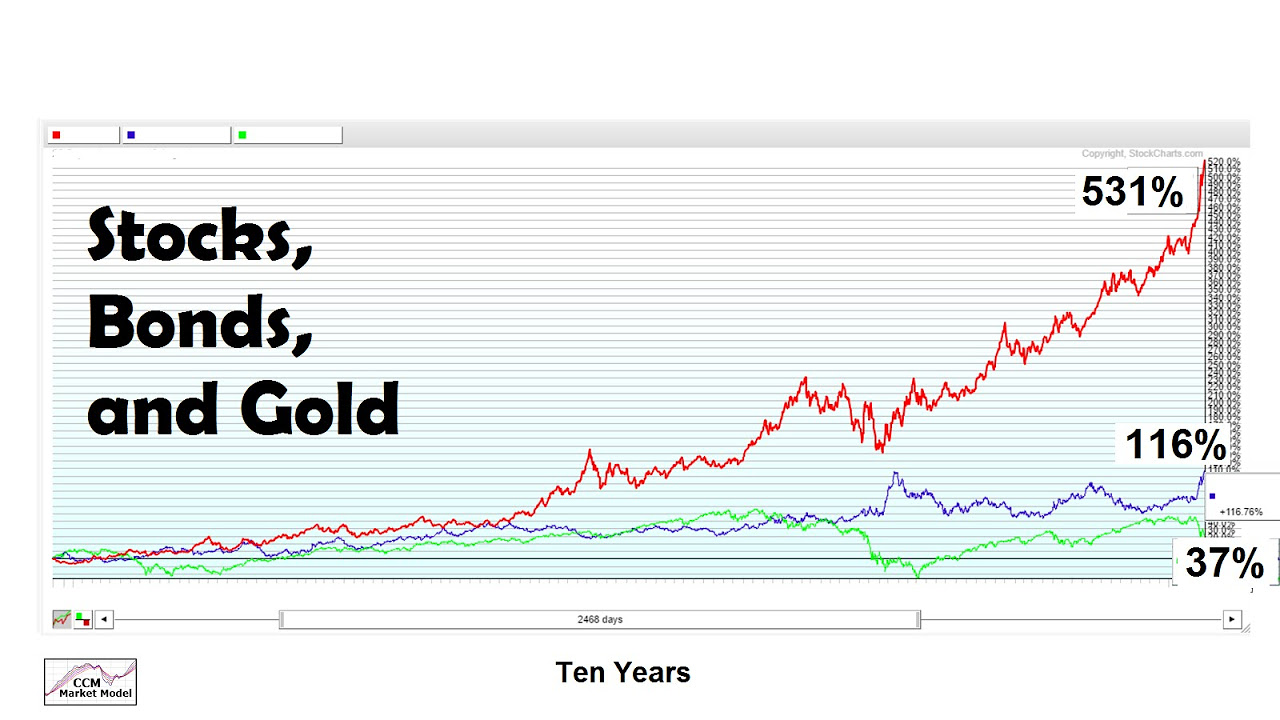
Gold: Why It Hit All-Time Highs, Central Banks, & Portfolio Strategies w/ Lyn Alden (TIP638)
Summary
TLDRThe video script delves into the dynamics of gold as an investment, discussing its historical performance during inflationary periods and its role as a diversifier in decades where stocks and bonds underperform. It explores the concept of 'paper gold' versus physical gold, the significance of central banks' gold reserves, and the factors influencing gold prices, including real interest rates and fiscal policies. The conversation also touches on the practical aspects of buying gold, such as the premiums over spot price and the verification process to ensure authenticity.
Takeaways
- 📈 Gold tends to perform well during times of increasing money supply and inflation, especially when central banks have not yet acted or failed to contain inflation.
- 🌐 The buying pattern for gold has shifted geographically, with significant purchases coming from foreign central banks and the private sector in Asia, rather than Western ETFs.
- 💰 Despite high nominal and real interest rates, which are typically不利 to gold, the metal has seen a price increase, indicating strong demand and other supportive factors.
- 🌟 Central banks have been net buyers of gold, with 2022 and 2023 marking record purchases, highlighting a strategic shift away from traditional reserve assets like US treasuries.
