Perfect Base Resistor Selection: Mastering Transistors
Summary
TLDRThis video script offers a comprehensive guide on selecting the optimal base resistor for a transistor. It explains the necessity of a base resistor to prevent damage to the transistor or voltage source. The script outlines two methods for determining the best resistor value: a simplified approach using basic parameters, and an advanced method utilizing data from the transistor's datasheet. Practical examples and the impact of incorrect resistor values are discussed, with an emphasis on ensuring the transistor operates in deep saturation for reliability and efficiency.
Takeaways
- 😀 The base resistor is essential in a transistor circuit to prevent damage to the transistor or the voltage source due to high current.
- 🤔 A poorly chosen base resistor value can lead to the transistor operating in the active region, causing high power dissipation and potential failure.
- 🔍 The simplified method for selecting the base resistor involves using standard values for parameters like collector current (IC), collector-emitter voltage (VCE), input voltage (VI), and base-emitter voltage (VBE).
- 📚 The advanced method utilizes specific values from the transistor's datasheet, providing a more accurate selection of the base resistor.
- 🔧 The base resistor's role is to ensure the transistor operates in deep saturation, which is crucial for reliable switching performance.
- 🔢 The base resistor value is calculated based on the base current (IB), which in turn is determined by the collector current (IC) and the transistor's current gain (HFE).
- 🛠️ For non-standard resistor values, it's recommended to choose the nearest standard value that is lower than the calculated value to ensure deeper saturation.
- ⚠️ Power dissipation must be considered when selecting the base resistor, and a resistor with an appropriate power rating should be used to avoid overheating.
- 🔎 Datasheets provide graphs and data that can help in estimating the base current and selecting the appropriate base resistor for specific transistors and loads.
- 🔄 The active and saturation regions of a transistor's operation are important for understanding how the base resistor affects the circuit's performance.
- 👨🏫 The video script provides examples and methods for calculating the base resistor value for different types of loads, such as resistive loads, relays, and DC motors.
Q & A
Why is a resistor necessary at the base terminal of a transistor?
-A resistor at the base terminal is necessary to limit the base current and prevent damage to the transistor or the voltage source. Without it, high current could be delivered to the junction, potentially destroying the transistor or the source.
What are the consequences of not having a proper base resistor?
-Without a proper base resistor, the transistor could be destroyed due to excessive current, or the voltage source could be damaged if it's not strong enough to supply the required current.
What are the two regions of operation for a transistor mentioned in the script?
-The two regions of operation for a transistor are the cut-off region (when the transistor is off and the collector-emitter voltage is maximum) and the saturation region (when the transistor is fully on and the collector-emitter voltage is negligible).
Why is it important for a transistor to operate in the saturation region?
-Operating in the saturation region ensures that the transistor acts as a perfect switch, minimizing the collector-emitter voltage and maximizing the current flow, which is essential for reliable switching in circuits.
What factors can affect the choice of base resistor value?
-Factors affecting the choice of base resistor value include the collector current, the desired operation region of the transistor (saturation or active), power dissipation, and the reliability of the circuit under varying conditions.
What is the simplified method for selecting the base resistor value?
-The simplified method involves using standard values for parameters like collector current (IC), collector-emitter voltage (VCE), input voltage (VI), and current gain (HFE) to calculate the base current (IB) and subsequently the base resistor (RB) using Ohm's Law.
What is the advanced method for selecting the base resistor value?
-The advanced method involves using the data sheet of the transistor and the specifications of the load to find exact values for parameters like VCE, VBE, and HFE, and then calculating the base resistor value accordingly.
Why is it important to consider power dissipation when selecting a base resistor?
-Considering power dissipation is important because a high power dissipation can lead to overheating and failure of the transistor. Choosing a base resistor that puts the transistor in the saturation region reduces power dissipation.
How can you estimate the base current (IB) from the data sheet?
-You can estimate the base current by looking at the graphs provided in the data sheet, which show the relationship between collector-emitter voltage and base current at different collector currents. By interpolating between the closest available points, you can estimate the IB for your specific collector current.
What is the significance of choosing a resistor with a higher power rating than the calculated power dissipation?
-Choosing a resistor with a higher power rating ensures that the resistor can safely dissipate the heat generated by the current flowing through it, preventing damage to the resistor and ensuring the long-term reliability of the circuit.
How can you verify if a transistor is operating in the saturation region?
-You can verify if a transistor is operating in the saturation region by monitoring the collector-emitter voltage (VCE). If VCE is very low and remains low even when the collector current is increased, it indicates that the transistor is in the saturation region.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
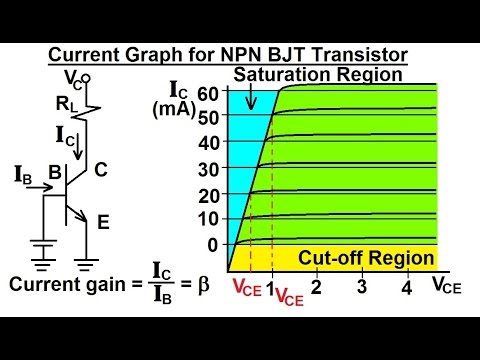
Electrical Engineering: Ch 3: Circuit Analysis (28 of 37) Current Graph for NPN BJT Transistor

Transistor Biasing | Base Resistor Biasing Method | Fixed Bias Circuit | Base Bias Circuit
BJT: Collector Feedback Bias Explained

PHOTOSHOP TRICK #01 : POTRAIT TEXT PHOTO (Bahasa Indonesia)

RAHASIA PEMBUATAN KUE ... #SecretFromChef | Part 1

Terungkap !!! Teknik Budidaya Vanili di Perkotaan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)