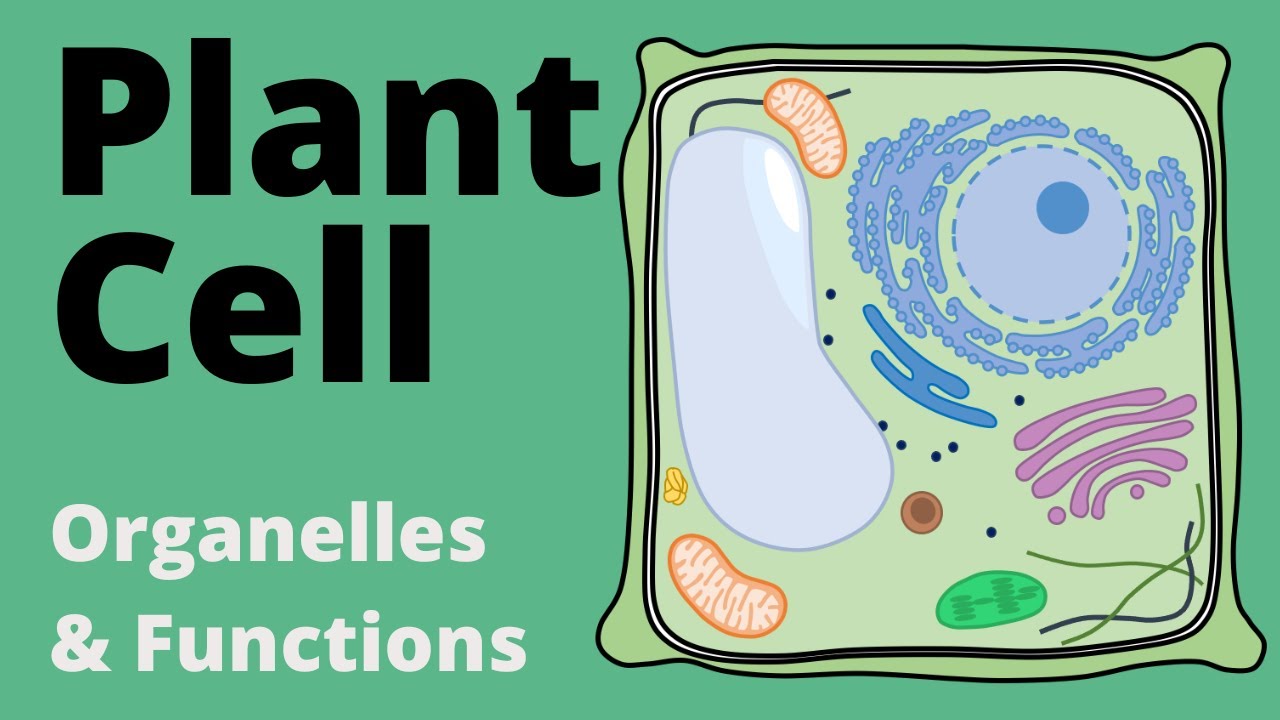
Part IV The Eukaryotic Cell
Summary
TLDRThis video script offers an insightful overview of the eukaryotic cell, highlighting its key components and their functions. It emphasizes the nucleus as the control center, containing DNA and chromatin for genetic packaging. The script also covers the roles of the Golgi complex in cellular product storage, lysosomes in waste digestion, and the plasma membrane's semi-permeable nature. It delves into the endoplasmic reticulum's lipid and protein synthesis, ribosomes' role in protein synthesis, and the cytosol's metabolite transport. The video concludes with the functions of centrioles, mitochondria, and microtubules, emphasizing their importance in cell division, energy production, and structural support. A final reminder to 'do the right thing' leaves a thoughtful impression.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The eukaryotic cell is characterized by a membrane-bound nucleus and is found in all life kingdoms except Monera.
- 🧬 The nucleus contains chromatin, a complex of DNA and proteins, which packages the long DNA molecule.
- 🚪 The nuclear envelope and nuclear pores play crucial roles in protecting genetic material and regulating the passage of molecules in and out of the nucleus.
- 🛍️ The Golgi complex is responsible for the storage and packaging of cellular products.
- 🗑️ Lysosomes digest cellular waste, maintaining the cleanliness within the cell.
- 🚀 Flagella are used for cell locomotion, allowing movement in certain eukaryotic cells.
- 🏛️ The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is the semi-permeable outer covering of the cell that controls the passage of substances.
- 🧴 The endoplasmic reticulum, both smooth and rough, is involved in the synthesis of lipids and proteins, respectively.
- 🧬 Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis, essential for the cell's metabolic activities.
- 🚰 The cytosol, or intracellular fluid, facilitates the transport of metabolites within the cell.
- 🚀 Vesicles transport materials within the cell, ensuring proper distribution and function.
- 🌀 Centrioles organize microtubule assembly during cell division, playing a key role in cellular reproduction.
- 🔋 Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell, responsible for cellular respiration and energy production.
- 🏗️ Microtubules provide structural support and help maintain the cell's shape.
Q & A
What is the main characteristic of a eukaryotic cell?
-The main characteristic of a eukaryotic cell is that it possesses a membrane-bound nucleus and is comprised of all life kingdoms except the kingdom Monera.
What is the function of the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell?
-The nucleus contains the hereditary material or DNA and directs the cell activities. It is responsible for packaging the long DNA molecule with the help of chromatin.
What is chromatin and what is its primary function?
-Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found inside the nucleus, and its primary function is to package the long DNA molecule.
What is the role of the nuclear envelope or nuclear membrane?
-The nuclear envelope or nuclear membrane encases the genetic material, providing a protective barrier around the nucleus.
Can you explain the function of the nuclear pore?
-The nuclear pore is a tiny hole in the nuclear membrane that allows for the transport of molecules in and out of the nucleus.
What is the role of the Golgi complex in a eukaryotic cell?
-The Golgi complex is responsible for storing and packaging cellular products for secretion or use within the cell.
What is the function of lysosomes in a eukaryotic cell?
-Lysosomes help to digest cellular waste and maintain the cell's internal environment by breaking down waste materials and cellular debris.
What is the purpose of flagella in a eukaryotic cell?
-Flagella are often used for locomotion, allowing certain cells to move through their environment.
What are the two types of endoplasmic reticulum and their functions?
-There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum: the smooth ER, which is involved in the synthesis of lipids for the production of cellular membranes, and the rough ER, which is specialized in the synthesis of proteins.
What is the role of ribosomes in a eukaryotic cell?
-Ribosomes perform the biological process of protein synthesis, translating the genetic code from mRNA into functional proteins.
What is the function of the cytosol in a eukaryotic cell?
-The cytosol, also known as the intracellular fluid or ICF, is involved in the transportation of metabolites and facilitates various biochemical reactions within the cell.
What is the purpose of vesicles in a eukaryotic cell?
-Vesicles are cellular envelopes used to transport materials from one part of the cell to another, playing a crucial role in intracellular transport.
What is the role of centrioles in a eukaryotic cell?
-Centrioles organize microtubule assembly during cell division, ensuring the proper segregation of genetic material.
What is the primary function of mitochondria in a eukaryotic cell?
-Mitochondria are the site for cellular respiration and are the primary producers of energy in the form of ATP for the cell.
What is the role of microtubules in a eukaryotic cell structure?
-Microtubules function as the primary support structure, providing shape and stability to the cell, and are involved in intracellular transport and cell division.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)