What Are The Levels Of Organization In The Body - Organization Of The Human Body
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the intricate organization of the human body across seven levels: from the chemical level of atoms and molecules to organelles within cells, cellular level with its diverse cell types, tissue level with its four major types, organ level where different tissues form functional organs like the liver, system level with 11 major interdependent systems, and finally, the organism level representing the complete human body. Each level is crucial for the body's complex and harmonious functioning.
Takeaways
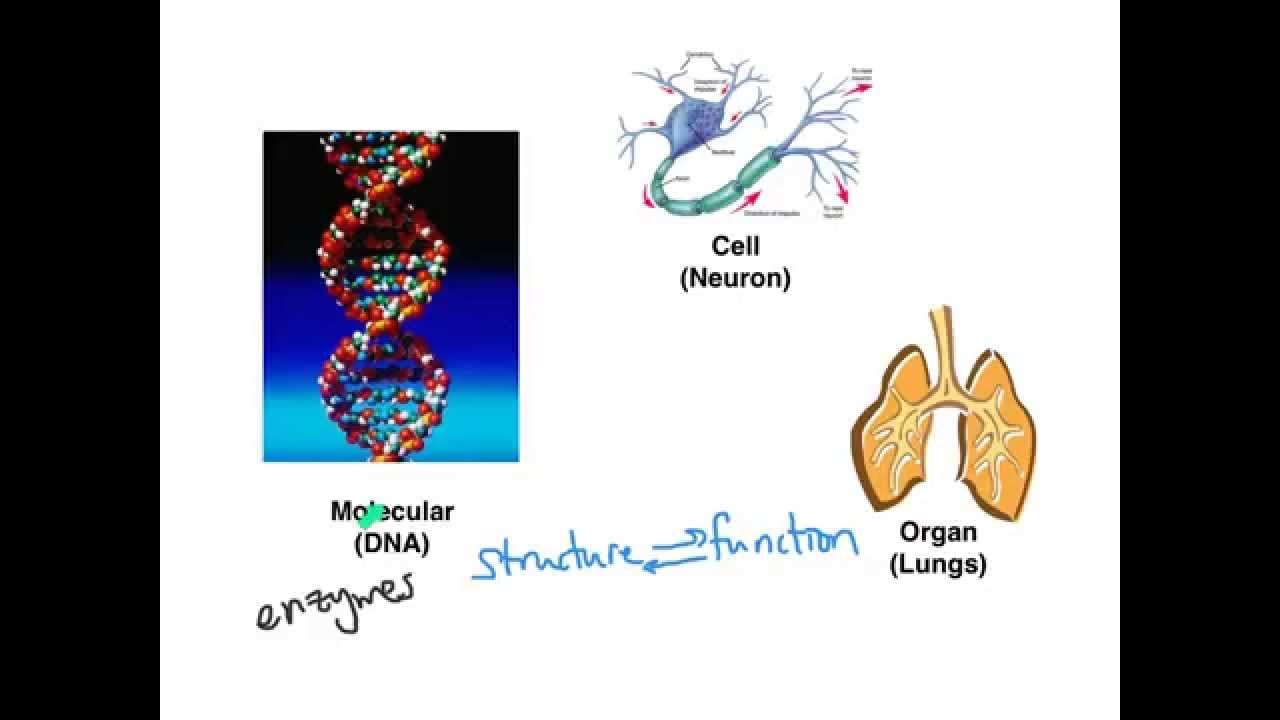
- 🌐 The human body's structure and function are organized into 7 levels, starting from the chemical level to the organism level.
- 🔬 The chemical level is the foundation, with atoms bonding to form molecules and macromolecules.
- 🌱 Organelles, such as mitochondria and ribosomes, are tiny organ-like structures within cells that perform specific functions.
- 💠 Cells are the smallest living units in the body, consisting of a membrane, nucleus, and cytoplasm with organelles.
- 🤲 Tissues are groups of similar cells that perform a specific function and are surrounded by a matrix.
- 🏋️♂️ There are four major types of tissues: connective, muscle, nervous, and epithelial, each with distinct roles.
- 👥 Organs are complex structures composed of different types of tissues, each with a specific function, like the liver storing vitamins and detoxifying blood.
- 🔄 Systems are groups of organs that work together to perform complex functions, such as the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
- 🤝 The 11 major systems in the body often collaborate to meet the body's needs, highlighting the body's integrated nature.
- 🧍♂️ The organism level represents the complete human body, an integrated system of all the previous levels working in harmony.
Q & A
What is the first level of organization in the human body as described in the script?
-The first level of organization in the human body is the chemical level, which starts with atoms.
How do atoms contribute to the formation of larger structures in the body?
-Atoms bond together to form molecules, which are larger chemical groupings. These molecules can further combine with other molecules and atoms to form macromolecules.
What is the role of organelles in the body's cellular structure?
-Organelles are tiny, organ-like structures within cells that are made up of chemical groupings and have specific functions necessary for cellular survival.
Why can't organelles live outside of cells?
-Organelles cannot live outside of cells because they are dependent on the cellular environment and infrastructure to perform their specific functions.
How many cells are estimated to be in the human body?
-It is estimated that the human body has around 100 trillion cells.
What are the main components of a cell?
-A cell is composed of a membrane, a nucleus, and cytoplasm that contains organelles required for the cell to function properly.
What are the four major types of tissues in the human body?
-The four major types of tissues in the human body are connective tissue, muscle tissue, nervous tissue, and epithelial tissue.
How do organs differ from tissues?
-Organs are made up of different kinds of tissues that work together to perform complex functions in the body, whereas tissues are groups of similar cells that perform a specific function.
What is an example of a function performed by the liver, as mentioned in the script?
-The liver performs various functions such as storing vitamins and minerals, storing glycogen (a stored form of energy), destroying old red blood cells, and detoxifying the blood to remove harmful substances.
How many major systems are there in the human body, and what is their role?
-There are 11 major systems in the human body, and they are comprised of organs that work together to perform more complex types of functions.
What is the highest level of organization in the human body as described in the script?
-The highest level of organization in the human body is the organism level, which is the overall human organism made up of all the previously mentioned levels.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Levels of Biological Organization

Structural Organization of the Human Body
Anatomical Organization of the Human Body From atoms and molecules to the entire organism as a whole

Introduction To Anatomy Physiology: Levels of Organization (01:03)

Anatomi Fisiologi Dasar : Sel dan Jaringan

NÍVEL DE ORGANIZAÇÃO CELULAR DOS SERES VIVOS: CÉLULA, TECIDO, ÓRGÃO, SISTEMA E ORGANISMO! #fyp
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)