Heart Failure Mngt
Summary
TLDRThe lecture discusses the potential complication of Covid-19 leading to heart failure, outlining its definitions, causes, and impact on patients. It differentiates between heart failure with reduced and preserved ejection fraction, emphasizing the importance of ejection fraction in diagnosis. The talk highlights clinical studies on medications like sacubitril/valsartan for heart failure management, showcasing their benefits in reducing hospitalization and cardiovascular death. It also addresses the significance of early diagnosis and treatment, the role of heart failure clinics in outpatient care, and considerations for patients with comorbidities like CKD.
Takeaways
- 📚 The lecture provides an in-depth understanding of heart failure, its complications, and the transition from hospital to outpatient care.
- 🔍 Heart failure is defined by the European Society of Cardiology as an abnormality leading to the heart's inability to deliver oxygen to tissues, despite normal filling pressures.
- 🇪🇺 The American Heart Association adds that heart failure is a complex clinical syndrome resulting from structural or functional impairments of the heart's pumping function.
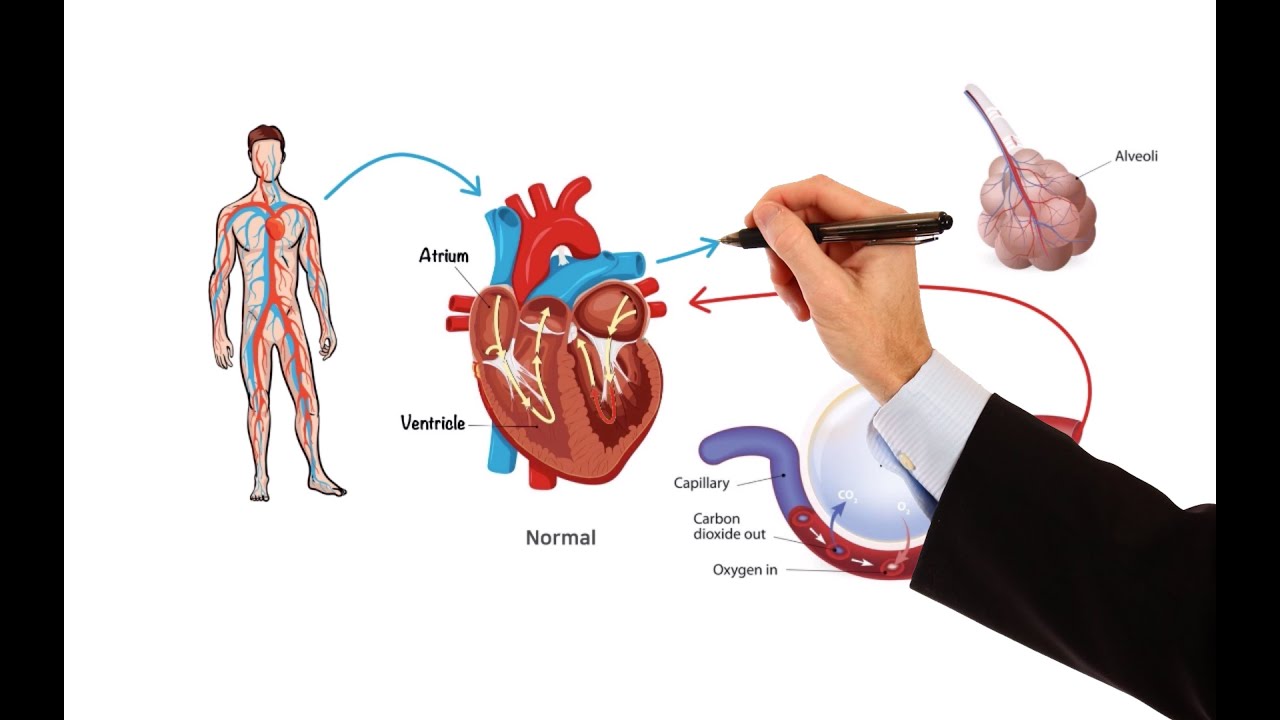
- 💊 The lecture discusses the significance of ejection fraction (EF) in categorizing heart failure into reduced EF (HFrEF) and preserved EF (HFpEF), with different treatment approaches.
- 🚑 Heart failure is a leading cause of hospitalization, particularly for those over 65, with high rates of readmission and mortality within the first year.
- 🩺 The impact of heart failure on patients includes physical and mental health issues, decreased quality of life, and the risk of sudden cardiac death.
- 🛑 The importance of early and effective management post-hospitalization is emphasized to reduce the risk of readmission and improve outcomes.
- 💡 The PARADIGM-HF study highlights the benefits of sacubitril/valsartan over enalapril in reducing cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization.
- 📈 The PIONEER and TRANSITION studies support the initiation of sacubitril/valsartan in hospitalized patients with reduced ejection fraction heart failure, showing improved outcomes and tolerability.
- 🏥 The establishment of a Heart Failure Clinic is presented as a strategy to bridge the gap between in-hospital and outpatient care, optimizing management and reducing hospital readmissions.
- 📊 The ongoing study by Dr. Katarina Modovar aims to assess the clinical profile of patients in the Heart Failure Clinic, providing insights into the demographics and treatment of heart failure patients.
Q & A
What is the definition of heart failure according to the European Society of Cardiology?
-Heart failure is defined as an abnormality of cardiac structure or function, leading to the heart's failure to deliver oxygen at the recommensurate requirements of the metabolizing tissues despite normal filling pressures.
How does the American Heart Association define heart failure?
-The American Heart Association defines heart failure as a complex clinical syndrome that results from any structural or functional impairment of the heart's ability to relax or eject blood.
What does HFrEF stand for and what does it indicate?
-HFrEF stands for Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction, indicating a condition where the left ventricular ejection fraction is less than or close to 35-40%.
What is the difference between HFrEF and HFpEF?
