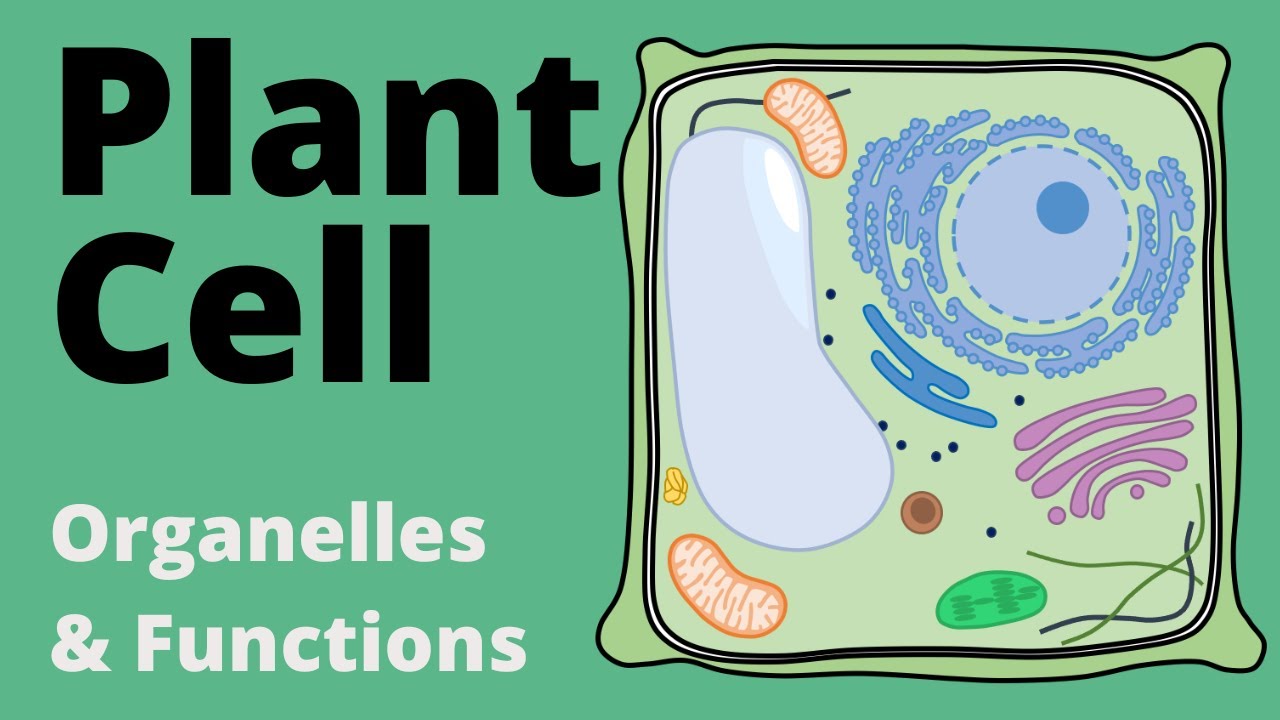
Structure and Function of the ANIMAL CELL explained (Organelles)
Summary
TLDRThis video script offers an insightful look into the complex world of animal cells. It highlights the plasma membrane's selective permeability and its role in regulating nutrient transport. The nucleus, with its DNA and nucleolus, is emphasized for genetic information storage and ribosome production. The script also touches on the endoplasmic reticulum for protein synthesis, the Golgi apparatus for protein sorting, and lysosomes for cellular digestion. Mitochondria are noted as the cell's power source, while peroxisomes neutralize harmful peroxides. The cytoskeleton's role in cell shape and movement is discussed, along with the centrosome's function in microtubule production and cell division. The script invites viewers to explore plant cell structure for further comparison.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are distinguished in cell biology, with animal cells being a type of eukaryotic cell.
- 💧 The plasma membrane of animal cells is a selectively permeable phospholipid double layer that regulates the transport of nutrients and minerals.
- 🌐 The cytoplasm contains cytosol, which is filled with nutrients and organelles that perform various functions within the cell.
- 🧬 The nucleus is an iconic cell compartment that stores genetic information in the form of DNA and is involved in replication and transcription.
- 🌀 The nucleolus within the nucleus is responsible for the production and assembly of ribosomes, which are essential for protein synthesis.
- 🧲 The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is connected to the nucleus and has two forms: rough ER for protein synthesis and modification, and smooth ER for lipid synthesis.
- 📦 The Golgi apparatus sorts, packages, and transports proteins to their respective locations within the cell, and also performs modifications like glycosylation.
- 🔄 Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes that break down unwanted cellular parts or foreign molecules, and function optimally at a low pH.
- ⚡ Mitochondria are known as the 'powerhouses' of the cell, providing energy for biochemical processes and producing ATP, the cell's energy currency.
- 🚑 Peroxisomes help to accumulate and degrade peroxides, which can be dangerous to other cell compartments, thus diffusing potential cellular damage.
- 🌿 The cytoskeleton in animal cells includes microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments, contributing to cell shape and organelle movement.
- 🌐 The centrosome is a special organelle in animal cells that produces microtubules, supports cell structure, and is essential for cell division.
Q & A
What is the main function of the plasma membrane in an animal cell?
-The main function of the plasma membrane is to regulate the transport of nutrients and minerals into and out of the cell, as it is selectively permeable to certain molecules.
What is the primary role of the cytoplasm in an animal cell?
-The cytoplasm is a fluid that fills the cell and contains nutrients and organelles. It serves as the site for many cellular activities and helps maintain the cell's shape.
What is the nucleus and what does it store?
-The nucleus is one of the most iconic cell compartments that stores the majority of the cell's genetic information in the form of DNA.
What is the nucleolus and what is one of its functions?
-The nucleolus is a structure located inside the nucleus, and one of its functions is the production and assembly of ribosomes.
How does the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) contribute to protein synthesis in an animal cell?
-The endoplasmic reticulum, particularly the rough ER, is involved in protein synthesis, modification, and preparation for transport, with ribosomes attached to its surface aiding in this process.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in protein transport within an animal cell?
-The Golgi apparatus is responsible for taking up, sorting, packaging, and sending proteins to their respective locations within the cell, and it also facilitates further modifications like glycosylation.
What is the function of lysosomes in an animal cell?
-Lysosomes are spherical organelles that contain digestive enzymes to break down unwanted parts of the cell or foreign molecules. They operate at a low pH, which is crucial for their digestive function.
Why are mitochondria considered the 'powerhouse' of the cell?
-Mitochondria are known as the 'powerhouse' of the cell because they generate ATP, the cell's energy currency, which fuels the cell's biochemical processes.
What is the purpose of peroxisomes in an animal cell?
-Peroxisomes are organelles that accumulate and degrade peroxides, which can be dangerous to other cell compartments, thus diffusing the danger posed by these byproducts of biochemical reactions.
How does the cytoskeleton contribute to the structure and function of an animal cell?
-The cytoskeleton, which includes microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments, contributes to the cell's shape, helps organize and move organelles, and is also involved in the cell's motility.
What is the centrosome and what is its role during cell division?
-The centrosome is a special organelle that serves as the production site for microtubules. It supports the cell's structure and has essential organizational functions during cell division.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)