How a Gyroscope Works ⚡ What a Gyroscope Is
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the workings of gyroscopes, devices that measure orientation and angular velocity. It covers mechanical gyroscopes, which rely on Newton's laws and the concept of precession, to determine orientation and speed. The script also explores the Coriolis effect in vibrating gyroscopes, used in smartphones for their compact size and low cost, despite their sensitivity to linear accelerations. Finally, it introduces optical gyroscopes, which leverage the Sagnac effect for high accuracy and are now miniaturized, illustrating the evolution and applications of gyroscopes in various fields.
Takeaways
- 🌀 A gyroscope can measure either the orientation change or the angular velocity of a system relative to a reference axis.
- 📱 Gyroscopes are used in various applications including smartphones, aeronautics, video games, and robotics, and the human body has a natural gyroscope in the form of the vestibular system.
- 🔧 Mechanical gyroscopes work on the principles of torque and angular momentum, and their operation can be understood through Newton's laws of motion.
- 🎯 The spatial rigidity of a rotating object allows a gyroscope to maintain its orientation even when the rest of the system rotates, which was historically used for navigation.
- 🚴 Precession, a circular motion resulting from a force applied to a rotating object, is used in mechanical gyroscopes to determine the angular velocity of a system.
- 🏗️ The limitations of mechanical gyroscopes include their size and sensitivity to the moment of inertia of the rotating mass, which affects their accuracy and usability.
- 🌊 Coriolis effect gyroscopes are widely used due to their small size and low cost, making them suitable for integration into electronic devices like smartphones.
- 🔄 Coriolis acceleration is a key principle in vibrating gyroscopes, which can calculate angular velocity based on the force experienced by an oscillating mass.
- 🚫 Vibrating gyroscopes can be affected by linear accelerations, which may compromise their accuracy if the system is exposed to large accelerations.
- 💡 Optical gyroscopes operate based on the Sagnac effect, where the difference in distance traveled by light beams in opposite directions within a rotating system allows for the calculation of angular velocity.
- 🔬 Optical gyroscopes offer high accuracy and reliability, with no moving parts, and have been miniaturized to as small as 2 millimeters square in recent advancements.
Q & A
What are the two primary functions of a gyroscope?
-A gyroscope can provide information about the variation of the orientation of a system with respect to a reference axis and provide information about the rate at which the orientation of a system varies when it is rotating, which is its angular velocity.
In what applications are gyroscopes commonly used?
-Gyroscopes are used in a wide range of applications including smartphones, aeronautics, video game consoles, and robotics.
What is the human body's built-in gyroscope known as?
-The human body has a built-in gyroscope known as the vestibular system, which provides information about our orientation and helps us maintain balance.
What are the two factors that determine angular momentum in a rotating system?
-Angular momentum is determined by the moment of inertia of the system, which depends on its shape and mass distribution, and the angular velocity, which indicates how many degrees the system rotates during a defined period of time.
How does the spatial rigidity of a rotating object relate to the operation of a mechanical gyroscope?
-The spatial rigidity of a rotating object means that if a disk is rotating at a certain angular velocity and there are no other forces generating torque, its angular momentum will be conserved, allowing it to maintain its orientation even if the rest of the system moves.
What is precession and how is it used in mechanical gyroscopes?
-Precession is a circular motion generated when a rotating object is affected by a force that causes it to change its orientation. In mechanical gyroscopes, precession is used to determine the speed of a system by measuring the torque generated on a torsion bar when the system is rotated about an axis.
What is the limitation of mechanical gyroscopes in terms of size and accuracy?
-Mechanical gyroscopes' operation depends on the moment of inertia of the rotating disc, which is related to its mass. Therefore, it is impossible to reduce the size of these systems without affecting their accuracy or rotation time.
What is the principle behind the operation of a Coriolis effect vibrating gyroscope?
-Coriolis effect vibrating gyroscopes operate based on the Coriolis acceleration, which occurs when an oscillating mass experiences a force due to the system's rotation, causing it to move laterally. This displacement can be measured to calculate the angular velocity of the system.
How do optical gyroscopes detect angular velocities independent of linear accelerations?
-Optical gyroscopes work on the Sagnac effect, where two beams of light travel in opposite directions in a fiber optic ring. The difference in the distance traveled by the light beams due to the system's rotation allows for the calculation of angular velocity, independent of linear accelerations.
What is the advantage of optical gyroscopes over mechanical and Coriolis effect vibrating gyroscopes in terms of operation?
-Optical gyroscopes have the advantage of being highly accurate and reliable, as they can operate without moving parts. They are also not affected by linear accelerations, which can compromise the accuracy of mechanical and Coriolis effect vibrating gyroscopes.
What was a significant development in the size of optical gyroscopes in 2018?
-In 2018, scientists at Caltech were able to build an optical gyroscope that was just two millimeters square, showing that size is no longer a limitation for these types of gyroscopes.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Accelerometer vs. Gyroscope - What's the Difference Between These Popular Sensors?

