Carbon Dioxide | HOMEOSTASIS | Easy to understand
Summary
TLDRIn this biology lesson, Miss Angler explains the concept of homeostasis, focusing on the body's regulation of carbon dioxide levels, not oxygen. She clarifies common misconceptions, emphasizing the role of chemoreceptors in the carotid artery and aorta that detect pH changes, signaling the medulla oblongata to adjust breathing rate and depth. This process helps maintain blood pH and prevent acidosis, illustrating the body's efforts to preserve a stable internal environment.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is a biology class by Miss Angler focusing on homeostasis, particularly the regulation of carbon dioxide in the bloodstream.
- 🔍 The body can't regulate oxygen levels but can regulate carbon dioxide, which is a common mistake in exam answers.
- 🌡️ Carbon dioxide plays a role in maintaining the pH of the blood, which is crucial to prevent enzymes from denaturing.
- 🧠 Homeostasis and pH maintenance are interconnected, and understanding this link is key to answering related exam questions.
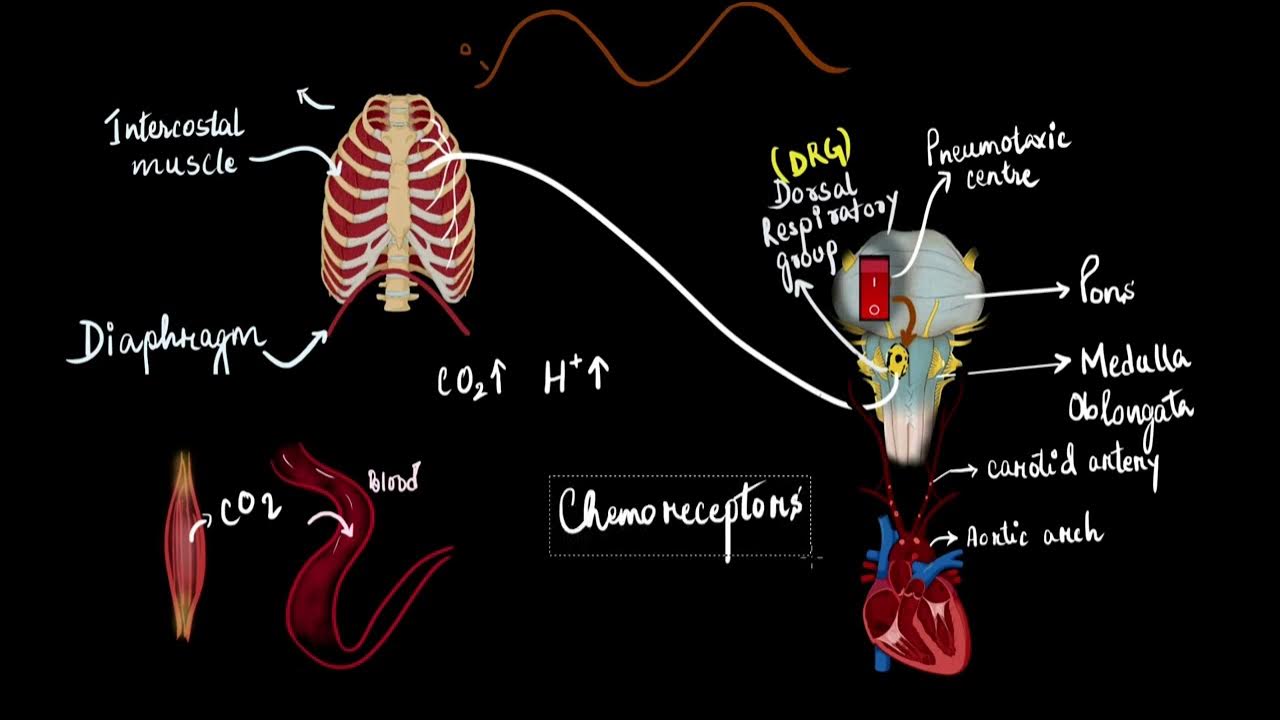
- 🚀 Carbon dioxide is regulated in the blood vessels, not in the lungs, specifically in the carotid artery and the aorta.
