Functions of Proteins in Living Organisms with Examples|Protein Function|Biochemistry@biologyexams4u
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial delves into the diverse functions of proteins, the most versatile biomolecules in cells. Proteins, made of amino acids, perform a variety of roles, including enzymatic activity (speeding up reactions), structural support (e.g., collagen in tissues), transport (e.g., hemoglobin for oxygen), and storage (e.g., ferritin for iron). They also play key roles in locomotion, defense (e.g., antibodies), regulation (e.g., insulin), and even producing toxic substances for defense. The video highlights the essential roles of proteins in maintaining cellular function and overall health.
Takeaways
- 😀 Proteins are the most diverse biomolecules in the cell, with a wide range of functions across the body.
- 😀 Proteins are made up of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, with each amino acid having a central carbon, amino group, carboxyl group, and a variable side chain.
- 😀 The formation of peptide bonds between amino acids occurs through a dehydration reaction, resulting in a C-N bond.
- 😀 Enzymatic activity is one of the most important functions of proteins, acting as biological catalysts that speed up reactions without changing themselves.
- 😀 Structural proteins, such as collagen and keratin, provide support and structure to various parts of the body, like skin, nails, and hair.
- 😀 Transport proteins like hemoglobin carry oxygen to tissues, while others transport lipids and metals such as copper across the body.
- 😀 Proteins function in storage, with examples including ovalbumin (found in eggs) and ferritin (which stores iron in bacteria).
- 😀 Proteins are essential for movement, with motor proteins like actin and myosin involved in muscle contraction and tubulin facilitating chromosome movement during cell division.
- 😀 Defense proteins like antibodies and blood clotting proteins (e.g., fibrinogen, thrombin) help protect the body from infections and prevent blood loss.
- 😀 Regulatory proteins, such as insulin and peptide hormones, play critical roles in signaling pathways that control various physiological functions in the body.
Q & A
What are proteins made of?
-Proteins are biomolecules made up of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon, a hydrogen atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain that varies between different amino acids.
What is a peptide bond?
-A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another, with the removal of a water molecule. This bond links amino acids together to form a protein.
What is the most important function of proteins inside cells?
-The most important function of proteins inside the cell is their enzymatic activity. Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy without being consumed in the reaction.
Can you name some examples of enzymes and their functions?
-Some examples of enzymes include proteases, which degrade proteins, catalases, which break down hydrogen peroxide, and lipases, which break down fats. These enzymes facilitate various biological reactions within the cell.
What are structural proteins, and can you give an example?
-Structural proteins provide support and shape to cells and tissues. An example is collagen, the most abundant structural protein in animals, found in connective tissues like skin, tendons, and bones.
How do proteins function as carriers in the body?
-Proteins like hemoglobin and myoglobin are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. Other transport proteins, like lipoproteins, carry lipids, while copper transport proteins, such as ceruloplasmin, move copper in the blood.
What is the role of proteins in movement?
-Proteins like actin and myosin are motor proteins involved in muscle contraction and movement. Tubulin forms microtubules, which are critical for chromosome movement during cell division.
How do defense proteins work in the immune system?
-Defense proteins such as antibodies play a crucial role in the immune system by recognizing and neutralizing pathogens. Other proteins, like fibrinogen and thrombin, are involved in blood clotting to prevent excessive bleeding after injury.
What are regulatory proteins, and what is their function?
-Regulatory proteins, such as hormones like insulin, regulate various physiological processes. For example, insulin regulates sugar metabolism, and certain gene-protein complexes act as secondary messengers in signal transduction pathways.
What are toxic proteins, and how do they protect organisms?
-Toxic proteins, such as those found in snake venom or bacterial toxins, serve as a defense mechanism. These proteins give the organism an advantage by harming or neutralizing potential threats, such as predators or pathogens.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Protein Structure
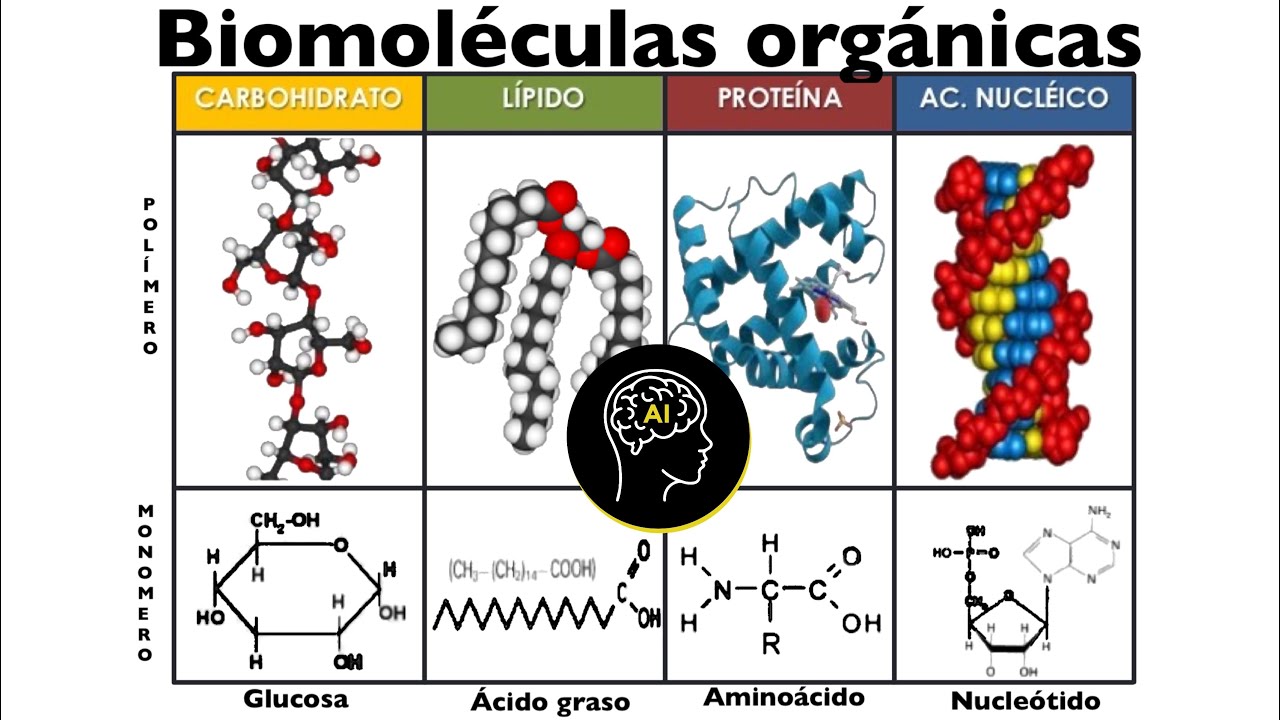
Biomoléculas presentes en células (orgánicas): carbohidratos, lípidos, proteínas y ácidos nucleicos

Proteínas: Estructura, Clasificación, Función y Desnaturalización 🔬

Complement Anaphylatoxins (C5a, C3a, C4a)

Biomolecules Mind maps 🧠with PDF in just 10 minutes 😍 NEET 2024🔥ONE SHOT Revision

Introduction to Biochemistry
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
