Genetics - Central Dogma of Life - Lesson 17 | Don't Memorise
Summary
TLDRThis script explores the central dogma of life, detailing the processes of transcription and translation in eukaryotic cells. It explains how DNA is transcribed into mRNA, which is then translated into proteins by ribosomes and tRNA. The video script highlights the importance of these processes in gene expression and contrasts the organization in eukaryotes with the simpler mechanisms in prokaryotes, inviting viewers to subscribe for more insights into genetics.
Takeaways
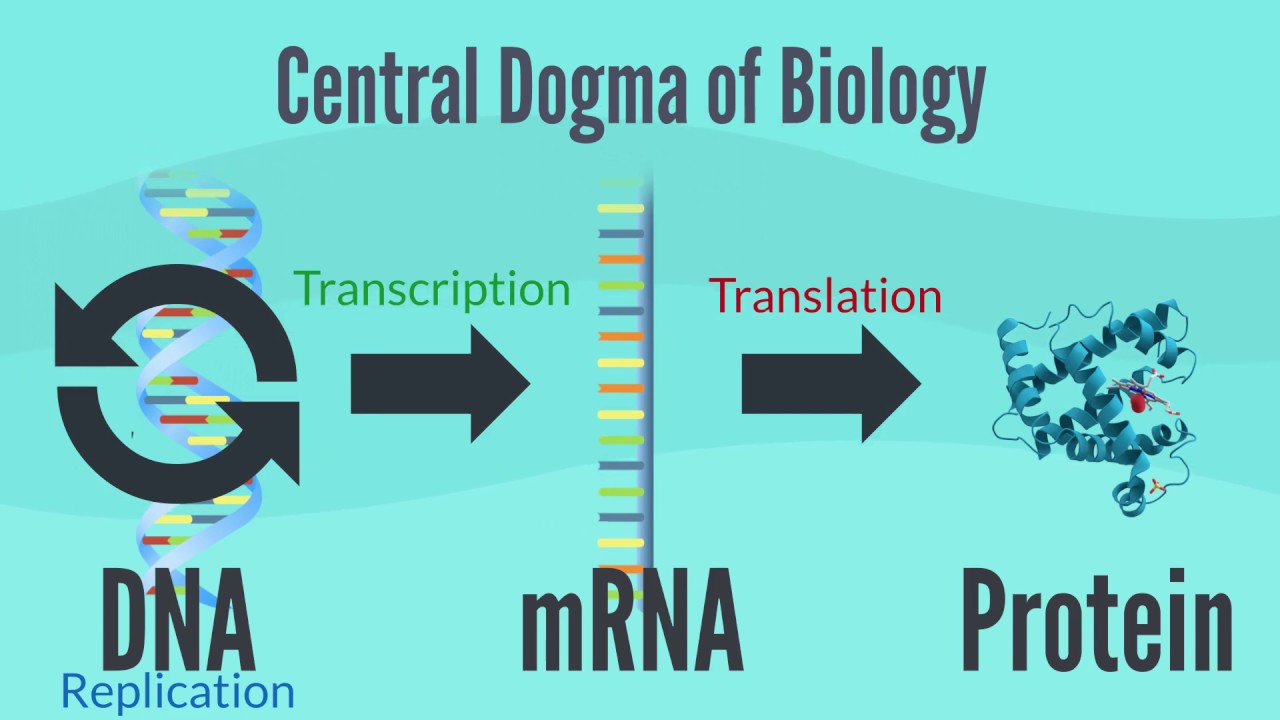
- 📜 The central dogma of life describes the process by which DNA is replicated, transcribed into mRNA, and then translated into proteins.
- 🧬 DNA replication is semiconservative, meaning each new DNA molecule consists of one original and one new strand.
- 📝 Transcription is the process where a segment of DNA, known as a gene, is copied into mRNA, which serves as a template for protein synthesis.
- 🔬 mRNA is single-stranded and contains uracil instead of thymine, which is found in DNA.
- 🧬 The directionality of mRNA is crucial, with the 5' end being recognized by a methyl cap and the 3' end by a poly A tail.
- 📚 The ribosome is the molecular machine responsible for translation, assembling amino acids into proteins based on the mRNA code.
- 🔠 Translation requires the ribosome to bind to the mRNA at the 5' end, with the help of specific initiation factors.
- 🌐 tRNA plays a critical role in translation by bringing the correct amino acid to the ribosome based on the mRNA codon.
- 🔗 The process of translation results in a chain of amino acids that form a protein, which may undergo further modifications for functionality.
- 🌱 Gene expression involves both transcription and translation, converting the genetic code into functional proteins.
- 🔬 Eukaryotic cells, which have a well-defined nucleus, undergo complex processes of transcription and translation, unlike prokaryotic cells which lack a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles.
Q & A
What is the central dogma of life?
-The central dogma of life is the concept that DNA makes copies of itself through replication, and then the genetic information in DNA is transcribed into mRNA, which is subsequently translated into proteins.
How is DNA replication described in the script?
-DNA replication is described as a semiconservative process where the DNA double helix opens at specific points, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand.
What is the purpose of transcription in the context of the central dogma?
-Transcription is the process where the genetic information from a gene is copied into a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA), which will later serve as a template for protein synthesis.
What is mRNA and why is it important for protein synthesis?
-mRNA, or messenger RNA, is a single-stranded RNA molecule that carries the genetic information from DNA for protein synthesis. It is important because it serves as the template for translating the genetic code into a specific sequence of amino acids to form a protein.
How does the script describe the difference between DNA and mRNA?
-The script describes that mRNA is single-stranded unlike the double-stranded DNA, and it contains the base uracil instead of thymine.
What is the role of the ribosome in the translation process?
-The ribosome is a molecular machine that reads the mRNA sequence and facilitates the assembly of amino acids into a polypeptide chain, which will fold into a functional protein.
What is the function of tRNA in protein synthesis?
-tRNA, or transfer RNA, carries specific amino acids to the ribosome during translation. Each tRNA molecule has an anticodon that pairs with the corresponding codon on the mRNA, ensuring the correct sequence of amino acids in the protein.
Why is directionality important in mRNA translation?
-Directionality is important because it helps the ribosome recognize where to start the translation process. The ribosome binds near the 5' end of the mRNA, which is identified by the presence of a methyl cap.
What is the significance of the poly A tail in mRNA?
-The poly A tail, a series of adenine nucleotides at the 3' end of the mRNA, plays a role in stabilizing the mRNA and is a marker for the directionality of the mRNA molecule.
How does the script differentiate between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells regarding gene expression?
-Eukaryotic cells have a well-defined nucleus and undergo complex processes like transcription and translation. Prokaryotic cells lack a membrane-bound nucleus and do not undergo such sophisticated processes, making their replication process slightly different.
What is gene expression as described in the script?
-Gene expression is the process where the genetic information stored in DNA is converted into functional products, such as proteins. It involves two main steps: transcription of DNA into mRNA, and translation of mRNA into proteins.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
Sintesis Protein | Transkripsi

TRANSLATION | INTRODUCTION | Difference In Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes | In Malayalam

Ekspresi Gen Sel Eukariotik

TRANSCRIPTION CHEZ LES EUCARYOTES | ACIDES NUCLEIQUES Partie 3 | Biochimie Facile

Regulation of Gene Expression: Operons, Epigenetics, and Transcription Factors
Central Dogma of Biology
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