- 🧐 The carotid artery is important because it supplies the brain with oxygen-rich blood, and the aorta carries blood to all organs.
- 📈 Chemoreceptors in the aorta and carotid artery detect changes in blood pH and carbon dioxide levels, triggering a response.
- 💡 The medulla oblongata in the brain acts as the control center for breathing rate and is alerted by chemoreceptors about blood pH changes.
- 🏃♂️ The corrective measures involve the heart beating faster and breathing muscles contracting faster and deeper to exhale more carbon dioxide.
- 🔄 The goal of these corrective measures is to prevent acidosis, maintaining a balanced pH and thus homeostasis in the blood.
- 📝 Key terms to remember for exams include chemoreceptors, aorta, carotid artery, medulla oblongata, and breathing muscles.
Q & A
What is the main topic of Miss Angler's biology class video?
-The main topic of the video is homeostasis, specifically focusing on how the body regulates carbon dioxide levels in the bloodstream.
Which grades does Miss Angler suggest should pay attention to this topic?
-Miss Angler suggests that students in both grade 11 and grade 12 should pay attention to this topic, as it relates to the respiratory system and homeostasis.
What is the common mistake students make regarding the regulation of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body?
-The common mistake is that students often believe the body can regulate oxygen levels in the bloodstream, when in fact, it can only regulate carbon dioxide levels.
Why is it important to maintain the pH of our blood?
-Maintaining the pH of our blood is important to prevent enzymes from denaturing, which could impair their function.
Which two blood vessels are primarily responsible for regulating carbon dioxide levels?
-The carotid artery and the aorta are the two blood vessels primarily responsible for regulating carbon dioxide levels.
What is the role of the carotid artery in carbon dioxide regulation?
-The carotid artery brings fresh blood to the brain, and if it detects high levels of carbon dioxide, it alerts the body to initiate changes.
What is the role of the aorta in carbon dioxide regulation?
-The aorta is responsible for distributing blood to all body organs, and if it detects high carbon dioxide levels, it alerts the breathing muscles to increase the rate and depth of breathing.
What is the process that the body follows to respond to increased carbon dioxide levels?
-The process involves a stimulus (increased CO2 levels), receptors (chemoreceptors), a control center (medulla oblongata), corrective measures (heart and breathing muscles), and the effect of these measures to reduce CO2 levels.
What is the corrective measure that the medulla oblongata sends to the heart and breathing muscles?
-The corrective measure involves the heart beating faster to circulate blood more quickly and the breathing muscles contracting faster and deeper to inhale more air and exhale more carbon dioxide.
What is acidosis and why is it important to prevent it?
-Acidosis is a condition where the blood has an overly acidic pH. It is important to prevent because it can lead to the denaturation of enzymes, impairing their function.
How does the regulation of carbon dioxide levels assist in maintaining homeostasis?
-By regulating carbon dioxide levels, the body maintains the pH of the blood within a narrow range, preventing fluctuations that could disrupt enzyme function and overall homeostasis.
What are chemoreceptors and where are they located?
-Chemoreceptors are cells that detect changes in the blood's carbon dioxide levels and pH. They are located in the aorta and carotid arteries.
What is the medulla oblongata and what role does it play in the body?
-The medulla oblongata is a region of the brain responsible for maintaining the breathing rate. It acts as the control center for the body's response to changes in carbon dioxide levels.
What are the breathing muscles mentioned in the video, and what is their function in carbon dioxide regulation?
-The breathing muscles mentioned are the diaphragm and intercostal muscles. They work in conjunction with the heart to facilitate deeper and faster breathing, helping to exhale more carbon dioxide.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)