Structural Organization of the Human Body
Summary
TLDRThis educational script delves into the structural hierarchy of the human body, outlining its organization from the atomic to the organismal level. It covers the chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and organismal levels, emphasizing the interdependence of these components for life's functions. The script also highlights 11 major organ systems, each with specific roles, and underscores the complexity of human anatomy and physiology.
Takeaways
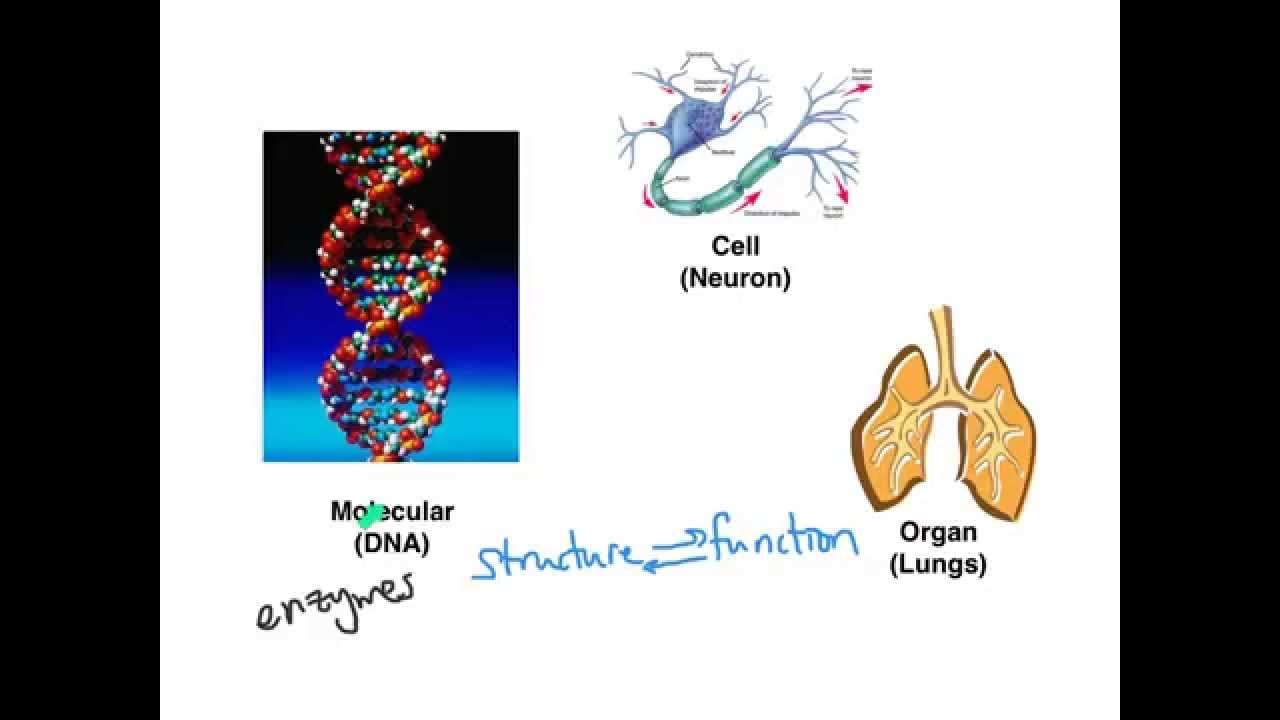
- 🌐 The human body's structural organization is discussed across six levels of increasing complexity: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and organism.
- 🔬 At the chemical level, atoms bond to form molecules that serve as the building blocks of all body structures.
- 🌿 A cell is the smallest independently functioning unit of life, performing all functions of life in both single-celled and multicellular organisms.
- 🤝 Tissues are formed by communities of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function.
- 🏠 Organs are composed of two or more different tissue types and perform one or more specific physiological functions.
- 🔄 Organ systems consist of multiple organs that collaborate to perform major functions or meet the body's physiological needs.
- 👤 The integumentary system protects internal structures and contains sensory receptors, including skin, hair, and nails.
- 🦴 The skeletal system, along with the muscular system, supports body movement and structure through bones, cartilage, and joints.
- 🧠 The nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord, detects and processes sensory information, activating the body's responses.
- 💧 The cardiovascular system, with the heart and blood vessels, delivers oxygen and nutrients to tissues and helps regulate body temperature.
- 🌱 The respiratory system, comprising the lungs and airways, is responsible for gas exchange, removing carbon dioxide and delivering oxygen.
Q & A
What are the fundamental levels of organization in the human body?
-The levels include subatomic particles, atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, and the biosphere.
What are the six distinct levels of structural organization of the human body?
-The six levels are the chemical level, cellular level, tissue level, organ level, organ system level, and organism level.
What occurs at the chemical level of organization?
-At the chemical level, atoms bond to form molecules, which are the building blocks of all body structures.
What defines the cellular level of organization?
-The cellular level involves the combination of molecules to form the fluid and organelles of cells, which are the smallest independently functioning units of a living organism.
What is the role of tissues in the body?
-Tissues are groups of similar cells that work together to perform specific functions within the body.
How are organs formed and what is their function?
-Organs are formed by two or more different tissue types that work together to perform specific physiological functions.
What is the purpose of an organ system?
-An organ system is a group of organs that work closely together to perform major functions or meet physiological needs of the body.
What is the highest level of organization in the human body?
-The organism level is the highest level of organization, where all cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems work together to maintain life and health.
How do cells contribute to the physiology of the human body?
-Cells perform all functions of life, such as processing nutrients, reproducing, and responding to environmental changes, or initiate these processes.
Can organs belong to more than one organ system?
-Yes, organs can function integrally with multiple systems, contributing to more than one organ system within the body.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Levels of Biological Organization

What Are The Levels Of Organization In The Body - Organization Of The Human Body

◣มสธ.◢ 50102 รายการที่ 1 ตอนที่ 1 ความรู้เกี่ยวกับร่างกายมนุษย์ (1)
Anatomical Organization of the Human Body From atoms and molecules to the entire organism as a whole
Tabela Periódica [Mapa Mental] [COMPLETO] - Mapas da Química

Coordination & Control | Mdcat Biology Lecture || Mdcat 2023
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)