FISICA! parliamo di SCOMPOSIZIONE VETTORIALE, scomposizione vettori, scomposizione di un vettore
Summary
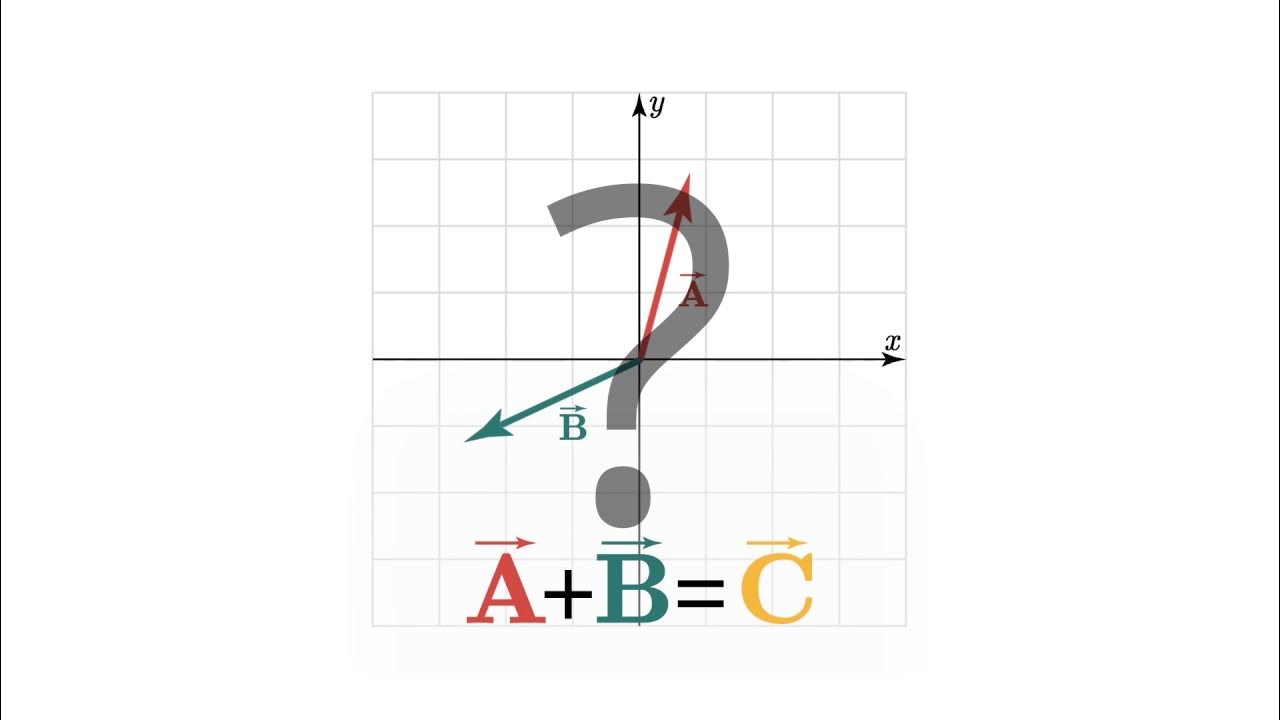
TLDRThe video script discusses the concept of vector decomposition, which is the reverse process of vector addition. It explains how to break down a vector into two components along two given directions, using an example with vectors 'a' and 'b'. The process involves shifting the vector to the intersection of the directions and then drawing parallels to find the intersection points, which represent the heads of the decomposed components. The script emphasizes the method's practicality and its relation to vector addition, highlighting the educational value of understanding both operations.
Takeaways
- 📚 The script discusses the concept of vector decomposition, which is the opposite of vector addition.
- 🔍 It explains that vector decomposition involves breaking down a single vector into two components.
- 🎥 The video is a direct demonstration of the process, likely using visual aids to illustrate the concept.
- 📏 The script mentions the need for two directions, 't' and 'v', along which the original vector is decomposed.
- 📐 The process involves translating a part of the vector to the intersection of the two directions to find the components.
- 📍 The script describes an operation where the vector is translated and then parallel lines are drawn to the directions 't' and 'v'.
- 📝 It emphasizes the importance of drawing the components correctly and the significance of their intersection points.
- 🧭 The components of the vector are represented by the intersection points, which are labeled with the original vector's name and the direction.
- 🔄 The script highlights that the decomposition process is the reverse of the vector addition method.
- 📉 The components are named 'hd' and 'hc', representing the vector's projection along the 'h' and 'v' directions, respectively.
- 🔠 The script concludes by restating that the vector 'h' has been decomposed into 'hd' plus 'hc', mirroring the vector addition process in reverse.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the script?
-The main topic discussed in the script is the concept of vector decomposition, which is the process of breaking down a single vector into two components along specific directions.
What is the opposite operation of vector decomposition?
-The opposite operation of vector decomposition is vector addition, where two or more vectors are combined to form a single resultant vector.
What are the two directions needed for vector decomposition according to the script?
-The script mentions that two directions, represented as 't' and 'v', are needed for the vector decomposition process.
How is the vector 'h' decomposed in the script?
-The vector 'h' is decomposed into two components along the directions 't' and 'v', which are represented as 'hd' and 'hc' respectively.
What are the two components obtained after decomposing the vector 'h'?
-The two components obtained after decomposing the vector 'h' are 'hd', which is the component along the direction 't', and 'hc', which is the component along the direction 'v'.
What is the significance of the intersection point of the decomposition lines?
-The intersection point of the decomposition lines is significant as it represents the tail of the original vector 'h' after being translated to the intersection of the directions 't' and 'v'.
Why is it important to translate the vector to the intersection of the directions?
-Translating the vector to the intersection of the directions is important because it allows for the correct positioning of the vector components along the chosen directions 't' and 'v'.
What does the script suggest about the relationship between the components and the original vector?
-The script suggests that the original vector 'h' can be represented as the sum of its components 'hd' and 'hc', which is the reverse process of vector decomposition.
What is the practical application of vector decomposition mentioned in the script?
-The script does not explicitly mention a practical application, but it implies that understanding vector decomposition is fundamental in various fields where vector operations are used.
How does the script describe the process of finding the components of the vector 'h'?
-The script describes the process of finding the components by drawing parallels to the directions 't' and 'v' from the tail of the translated vector 'h', and then identifying the intersection points with the original vector as the components.
What is the script's stance on the method of vector decomposition compared to vector addition?
-The script presents vector decomposition as the inverse operation of vector addition, emphasizing that it is a fundamental concept and necessary for understanding how vectors can be broken down into simpler components.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)