Earth's Magnetic Field | Earth Itself Is a Huge Magnet | Magnetosphere | Arbor Scientific
Summary
TLDRThis script explores Earth's magnetic field, akin to a bar magnet, which shields us from solar winds. The source of Earth's magnetism is largely due to convection currents within its interior, though it remains a mystery. The magnetic poles wander and change, with the northern magnetic pole moving from Canada to Siberia. Compasses point to geomagnetic poles, which differ from the geographic poles and are associated with auroras. Magnetic reversals, evidenced by ocean floor studies, have occurred throughout history without significant impact on life, and while the field may weaken during a reversal, it remains protective.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Earth is a huge magnet with a magnetic field similar to that of a bar magnet.
- 🛡️ Earth's magnetosphere acts as a shield against the ionized solar wind from the Sun.
- 🌐 The source of Earth's magnetism is not completely understood but is attributed to convection currents within the Earth's interior.
- 🔄 The direction and strength of Earth's magnetic field change over time.
- 🧭 A compass needle points vertically at the Earth's magnetic poles where the field lines are perpendicular to the surface.
- 🌀 The magnetic poles are not fixed and tend to wander, as shown in historical maps of their location.
- 🗺️ Magnetic declination maps are useful for navigation, showing the deviation of compass readings from the geographic poles.
- 🌌 Geomagnetic poles are different from magnetic poles and are related to the average variations of the magnetic field across the planet.
- 🌈 Auroras are generally centered about the geomagnetic poles because of the interaction with ions from outer space.
- 🔧 Geomagnetic poles migrate around the geographic poles over thousands of years, and their positions average out to the geographic pole's location.
- 🔁 The Earth's magnetic poles have flipped orientation in the past, with evidence from ocean sea floors showing magnetic reversals.
- ⏳ Magnetic reversals do not significantly impact life-forms and take hundreds to thousands of years to occur.
Q & A
What is the Earth's magnetosphere and how does it function?
-The Earth's magnetosphere is the region around our planet dominated by its magnetic field. It acts as a shield, protecting us from the solar wind, which is a stream of charged particles emitted by the Sun.
Why do Earth's magnetic field lines bend away from the planet?
-The magnetic field lines bend away from Earth due to the ionized solar wind from the Sun that encounters the Earth's magnetic field, causing the lines to be distorted as they extend into space.
What is the source of Earth's magnetism and why is it not completely understood?
-The source of Earth's magnetism is attributed to convection currents within the Earth's interior. However, it is not completely understood due to the complex and dynamic nature of the Earth's core and the processes occurring within it.
How does the direction and strength of Earth's magnetic field change over time?
-The direction and strength of Earth's magnetic field change over time due to the shifting of the convection currents in the Earth's interior, which in turn affects the magnetic field's orientation and intensity.
What is the difference between Earth's magnetic poles and geomagnetic poles?
-Earth's magnetic poles are where the magnetic field lines are perpendicular to the surface, and a compass needle would point straight up or down. Geomagnetic poles, on the other hand, are the broad scale view of the magnetic poles and represent the average of all variations found across the planet.
Why do the magnetic poles wander and how is this tracked?
-The magnetic poles wander due to the dynamic nature of the Earth's core and the movement of its magnetic field. This wandering is tracked over time by observing changes in the magnetic field and mapping the location of the poles.
What is a magnetic declination map and why is it useful for navigation?
-A magnetic declination map shows the difference between magnetic north and true north, indicating how far off a compass reading is from the geographic pole. It is useful for navigation to correct for the偏差偏差 of a compass and provide more accurate directions.
How does the Earth's magnetic field relate to the aurora phenomenon?
-The aurora phenomenon is generally centered about the geomagnetic poles because these are the areas where ions from outer space encounter the Earth's magnetic field, leading to the beautiful light displays known as auroras.
What evidence do we have that Earth's magnetic poles have flipped in the past?
-The most direct evidence of past magnetic pole flips comes from the ocean sea floors. As the floor spreads apart, molten rock containing metal solidifies and captures the orientation of the magnetic poles at that time, creating bands of magnetic orientation that are flipped on opposite sides of the ocean ridge.
What impact do magnetic pole reversals have on life-forms according to geologic records?
-Geologic records show that past magnetic reversals have had no significant impact on life-forms. This suggests that even though the magnetic field might weaken during a flip, enough remains to deflect solar winds and protect life on Earth.
How long does a magnetic pole reversal typically take and what is the current status of the next reversal?
-A magnetic pole reversal typically takes hundreds or thousands of years to occur, which is relatively quick on geological timescales. The next magnetic reversal could happen at any time, but currently, there is no immediate cause for concern.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Earth and Compasses | Magnetism | Physics | FuseSchool
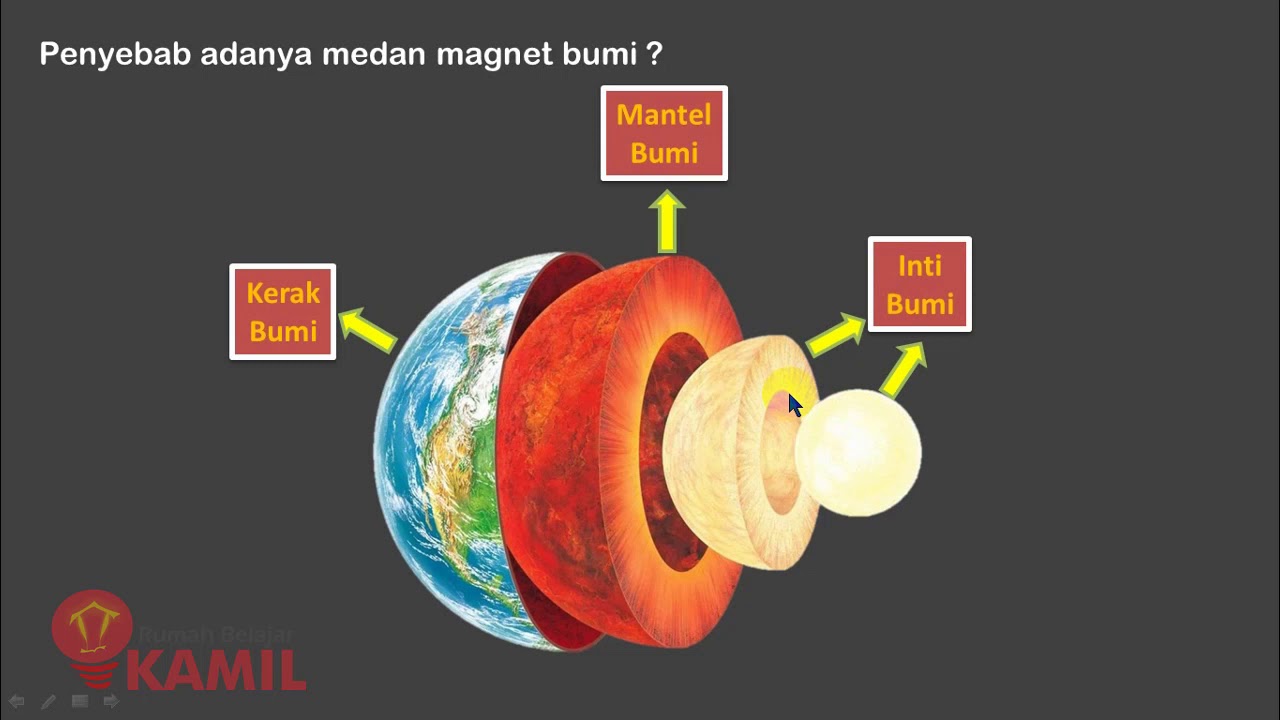
IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Kemagnetan (Part 2 : Medan Magnet dan Magnet pada Bumi)

