Genetics: Nondisjunction & Meiosis
Summary
TLDRThe video script delves into the concept of nondisjunction during meiosis, illustrating how this error can lead to abnormal chromosome counts in gametes. It explains two types of nondisjunction: one occurring in meiosis I, affecting all gametes, and the other in meiosis II, impacting only half. The script uses human chromosomes as an example, showing how nondisjunction results in gametes with either an extra or missing chromosome, emphasizing the significance of proper chromosome separation in genetic health.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Nondisjunction is a genetic error that occurs during meiosis, leading to an abnormal chromosome count in gametes.
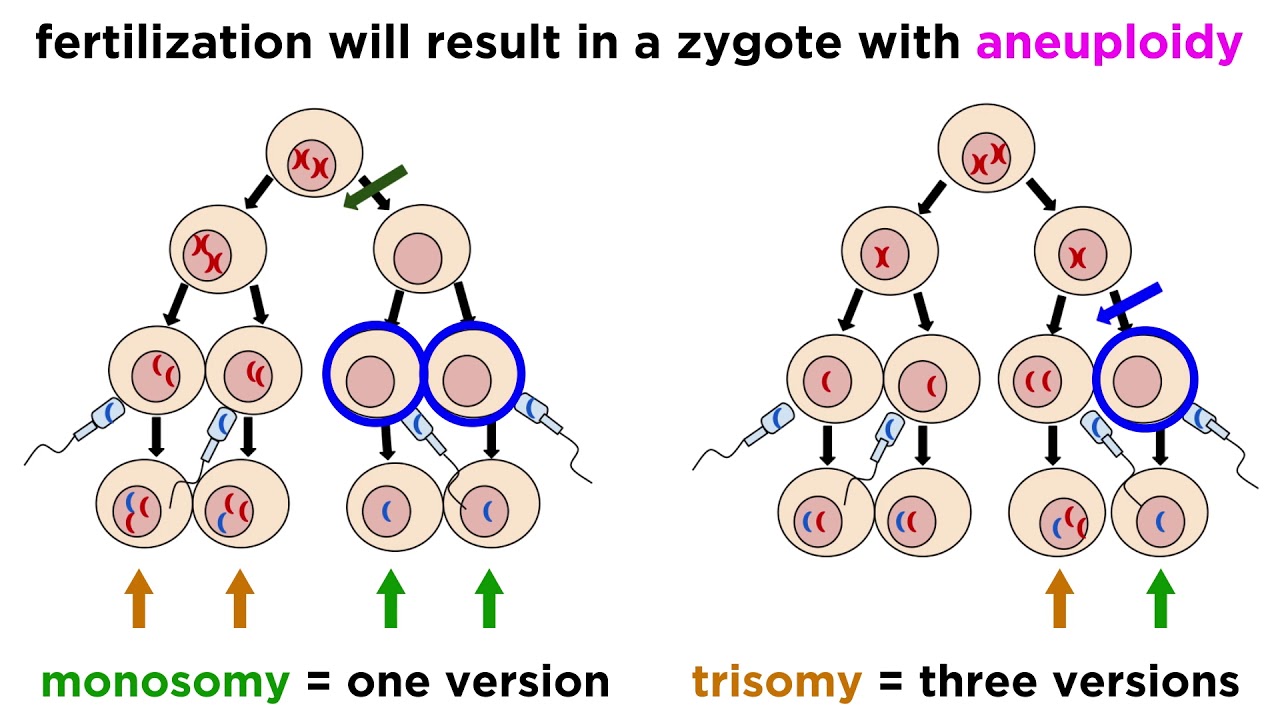
- 🤔 During meiosis I, nondisjunction happens when homologous chromosomes fail to separate properly during anaphase, resulting in cells with an extra or missing chromosome.
- 🔄 If nondisjunction occurs in meiosis I, it affects all gametes, causing them to have either one extra or one less chromosome compared to the normal count.
- 🧐 In contrast, nondisjunction in meiosis II affects only half of the gametes, as it happens after the separation of homologous chromosomes.
- 📈 Nondisjunction in meiosis I results in gametes with either 24 (n+1) or 22 (n-1) chromosomes, while normal gametes should have 23 chromosomes.
- 🌟 Nondisjunction can lead to genetic disorders such as Down syndrome, which is caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21.
- 🔬 Identifying nondisjunction requires chromosome counting, which can be done through genetic testing.
- 📚 The video references material from a specific textbook, indicating that the concepts are tailored to students studying genetics.
- 🏫 The video mentions free tutoring services for Baylor students, suggesting resources available for those struggling with genetics concepts.
- 🗓️ Students can schedule a 30-minute one-on-one tutoring session or drop in during business hours for assistance.
- 💻 For more information about tutoring services, the video directs viewers to a website, emphasizing the availability of support.
Q & A
What is nondisjunction?
-Nondisjunction is a type of error that occurs during cell division, specifically in meiosis, where chromosomes or chromatids fail to separate properly, leading to an abnormal number of chromosomes in the resulting gametes or daughter cells.
What happens during metaphase in meiosis I?
-During metaphase in meiosis I, the homologous chromosomes align on the metaphase plate, preparing to separate during anaphase.
What is the consequence of nondisjunction during anaphase of meiosis I?
-If nondisjunction occurs during anaphase of meiosis I, both members of a chromosome pair may end up in the same daughter cell, resulting in an abnormal chromosome count in the subsequent cell divisions.
How does nondisjunction in meiosis I affect the resulting gametes?
-Nondisjunction in meiosis I results in all gametes having an abnormal chromosome count, either with one extra chromosome (n+1) or one less (n-1), compared to the normal count of 23 in humans.
What is the difference between nondisjunction in meiosis I and meiosis II?
-Nondisjunction in meiosis I affects all resulting gametes, causing them all to be abnormal. In contrast, nondisjunction in meiosis II affects only half of the gametes, as it occurs after the separation of homologous chromosomes.
What happens during meiosis II if nondisjunction occurred in meiosis I?
-If nondisjunction occurred in meiosis I, meiosis II will proceed with the abnormal chromosome count, but the error will not be corrected or compounded, resulting in gametes with either n+1 or n-1 chromosomes.
What is the normal chromosome count in human gametes?
-The normal chromosome count in human gametes is 23.
How does nondisjunction affect the genetic information of an offspring?
-Nondisjunction can lead to genetic disorders in offspring, such as Down syndrome, if the abnormal chromosome count is passed on during fertilization.
What is the significance of nondisjunction in genetic counseling and prenatal testing?
-Nondisjunction is significant in genetic counseling and prenatal testing as it can indicate a higher risk for chromosomal abnormalities in the developing fetus, prompting further diagnostic testing.
Can nondisjunction be detected through genetic testing?
-Yes, nondisjunction can be detected through various genetic testing methods, such as karyotyping, which can identify the presence of abnormal chromosome numbers in cells.
What resources are available for students at Baylor University to enhance their understanding of genetics?
-Baylor University offers free tutoring services for enrolled students on the first floor of Sid Richardson, where they can schedule a 30-minute one-on-one tutoring session or drop in during normal business hours.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)