Endomembrane system | Structure of a cell | Biology | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video offers an insightful overview of the endomembrane system in eukaryotic cells, highlighting its integral components such as the cell membrane, nuclear envelope, and endoplasmic reticulum. It explains the phospholipid bilayer structure and delves into the synthesis and maturation of proteins within the system. The script also touches on the Golgi apparatus's role in protein modification and the significance of vesicles in protein transport. Furthermore, it mentions other organelles like vacuoles and lysosomes, emphasizing the complexity and beauty of cellular processes.
Takeaways
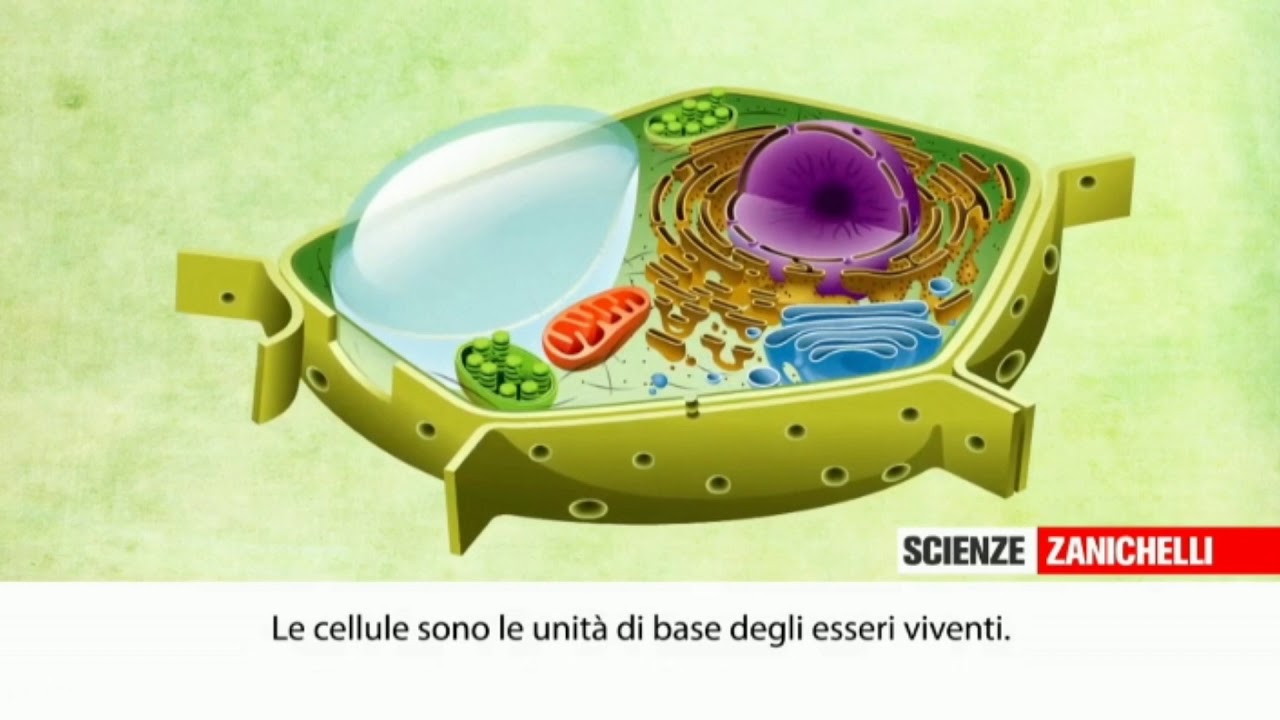
- 🌐 The endomembrane system in eukaryotic cells comprises all the membranes that interact within the cell, including the cell membrane and various organelles.
- 🧬 Phospholipid bilayers are the fundamental structure of the membranes, with hydrophilic heads facing outward and hydrophobic tails facing inward.
- 🔬 The cell membrane, outer nuclear membrane, and endoplasmic reticulum are continuous and share the same phospholipid bilayer structure.
- 🌟 The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) can represent more than 50% of the cell's phospholipid membrane and is involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
- 🛠️ The lumen of the ER is the site of protein and lipid synthesis, with the smooth ER playing a role in further processing these molecules.
- 🚀 The transitional ER is where proteins are packaged into vesicles for transport to other parts of the cell, such as the Golgi apparatus.
- 🔄 The Golgi apparatus is responsible for maturing proteins, which can include adding saccharides to form glycoproteins and preparing them for various cellular roles.
- 🚪 Vesicles are small compartments with membranes that transport proteins and other molecules throughout the cell.
- 🌱 In plant cells, vacuoles serve as large, membrane-bound organelles for storage and structural support.
- 🗑️ Lysosomes in animal cells are membrane-bound structures that recycle or break down cellular materials in an acidic environment.
- 🔧 The endomembrane system highlights the complexity and beauty of cellular processes, involving a coordinated network of membranes and organelles.
Q & A
What is the endomembrane system in eukaryotic cells?
-The endomembrane system in eukaryotic cells is a network of membranes that interact with each other within the cell, including the cell membrane, nuclear membrane, and membranes of various organelles.
What are the main components of the bilayer of phospholipids?
-The bilayer of phospholipids consists of hydrophilic heads pointing outwards and hydrophobic tails pointing inwards, forming the basic structure of cell membranes.
How is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) related to the nuclear envelope?
-The endoplasmic reticulum is continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope, forming a part of the endomembrane system.
What percentage of the cell's phospholipid membrane is associated with the endoplasmic reticulum?
-The endoplasmic reticulum can represent up to or even more than 50% of the phospholipid membrane associated with the cell.
What happens in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum?
-The lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum is the site where proteins and lipids are synthesized.
What is the transitional endoplasmic reticulum and its function?
-The transitional endoplasmic reticulum is the area where newly synthesized proteins are transported out of the ER in vesicles, moving towards the Golgi apparatus for further processing.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in the endomembrane system?
-The Golgi apparatus is responsible for the maturation of proteins, including the addition of saccharides to form glycoproteins and tagging for various cellular functions.
How do proteins move from the ER to the Golgi apparatus?
-Proteins are transported from the ER to the Golgi apparatus in vesicles, which then merge with the Golgi membrane, releasing their contents for further processing.
What are vesicles and their purpose in the endomembrane system?
-Vesicles are small compartments with a membrane around them, used for transporting proteins and other molecules within the cell.
What is the function of vacuoles in plant cells?
-In plant cells, vacuoles are used for storage and provide structural support, sometimes becoming quite large and contributing to the plant's shape.
What is a lysosome and its role in the endomembrane system?
-A lysosome is a membrane-bound organelle in animal cells where materials are broken down and recycled, functioning as a site for degradation and digestion of cellular components.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)