Understand Electroporation In Under 3 Minutes
Summary
TLDRElectroporation is a technique for introducing nucleic acids into cells using an electrical pulse, which temporarily permeates the cell membrane. The process involves placing cells and nucleic acids in a conductive solution, applying an optimized electrical pulse, allowing nucleic acids to enter the cell due to the electric potential, and finally, enabling the cell to recover. While electroporation is efficient and suitable for all cell types, it may result in significant cell death due to the high voltage used. This summary provides a concise insight into the method, its advantages, and limitations.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Electroporation is a physical transfection method used to introduce nucleic acids like DNA or RNA into cells.
- 💡 It operates by using an electrical pulse to create temporary pores in the cell membrane, allowing for the entry of nucleic acids.
- 🌐 The process involves four steps: placing cells and nucleic acids in a conductive solution, applying an electrical pulse, nucleic acids entering the cell due to the electric potential, and cell recovery.
- 🔋 The electrical pulse disturbs the phospholipid bilayer, creating pores that facilitate the movement of negatively charged nucleic acids from a more negative to a more positive environment.
- 🚀 Electroporation is advantageous for its ease, speed, and stability, and its ability to transfect a large number of cells quickly and across all cell types.
- 🔄 The process requires an optimized timing and voltage for the electrical pulse to be effective without causing excessive cell damage.
- ⚠️ A major disadvantage of electroporation is the potential for substantial cell death due to the high voltage pulse, which may prevent full cell recovery.
- 🔬 The script suggests that electroporation is a topic within the broader field of biotechnology, hinting at the existence of other transfection methods.
- 📈 The video is part of a series on biotechnology topics, encouraging viewers to subscribe for more information.
- 📺 Viewers are invited to click on a video for more information on transfection methods, indicating a related resource is available.
- 🌞 The video concludes with a friendly sign-off, wishing viewers a beautiful day and expressing gratitude for their time.
Q & A
What is electroporation?
-Electroporation is a physical transfection method used to artificially introduce nucleic acids, such as DNA or RNA, into cells using an electrical pulse to create temporary pores in the cell membrane.
How does electroporation work in four steps?
-The process involves: 1) Placing host cells and nucleic acids in a conductive solution. 2) Enclosing an electrical field around the mixture. 3) Applying an optimized electrical pulse to disturb the phospholipid bilayer and force the nucleic acids into the cell due to the electric potential. 4) Allowing the cell to recover and regenerate its phospholipid bilayer.
Why is electroporation useful?
-Electroporation is useful because it is a rapid, stable method that can transfect a large number of cells in a short time and is applicable to all cell types.
What are the consequences of the electrical pulse on the cell membrane during electroporation?
-The electrical pulse creates small temporary holes or pores in the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane, allowing the nucleic acids to enter the cell.
How does the electric potential affect the movement of nucleic acids during electroporation?
-The electric potential, created by the applied voltage, causes the negatively charged nucleic acids to move from the negatively charged outside to the slightly more positive inside of the cell.
What is the main disadvantage of using electroporation?
-The main disadvantage of electroporation is the substantial cell death it can cause due to the high voltage pulse, which may leave cells unable to fully recover.
What happens to the cell after the nucleic acids are introduced during electroporation?
-After the nucleic acids are introduced, the cell is allowed to recover, with the hope that it will regenerate its phospholipid bilayer and resume normal function.
Is electroporation the only transfection method available?
-No, electroporation is one of several transfection methods available for introducing nucleic acids into cells. Other methods include lipofection, microinjection, and viral vectors.
How does the charge distribution affect the electroporation process?
-The charge distribution, with the outside being more negatively charged and the inside more positive, is crucial for the electroporation process as it drives the negatively charged nucleic acids into the cell.
What is the role of the conductive solution in electroporation?
-The conductive solution serves as the medium for the electrical pulse to be applied effectively to the cells and nucleic acids, facilitating the creation of pores in the cell membrane.
Can electroporation be used for all types of cells?
-Yes, electroporation is applicable for all cell types, making it a versatile method for introducing nucleic acids into various cell lines.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Electroporation