Kemagnetan : Medan Magnet dan Kemagnetan Bumi
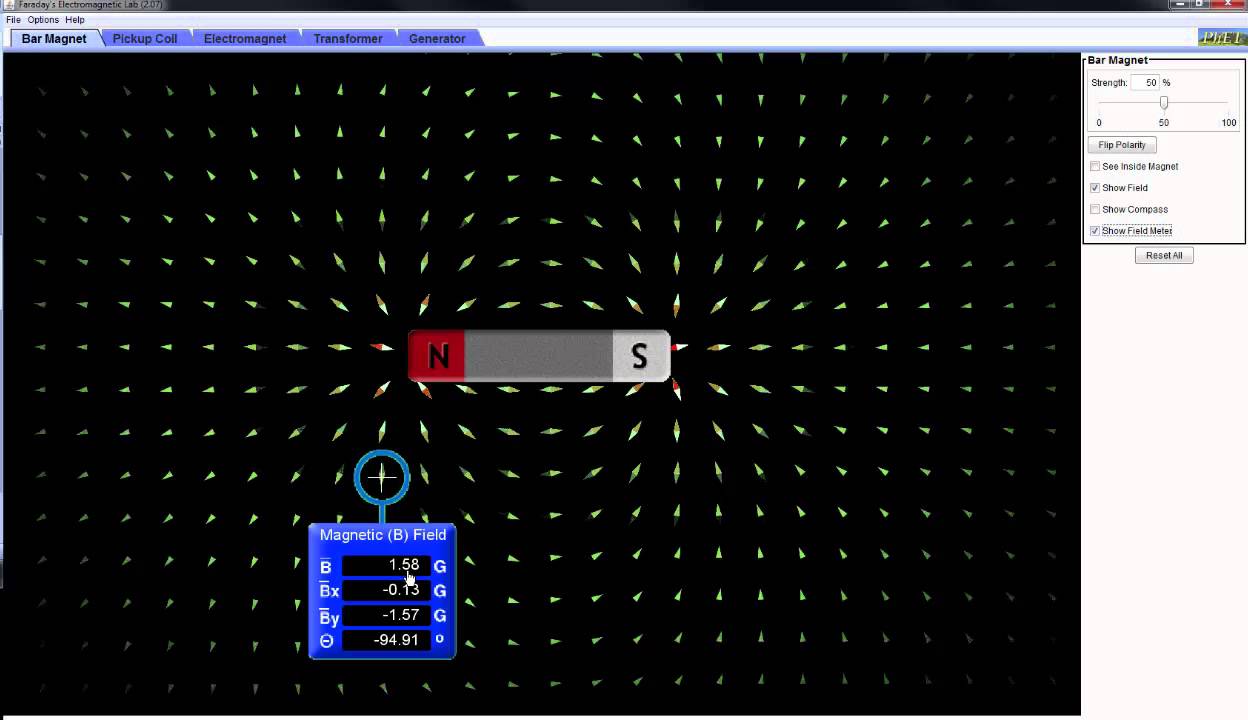
Phet Simulation: Faraday's Lab on the Bar Magnet

EARTH'S INTERNAL HEAT / Primordial & Radioactive Heat / EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE / SCIENCE 11 - MELC 6

Konsep Garis Medan Magnet | Fisika
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)