Complete History Through Animation | Lec 1 | Pre-Historic Age in India | By Aadesh Singh
Summary
TLDRThe script delves into the prehistoric period of India, exploring the Stone Age from the Lower Paleolithic to the Iron Age. It discusses the evolution of human life, the development of tools from stone implements to polished stone tools, and the advent of agriculture and domestication of animals. The script also touches upon the Megalithic period, marking the transition from prehistory to history with the emergence of monuments and memorials, and the use of iron tools and writing.
Takeaways
- 📚 The script discusses the prehistoric period in India, covering the study of history through inquiry and past knowledge, emphasizing the importance of historical sources in reconstructing the past.
- 🗺️ The prehistoric period in India is divided into different phases, starting from the Paleolithic Age, continuing through the Mesolithic and Chalcolithic Ages, and leading into the Iron Age.
- 🌟 The Paleolithic Age is characterized by the use of stone tools, with evidence suggesting humans were hunter-gatherers and relied on archaeological findings such as stone tools and artifacts.
- 🔍 The Mesolithic Age saw advancements in tool-making, with microliths being the primary tools, used for hunting small animals and various composite tools for activities like plant gathering and harvesting.
- 🏡 The Chalcolithic Age marked a transition with the beginning of agriculture, the domestication of animals, and the use of polished stone tools, indicating a shift from hunter-gatherers to food producers.
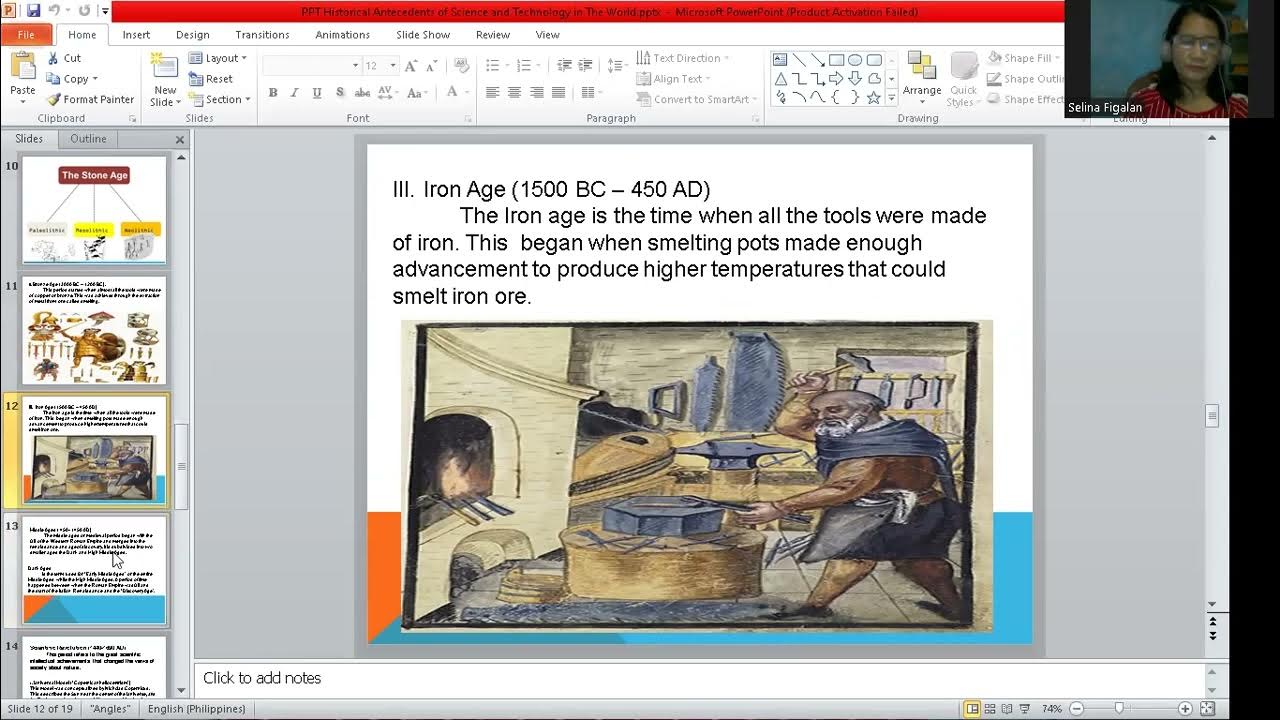
- 🛠️ The Iron Age introduced the use of iron tools and weapons, signifying a major technological advancement and the emergence of more complex societies.
- 🏰 The script mentions the construction of megalithic structures during the Iron Age, which were large stone monuments used for burials and memorials, indicating social stratification and cultural practices.
- 👥 It highlights the presence of social inequality during the megalithic period, with evidence of different social statuses such as village chiefs and common people.
- 🎨 The script also touches on the artistic aspects of the prehistoric period, including rock paintings, pottery, and craftwork, reflecting the cultural and religious beliefs of the time.
- 📝 The development of writing is mentioned towards the end of the script, marking the transition from prehistoric to historic periods in India.
- 🔑 The study of the prehistoric period is crucial for understanding human evolution and development, leading to the emergence of the Harappan civilization in the protohistoric period.
Q & A
What does the term 'history' derive from and what does it mean?
-The term 'history' is derived from the Greek word 'historia', which means inquiry, investigation, or knowledge about the past. It involves the study of past events, the collection and interpretation of data related to these events, and the reconstruction of the past based on historical sources.
What are the two main types of historical sources mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of historical sources mentioned are non-literary sources and literary sources. Non-literary sources pertain to the prehistoric period before the invention of writing and are based on archaeological evidence, while literary sources are based on written records.
What is the significance of stone tools in understanding prehistoric periods?
-Stone tools are significant in understanding prehistoric periods because they provide the most abundant archaeological evidence. They help in classifying the Stone Age into different phases, such as the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic, based on the types and uses of these tools.
