PROKARYOTES VS EUKARYOTES- How cells are different?
Summary
TLDRThe video script from moomoomath and science explores the distinctions between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, which are the fundamental units of all living organisms. It highlights that while both types of cells share basic components like ribosomes, DNA, and RNA, eukaryotic cells are more complex, featuring a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells, found in bacteria and archaea, are simpler, lacking a nucleus and specialized organelles, yet they play crucial roles in various environments. The script also clarifies the terminology for referring to individual cells versus organisms, emphasizing the diversity and importance of both cell types in the biological world.
Takeaways
- 🌿 All living organisms are composed of cells, which can be classified into two categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic.
- 🐶 The term 'eukaryote' is used to refer to organisms, while 'eukaryotic' is used for individual cells, and similarly for 'prokaryote' and 'prokaryotic'.
- 🦠 Prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea, whereas eukaryotes encompass protists, plants, animals, and fungi.
- 🔬 Prokaryotic cells are smaller and lack membrane-bound organelles, but they possess a cell membrane, ribosomes, and genetic materials like DNA and RNA.
- 🌀 The DNA in prokaryotes is found in the cytoplasm or in a circular form known as a plasmid.
- 🚀 Prokaryotes, due to their simplicity, can replicate quickly, which is advantageous for bacteria and archaea that inhabit diverse environments.
- 🏃 Some prokaryotes have a flagellum for movement but do not have complex organelles like mitochondria or a nucleus.
- 🌳 Eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, and contain membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and Golgi apparatus.
- 🌿 Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells share common features like ribosomes, genetic materials, cytoplasm, and a cell membrane.
- 🌐 Eukaryotic cells can be either unicellular, like some protists, or multicellular, like animals, plants, and fungi.
Q & A
What is the modern cell theory?
-The modern cell theory states that all living things are made of cells, and that the human body, for example, is composed of trillions of cells working together to sustain life.
What is the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell?
-Prokaryotic cells are smaller, lack membrane-bound organelles, and do not have a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, contain membrane-bound organelles, and can be either unicellular or multicellular.
What is the term used to describe an organism that has cells without a nucleus?
-An organism with cells without a nucleus is referred to as a prokaryote.
What are the two main classifications of prokaryotes?
-Prokaryotes can be classified as either bacteria or archaea.
What does the term 'prokaryote' mean, and how does it relate to the nucleus?
-The term 'prokaryote' means 'before kernel,' which refers to the absence of a nucleus in these cells.
How do prokaryotes replicate, and what is an advantage of their simplicity?
-Prokaryotes are simple unicellular organisms that can duplicate quickly, which is an advantage due to their simple structure.
What is a characteristic feature that some prokaryotes have that allows them to move?
-Some prokaryotes have a flagellum, which allows them to move.
What are the membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells?
-Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and Golgi apparatus.
What does the term 'eukaryote' mean, and how does it differ from 'prokaryote'?
-The term 'eukaryote' means 'true kernel,' which refers to the presence of a nucleus or true nucleus, unlike prokaryotes.
What are the similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have ribosomes, genetic materials such as DNA and RNA, cytoplasm, and a cell membrane.
Can you provide an example of a eukaryotic single-celled organism?
-An example of a eukaryotic single-celled organism is a protist.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

EUKARYOTIC CELLS vs PROKARYOTIC CELLS | What's the difference?

Overview of Cell Structure

12. Biology | Cell Structure and Function | Basic Concepts of Cell Biology | MDCAT 2025

ELSC2111 2111 W06 EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE BIOENERGETICS DE JESUS MARILYNE

A2.2 Cell Structures and Processes [IB Biology SL/HL]
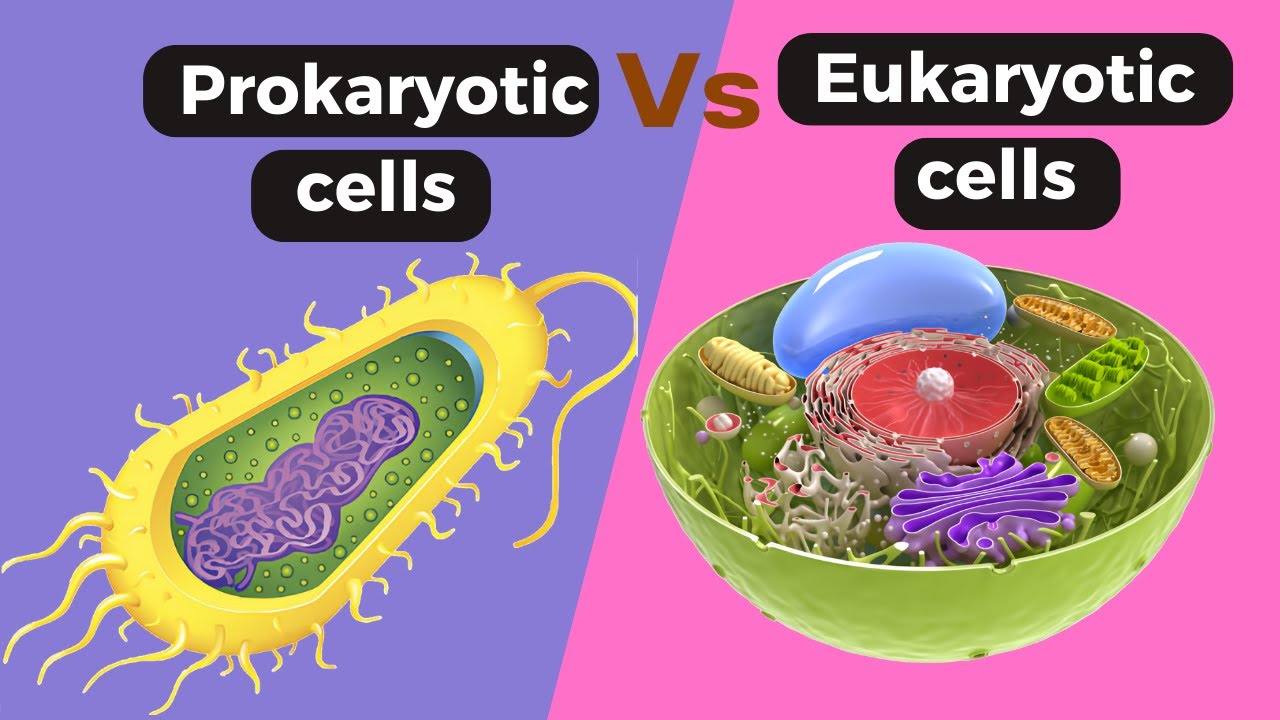
Prokaryotic cell Vs Eukaryotic cells|| Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)