-HFrEF refers to heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, while HFpEF, or heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, indicates a condition where the ejection function is more than 40%, also known as diastolic dysfunction.
What are the main causes of heart failure?
-The main causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, valvular heart disease, cardiomyopathies, and other conditions such as hypertension and diabetes.
How does heart failure impact patients physically and mentally?
-Heart failure can cause physical problems such as shortness of breath and fatigue, and it is associated with mental issues like depression, affecting about 1/3 of patients.
What is the significance of ejection fraction in heart failure management?
-Ejection fraction is the amount of blood pumped out of the ventricle over the total amount of blood in the ventricle. It helps in determining the severity of heart failure and guides treatment strategies.
What are the clinical outcomes for patients with heart failure within the first year?
-Within the first year, about 10% of patients may die in the hospital, 50% may be hospitalized, and there is a 30% chance of re-hospitalization within five years.
How do the PARADIGM-HF and PIONEER trials contribute to heart failure treatment?
-The PARADIGM-HF trial showed that sacubitril/valsartan reduced the risk of heart failure hospitalization and cardiovascular death compared to enalapril. The PIONEER trial confirmed the safety and efficacy of initiating sacubitril/valsartan in the hospital setting after hemodynamic stabilization.
What is the role of neprilysin inhibitors in heart failure treatment?
-Neprilysin inhibitors, such as sacubitril, have been shown to reduce the risk of heart failure hospitalization and cardiovascular death, making them an important part of heart failure treatment, especially in patients with reduced ejection fraction.
How does the use of sacubitril/valsartan affect patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)?
-While the trials primarily focused on patients with reduced ejection fraction, some clinicians may still consider using sacubitril/valsartan in HFpEF patients, especially if they present with significant heart failure symptoms.
Should sacubitril/valsartan be discontinued if a patient's ejection fraction improves?
-There is no study suggesting that sacubitril/valsartan should be discontinued after achieving a target ejection fraction. In fact, if a patient responds well to the medication, it should be continued.
How is sacubitril/valsartan used in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD)?
-For patients with moderate CKD, the full dose of sacubitril/valsartan (200 mg twice daily) can be used. For those with severe CKD (eGFR less than 30), a lower dose of 50 mg twice daily is recommended.
What are the considerations for initiating sacubitril/valsartan in patients hospitalized with heart failure?
-Initiation of sacubitril/valsartan in hospitalized patients with heart failure may be considered when they are hemodynamically stabilized and have a left ventricular ejection fraction less than 40%.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Frontiers and Innovations in Cardiac Research | Laman Gray | TEDxWesleyanU

The Difference Between Cardiac Arrest, Heart Attack, and Heart Failure - 3D Animation

(2/3) Patofisiologi Gagal Jantung (Left VS Right HF) : # HEART FAILURE
Pharmacology – HEART FAILURE (MADE EASY)

Congestive Heart Failure: Left-sided vs Right-sided, Systolic vs Diastolic, Animation.

Heart Failure
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