What is the Paleolithic Age, and how does it relate to the early human settlements in India?
-The Paleolithic Age, also known as the Old Stone Age, spans from around 200,000 BC to 10,000 BC. It is characterized by the use of stone tools by early humans in India, who were primarily hunter-gatherers. The discovery of stone tools in various regions indicates the spread of human settlements during this period.
How is the Mesolithic Age different from the Paleolithic Age in terms of tool development?
-The Mesolithic Age, or Middle Stone Age, is marked by the development of smaller, lighter, and more refined stone tools compared to the Paleolithic Age. Tools like microliths, which are small stone tools made from fine-grained rocks, were used for hunting smaller animals and for various tasks, indicating a more advanced tool-making technology.
What is the significance of the Neolithic Age in the context of human history?
-The Neolithic Age, or New Stone Age, is significant as it marks the transition from hunter-gatherer societies to food-producing societies. This period is characterized by the development of agriculture, animal domestication, and the use of polished stone tools, representing a major shift in human lifestyle and the beginning of settled communities.
What is the role of rock art in understanding the Mesolithic Age?
-Rock art, such as paintings found in various sites across India, provides insights into the lives, beliefs, and activities of Mesolithic people. These artworks often depict wild animals, hunting scenes, and other activities, reflecting the cultural and spiritual aspects of the society during this period.
How did the advent of agriculture impact the lifestyle of people in the Neolithic Age?
-The advent of agriculture during the Neolithic Age led to the establishment of permanent settlements, as people no longer needed to migrate in search of food. It allowed for the domestication of plants and animals, the development of more complex societies, and the eventual rise of civilizations.
What is the significance of the Copper Age in the transition from prehistoric to historic periods?
-The Copper Age, also known as the Chalcolithic Age, signifies a transitional period between the prehistoric Stone Age and the historic Bronze Age. It is marked by the use of copper tools and the emergence of more complex societies, including the beginnings of urbanization and the development of writing systems.
What are megalithic structures, and how do they relate to the Iron Age in India?
-Megalithic structures are large stone monuments, often used as burial sites or memorials, constructed using single large stones or multiple stones. The Megalithic Period in India, around 1000 BC to 500 BC, marks the end of the prehistoric era and the beginning of the Iron Age, characterized by the widespread use of iron tools and weapons and the development of early states and civilizations.
How do the findings from various archaeological sites contribute to our understanding of prehistoric India?
-Archaeological findings from sites across India provide valuable information about the lifestyles, technological advancements, cultural practices, and social structures of prehistoric communities. These findings, including tools, pottery, rock art, and burial sites, help reconstruct the history and evolution of human societies in India over thousands of years.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Science, Technology and Society - In the World: Ancient, Middle and Modern Ages

Manusia Prasejarah | Pembagian Zaman Batu dan Logam (Arkeologi & Geologi) | IPS Kelas 8

MASA PRAAKSARA || |Periodisasi Secara Arkeologis

Belajar Sejarah - Zaman Praaksara Arkeologi #BelajarDiRumah
Historical Antecedents of Science and Technology in the World

What If You Lived in the Prehistoric Era?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