Komponen kimiawi sel - biologi sma bab sel kelas - komponen sel

The Mechanism of Transformation with Competent Cells
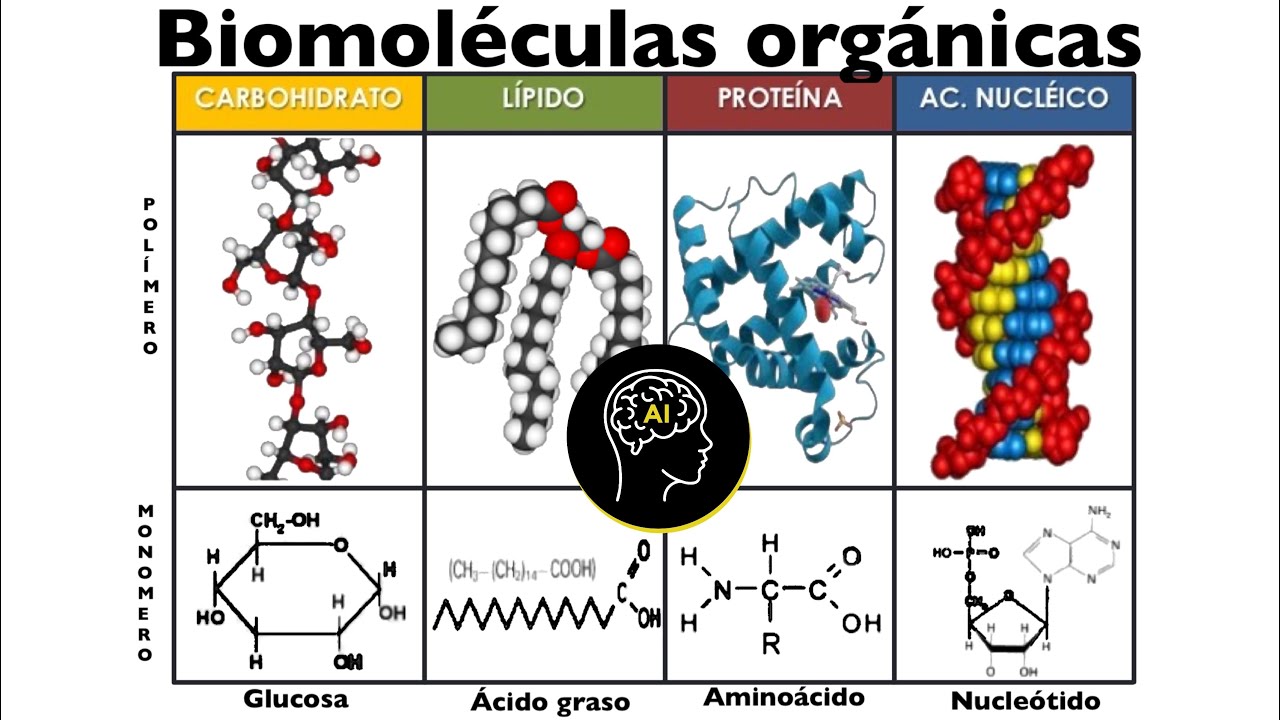
Biomoléculas presentes en células (orgánicas): carbohidratos, lípidos, proteínas y ácidos nucleicos
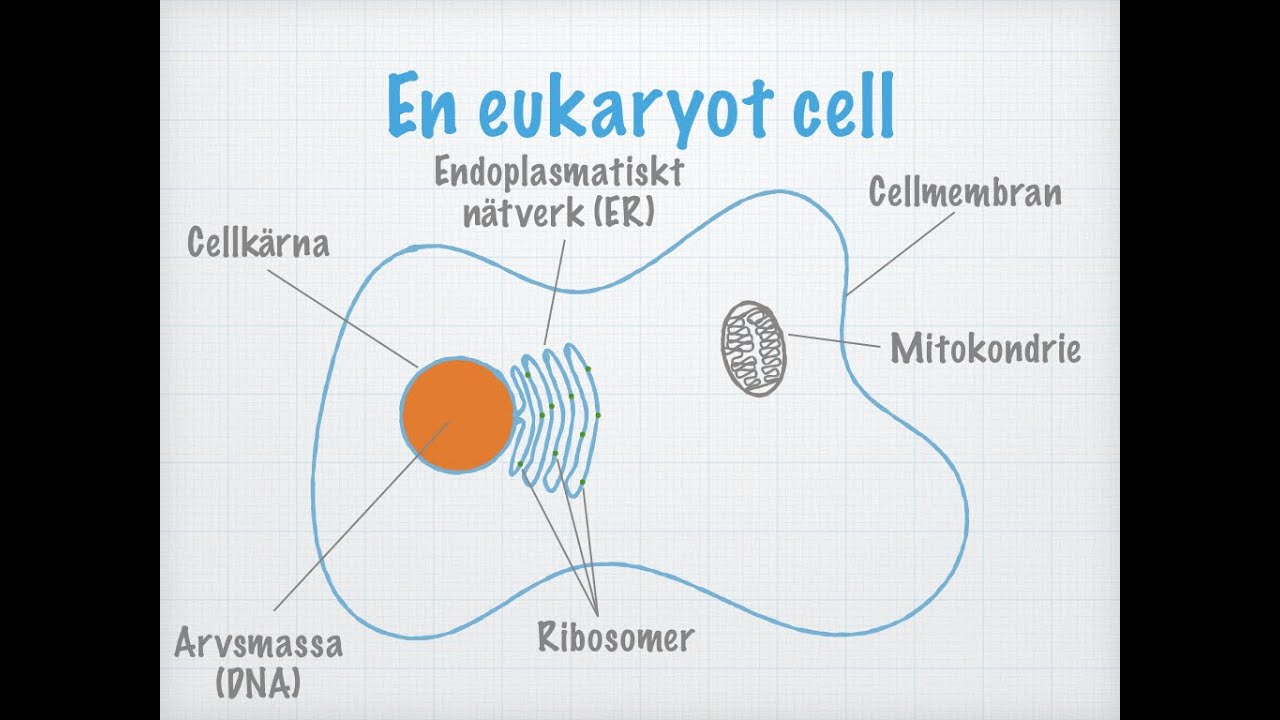
Cellteorin (Biologi 2)

Gli ACIDI NUCLEICI in poco più di 3 minuti | Biologia facile per il TOLC-MED
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
