dense region within the nucleus. Its primary function is to produce ribosomal RNA (rRNA), which is essential for the formation of ribosomes, the organelles responsible for protein synthesis.
How are ribosomes involved in protein synthesis?
-Ribosomes are responsible for translating messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins in a process called protein synthesis. mRNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus, then transported to the cytoplasm, where ribosomes use the mRNA sequence to assemble proteins.
Where can ribosomes be found within the cell?
-Ribosomes can be found either floating freely in the cytosol (free ribosomes) or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), forming rough ER. Both types of ribosomes play a role in protein synthesis.
What is the relationship between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the nucleus?
-The outer membrane of the nuclear envelope is continuous with the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), particularly the rough ER, which is involved in protein synthesis. Ribosomes on the rough ER synthesize proteins, some of which may be transported into or out of the nucleus.
How does the nuclear lamina support the structure of the nucleus?
-The nuclear lamina is a network of protein filaments that provides structural support to the nucleus, maintaining its shape and anchoring the nuclear pores. It also plays a role in organizing chromatin within the nucleus.
What happens to chromatin during cell division?
-During cell division, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, making the genetic material more compact and organized. This condensed form allows chromosomes to be easily separated and distributed into daughter cells during mitosis or meiosis.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)