- 🔄 The reasons for central banks' increased interest in gold include diversification, concerns over the security of other reserve assets, and a response to a multi-polar world trend.
- 💲 The strength of the US dollar has influenced central bank behavior, with stronger dollars often correlating to less accumulation of US treasuries and more interest in gold.
- 🏦 The allocation of gold in central bank reserves varies widely, with some countries like Russia holding a significant percentage of gold in their reserves, while others, like Canada, hold几乎没有.
- 🌱 The concept of 'paper gold' represents claims on gold that may not be backed by physical gold, highlighting the difference between owning physical gold and gold-related financial instruments.
- 🔑 Physical possession of gold provides a form of 'outside money' that is not reliant on financial institutions or governments, offering a level of security and autonomy.
- 💡 The price of gold is affected by various factors including inflation, real interest rates, fiscal policies, and geopolitical considerations, making it a complex asset to value and predict.
Q & A
Why does gold tend to perform well when money supply is increasing and inflation is building?
-Gold tends to perform well in such scenarios because it is seen as a hedge against inflation. When central banks have not yet acted to contain inflation or have been unsuccessful in doing so, gold's value can increase as it maintains purchasing power while the value of fiat currencies may decline.
What factors contribute to gold's performance in disinflationary times?
-Gold can perform well during disinflationary times if there is a rapid fall in real interest rates. This can make gold more attractive as an investment compared to other assets that may be offering lower returns.
Why are central banks significant buyers of gold, and what does this indicate about the current economic climate?
-Central banks are significant buyers of gold as they seek to diversify their reserves and hedge against inflation and currency risks. Their increased gold purchases can indicate concerns about the stability of other assets, such as government bonds, and a potential shift towards gold as a safer store of value.
How does the strength of the US dollar impact central banks' buying behavior of US treasuries?
-When the US dollar is strong, central banks tend to buy fewer treasuries. A strong dollar can make other currencies承压, leading central banks to focus more on currency defense rather than accumulating reserves, including US treasuries.
What is the difference between 'paper gold' and physical gold, and why might investors prefer one over the other?
-Paper gold refers to financial instruments that represent a claim on a certain amount of gold, such as futures contracts or ETFs, without the physical gold itself. Physical gold is the actual metal in the form of bars or coins. Investors might prefer physical gold for its tangibility and as a hedge against potential counterparty risk in the financial system.
Why might a central bank choose to hold a significant portion of its reserves in gold?
-A central bank might hold a significant portion of its reserves in gold to ensure financial stability and to protect against inflation, currency devaluation, and economic uncertainty. Gold serves as a reliable store of value and a diversifier in the reserve portfolio.
How does the concept of 'fiscal dominance' relate to the current situation of the US economy?
-Fiscal dominance occurs when fiscal policy constrains monetary policy, often due to high government debt levels. In the case of the US, the large fiscal deficits relative to the size of the private sector money creation can limit the Federal Reserve's ability to raise interest rates without significantly increasing the government's debt servicing costs.
What are the implications of a central bank revaluing its gold holdings?
-If a central bank revalues its gold holdings to reflect the market price or a higher price, it effectively increases its assets, which can then be used to inject money into the economy without increasing debt. This can lead to inflationary pressures and a devaluation of the currency relative to gold.
Why might a country with a stable currency and low inflation still accumulate gold reserves?
-A country with a stable currency and low inflation might still accumulate gold reserves as a long-term strategy for diversification, to protect against future economic uncertainties, and to maintain a strong reserve position in the global economy.
How does the size of a country's gold reserves compare to its money supply, and what does this indicate about the country's economic strategy?
-The size of a country's gold reserves relative to its money supply can indicate its economic strategy and risk management approach. A higher ratio might suggest a focus on maintaining stability and a hedge against inflation, while a lower ratio might indicate a reliance on other assets or a strategy that prioritizes growth over reserve accumulation.
What are some of the practical considerations for individuals looking to invest in physical gold?
-When investing in physical gold, individuals should consider factors such as the premium over the spot price, the verification of gold authenticity, storage and insurance costs, and the liquidity of the investment. They should also be aware of the differences between various forms of physical gold, such as coins and bars, and the associated costs and benefits.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)