The origins of the Hamas-Israel war explained | ABC News
Summary
TLDRThe script delves into the historical roots of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, starting from World War I through to the establishment of Israel and the ongoing disputes over territories like the West Bank and Gaza Strip. It highlights the UN's division plan, the Arab rejection, subsequent wars, and the current situation with Israel's occupation and blockade. The narrative also touches on the rise of Hamas and the challenges faced by Palestinians, including high unemployment and restricted movement, amid escalating tensions around religious sites and holidays.
Takeaways
- 🏛️ The script begins with historical context, tracing the conflict back to World War I and Britain's control over the region, which had an Arab majority and a Jewish minority.
- 🌐 The script mentions the Holocaust and the subsequent increase in Jewish migration, leading to the United Nations' 1947 decision to divide the British mandate for Palestine into a Jewish and an Arab state.
- 🇮🇱 Israel's acceptance of the UN's partition plan resulted in its formation as a state, while the Arab side's rejection led to a war.
- 📈 The script describes the displacement of Palestinians during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, known as the 'Nakba' or catastrophe, and the subsequent control of different territories by Israel, Egypt, Jordan, and Syria.
- 📅 The Six-Day War in 1967 is highlighted as a pivotal event where Israel seized control of the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and Golan Heights, leading to ongoing occupation and international objections.
- 🏠 The occupation has resulted in Israeli civilians living in disputed territories for various reasons, causing displacement and conflict with Palestinians.
- 📣 The script discusses the formation of Hamas in the late 1980s as a response to growing frustrations, with the group's goal being the destruction of Israel.
- 🗳️ Hamas won democratic elections in 2006 but was isolated internationally due to its refusal to renounce violence against Israel.
- 🚫 The Gaza Strip's situation is detailed, with Israel's withdrawal in 2005 but continued control over airspace, sea, and crossings, leading to a blockade and harsh living conditions.
- 🕋 Jerusalem's significance as a holy city for three major religions is mentioned as a point of contention, with religious holidays often escalating tensions.
- ⚔️ The script concludes by noting the potential for further escalation in the region, as recent attacks indicate an ongoing cycle of conflict.
Q & A
What historical event is mentioned at the beginning of the script that had a significant impact on the region?
-The script begins by mentioning World War I, when Britain took control of the region that is now known as Israel and Palestine.
What was the demographic composition of the region during the time of British control post-World War I?
-During the time of British control, the region had an Arab majority and a Jewish minority.
What significant event in the 20th century led to a large increase in Jewish migration to the region?
-The Holocaust targeting Jews during World War II led to a significant increase in Jewish migration to the region.
What was the United Nations' proposal in 1947 regarding the division of the British mandate for Palestine?
-In 1947, the United Nations proposed dividing the British mandate for Palestine into a Jewish State and an Arab State.
Why did the Arab side reject the UN's partition plan in 1947?
-The Arab side rejected the UN's partition plan because they did not agree with the division of the land into separate Jewish and Arab states.
What is the term Palestinians use to describe the displacement that occurred after the 1948 war?
-Palestinians refer to the displacement that occurred after the 1948 war as the 'Nakba', or catastrophe.
What territories did Israel seize control of during the Six-Day War in 1967?
-During the Six-Day War in 1967, Israel seized control of the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, and the Golan Heights.
What is the status of the West Bank and Gaza Strip according to the UN regarding Israeli occupation?
-The UN considers the Israeli occupation of the West Bank and Gaza Strip as illegal.
Why do Israeli civilians choose to live in the occupied territories despite objections from the international community?
-Israeli civilians choose to live in the occupied territories for various reasons, including political and religious beliefs, as well as for the affordability of housing.
What is the primary goal of Hamas, as mentioned in the script?
-The primary goal of Hamas, as mentioned in the script, is the destruction of Israel.
How does the Israeli blockade of Gaza affect the living conditions there?
-The Israeli blockade of Gaza has led to tough living conditions, with a high unemployment rate of 50%, as well as deteriorating health systems and infrastructure.
What is the significance of Jerusalem in the ongoing conflict, and how does it relate to religious tensions?
-Jerusalem is significant in the ongoing conflict because it is home to holy sites from three major religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Clashes in the region often escalate around major religious holidays.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Kenapa Wilayah Palestina terbagi dua?
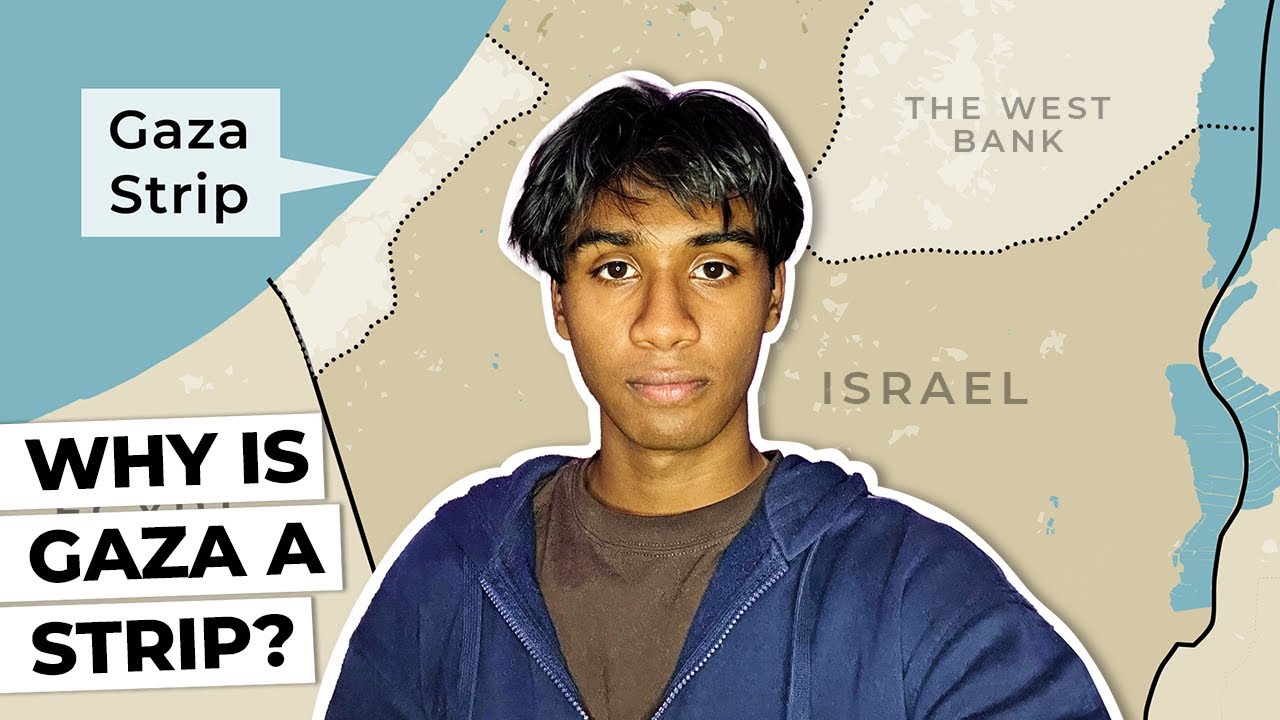

How the Gaza Strip came to be | A brief history of Gaza | CBC Kids News

Understanding Palestine in 10 Questions | Between the Lines with Palki Sharma

Israel, Palestine and Hamas explained in two minutes

Israel - Palestine Crisis Explained

How Benjamin Netanyahu Relies on Hamas
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)