Mengenal IP Address | Network Fundamental Learning Series #8
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial delves into the fundamentals of IP addresses, explaining what they are and their role in identifying devices on a computer network. It distinguishes between IPv4 and IPv6, highlighting their bit lengths and notational differences. The video also clarifies the concepts of public and private IP addresses, their uses, and the implications of using each. It introduces the idea of special IP addresses and their reserved purposes. Furthermore, it explores the structure of IPv4 addresses, including network and host IDs, and the function of subnet masks. The tutorial aims to aid understanding through practical demonstrations using Cisco Packet Tracer, emphasizing the importance of unique IP addresses within a network.
Takeaways
- 🌐 IP addresses are crucial for identifying devices on a computer network, allowing them to communicate with each other.
- 🔑 There are two versions of IP addresses: IPv4, which uses 32-bit numbers, and IPv6, which uses 128-bit numbers.
- 📊 IPv4 addresses are notated in decimal and separated by dots, while IPv6 uses hexadecimal notation and is visually longer.
- 🌟 IPv4 can support up to 4.3 billion addresses, whereas IPv6 has an exponentially larger address space, estimated at 2^128 or around 340 undecillion addresses.
- 🏢 IP addresses are categorized into public and private. Public IPs are used on the internet, while private IPs are reserved for local networks.
- 🔒 Public IPs are globally unique and assigned by ISPs, whereas private IPs are locally unique and managed by network administrators.
- 💡 Special IP addresses, like 127.0.0.1 for localhost, are reserved for specific purposes and are not used for general network communication.
- 📚 Understanding binary numbers and conversions is fundamental to grasping the structure and function of IP addresses.
- 🏷 The default subnet mask is determined by the class of the IP address, with different classes (A, B, C) having different default masks.
- 🔄 Network ID and Host ID are parts of an IP address that define the network segment and the specific device within that segment, respectively.
- 🛠 Tools like Cisco Packet Tracer can be used to practice and visualize IP addressing concepts in a simulated environment.
Q & A
What is an IP address?
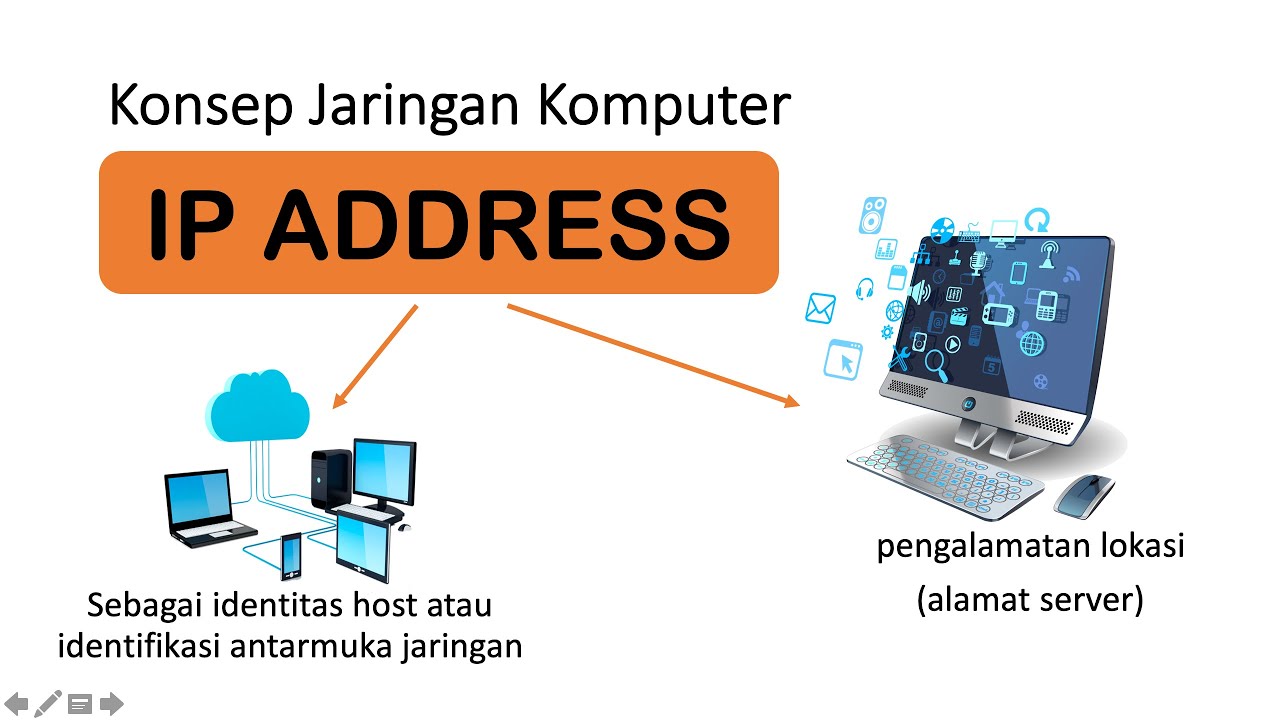
-An IP address is a system of addressing units on each device or host connected to a computer network. It serves as an identifier for devices on a network, allowing them to communicate with each other.
What are the two versions of IP addresses discussed in the script?
-The two versions of IP addresses discussed are IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 uses a 32-bit number, while IPv6 uses a 128-bit number.
How are IP addresses notated in IPv4 and IPv6?
-IPv4 addresses are notated using decimal numbers separated by dots, such as 192.168.1.1. IPv6 addresses use hexadecimal notation and are longer in comparison to IPv4 addresses.
What is the total number of IP addresses available in IPv4?
-IPv4 has a total of approximately 4.3 billion IP addresses.
How many IP addresses are available in IPv6?
-IPv6 has an extremely large number of IP addresses, estimated to be around 2^128 or 340 undecillion addresses.
What is the difference between a public IP address and a private IP address?
-A public IP address is used on the internet and is globally unique, while a private IP address is used within a local network and is not routable on the internet.
Who assigns public IP addresses and who assigns private IP addresses?
-Public IP addresses are assigned by Internet Service Providers (ISPs), while private IP addresses are assigned by network administrators within an organization or a local area network.
What is a special IP address and why are they used?
-Special IP addresses are reserved for specific purposes as agreed upon internationally and are not used for general network communication or implementation.
What are the two main components of an IPv4 address?
-The two main components of an IPv4 address are the Network ID, which identifies the network segment, and the Host ID, which identifies the individual device on that network.
What is a subnet mask and how does it relate to IP addresses?
-A subnet mask is a 32-bit number that separates the network ID from the host ID within an IP address. It is used to determine the scope of the network and the number of available host addresses.
What are the default subnet masks for each class of IP addresses?
-The default subnet masks vary by class: Class A is 255.0.0.0, Class B is 255.255.0.0, and Class C is 255.255.255.0.
How can you determine the Network ID and Host ID from an IP address?
-You can determine the Network ID and Host ID by using the default subnet mask for the class of the IP address and applying it to the IP address to separate the network and host components.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Konsep Dasar IP Address Komputer
MATERI (NETWORK FUNDAMENTAL) || CISCO || IT || NETWORK ENGINEER ||

Hub, Bridge, Switch, Router - Network Devices - Networking Fundamentals - Lesson 1b

IGCSE Computer Science 2023-25 - Topic 3: HARDWARE (7) - NETWORK HARDWARE, NIC, MAC, IPS, Routers

MAC Address Explained

Pengalamatan Jaringan Komputer (MAC, IP, Gateway, DNS) | Network Fundamental Learning Series #5
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)