How does an Accelerometer work? | 3D Animation
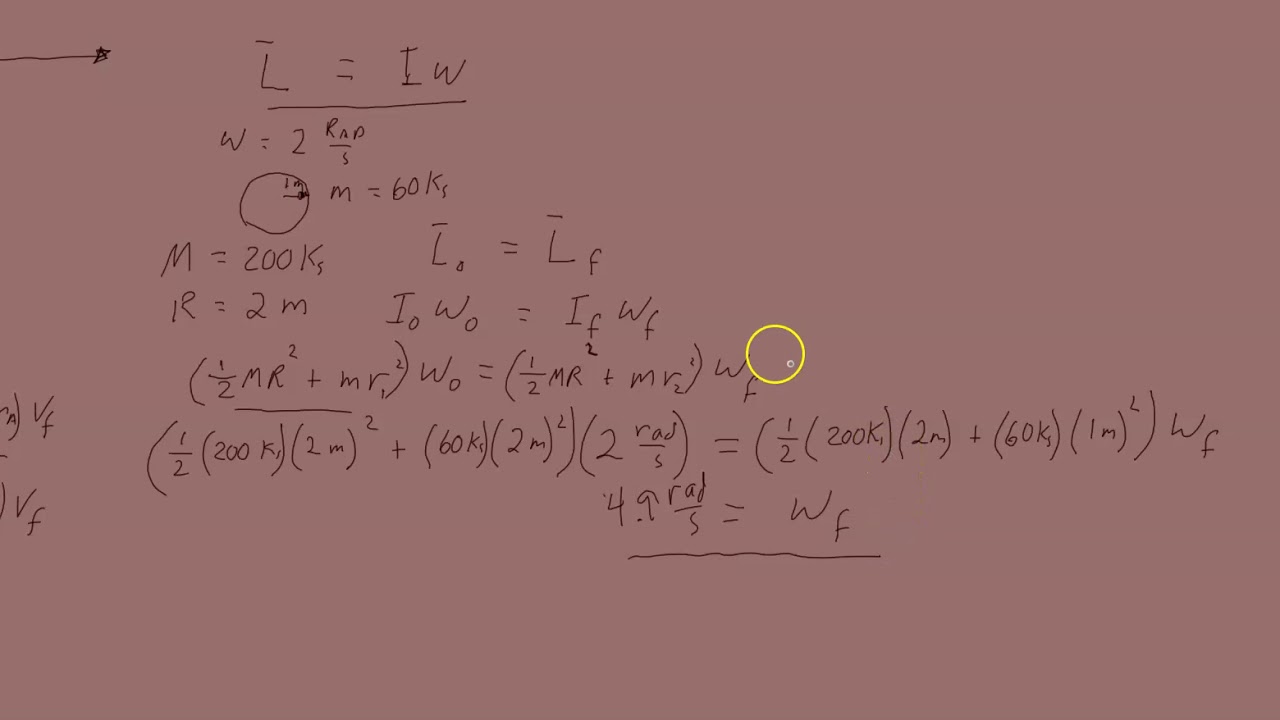
Physics - Angular Momentum

Me Salva! CIN11 - MCU
Angular Motion | Sport Science Hub: Biomechanics Fundamentals | Updated 2021 No Music

PHYS 121 - Week 6 Lecture 2 - Rotational Motion
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
