What is Materials Engineering?
Summary
TLDRMaterials engineering focuses on designing and analyzing solid materials' structure, properties, and performance. It plays a crucial role in various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing, where materials must withstand extreme conditions or possess specific properties. The field encompasses the study of metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites, with an emphasis on mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties. Materials engineers also address challenges like corrosion, fracture analysis, and improving material efficiency. The curriculum includes practical applications, lab work, and a balance of math and chemistry, preparing students for a broad range of sectors.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Materials engineering involves the design, processing, testing, and discovery of solid materials, focusing on their structure, properties, performance, and processing.
- 🔍 A Google search for 'materials engineering' reveals the interconnectedness of material structure, properties, performance, and processing, where changes in one aspect can affect the others.
- 🚀 Materials engineers play a crucial role in industries like aerospace, where they design materials to withstand high temperatures and friction in supersonic aircrafts.
- 🚗 In automotive engineering, materials engineers determine the right materials and structures for car safety, including the crumple zones designed to absorb energy during crashes.
- 🔬 Failure analysis is a significant part of a materials engineer's job, where they examine broken parts like jet engines or computer components to understand why they failed.
- 📏 Materials engineers study fracture, material properties, and the microstructure of objects to determine how structures fail and to improve designs.
- 💧 Corrosion is a major concern for materials engineers, especially in designing pipes and marine technologies that resist destructive effects from various environments.
- 🧬 Biomaterials, used in artificial organs and tissue replacements, require materials engineers to ensure compatibility and safety with the human body.
- 🚄 Superconductors, materials with zero electrical resistance, are an area of interest for materials engineers, with applications in high-speed circuits and magnetic levitation trains.
- 🌐 Nanotechnology allows materials engineers to manipulate atomic and molecular structures to create materials with improved mechanical, electrical, and magnetic properties.
- 📚 In college, materials engineering students study the four main classes of materials: metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites, with a focus on their mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties.
Q & A
What is materials engineering and what does it involve?
-Materials engineering is about designing, processing, testing, and discovering materials, mainly solids. It involves analyzing the structure, properties, performance, and processing of materials and objects. It also includes how changes in one aspect, like the structure of a material, can affect everything else.
How do materials engineers contribute to the aerospace industry?
-Materials engineers in the aerospace industry design materials that can withstand high temperatures and friction caused by supersonic speeds. They ensure the materials can handle the extreme conditions without failure.
What role do materials play in the safety of car crashes?
-Materials in cars are designed to crumple during a crash to absorb energy and protect the passengers. Materials engineers determine the right material and structure to ensure the car crumples in a way that saves lives.
Can you explain the importance of failure analysis in materials engineering?
-Failure analysis is crucial in materials engineering as it involves examining broken parts to determine the cause of failure. This helps in designing better materials and structures to prevent future failures.
What is the significance of understanding corrosion in materials engineering?
-Understanding corrosion is significant because it helps in designing materials that resist degradation from environmental factors. This is important for structures like pipelines, marine technologies, and vehicles where corrosion can lead to failure.
How do materials engineers work with biomaterials?
-Materials engineers work with biomaterials to construct artificial organs or replace bone and tissue. These materials need to interact well with the human body without causing harm.
What are some applications of nanotechnology in materials engineering?
-Nanotechnology in materials engineering involves manipulating atoms and molecules to form new structures with improved properties. This can lead to innovations like more efficient solar panels and stronger, unbreakable glasses.
What are the four main classes of materials studied in materials engineering?
-The four main classes of materials studied in materials engineering are metals, ceramics, polymers or plastics, and composites.
How does heat treating affect the properties of metals?
-Heat treating alters the properties of metals by changing their microstructure through heating and cooling processes. This can result in different mechanical properties such as hardness, ductility, and toughness.
What are some examples of mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties studied in materials engineering?
-Mechanical properties include hardness, ductility, and brittleness. Electrical properties refer to a material's ability to conduct electricity. Thermal properties involve how well heat can flow through an object.
How does the arrangement of atoms affect the properties of a material?
-The arrangement of atoms significantly affects a material's properties. For example, graphite and diamond, both composed of carbon, have vastly different hardness levels due to their atomic structures.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What is Mechanics of Materials and why it is important in engineering?
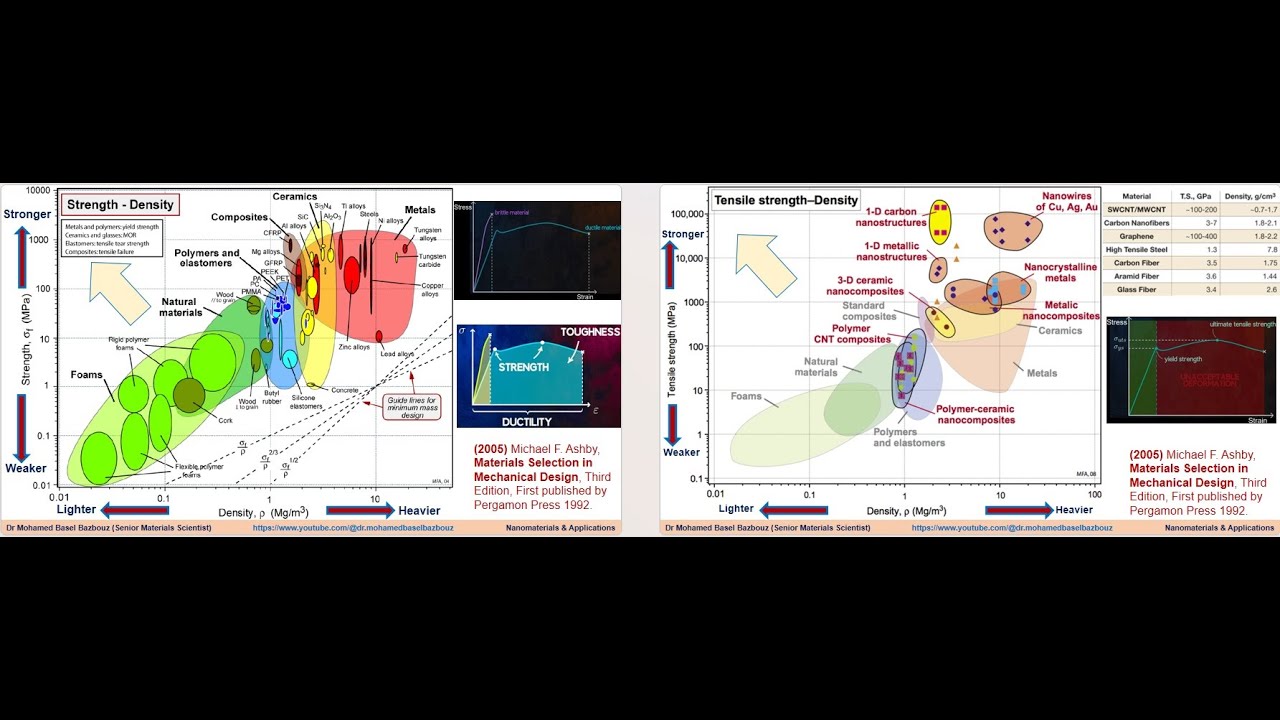
Ashby plots of Strength versus density for materials and nanomaterials المتانة والوزن النوعي

EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials

wan haliza stats interview

What is Materials Science?

Struktur dan Ikatan Antar Atom Pada Material | Agus Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)