Class Member Function Definition with Example | C ++ Tutorial | Mr. Kishore
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial provides an in-depth guide on how to define and call functions in C++, both inside and outside a class. It begins with the essentials of header file inclusion, followed by class declaration and definition. The video explains how to define member functions inside a class and how to declare them while defining them outside using the scope resolution operator. The final part walks through memory allocation for class objects and demonstrates function calling within the `main()` function. The tutorial is ideal for beginners learning object-oriented programming concepts in C++.
Takeaways
- 😀 Proper header file declaration is essential in C++ programming, like `#include <iostream.h>` for input/output operations and `#include <conio.h>` for console handling functions.
- 😀 In C++, classes are declared using the `class` keyword, and the private data members (e.g., `ID` and `name`) are typically declared within the class.
- 😀 Functions in C++ can be defined either inside the class or outside the class, with each having its own syntax and use cases.
- 😀 Inside the class, functions are usually defined directly within the class body, which is known as 'function definition inside the class'.
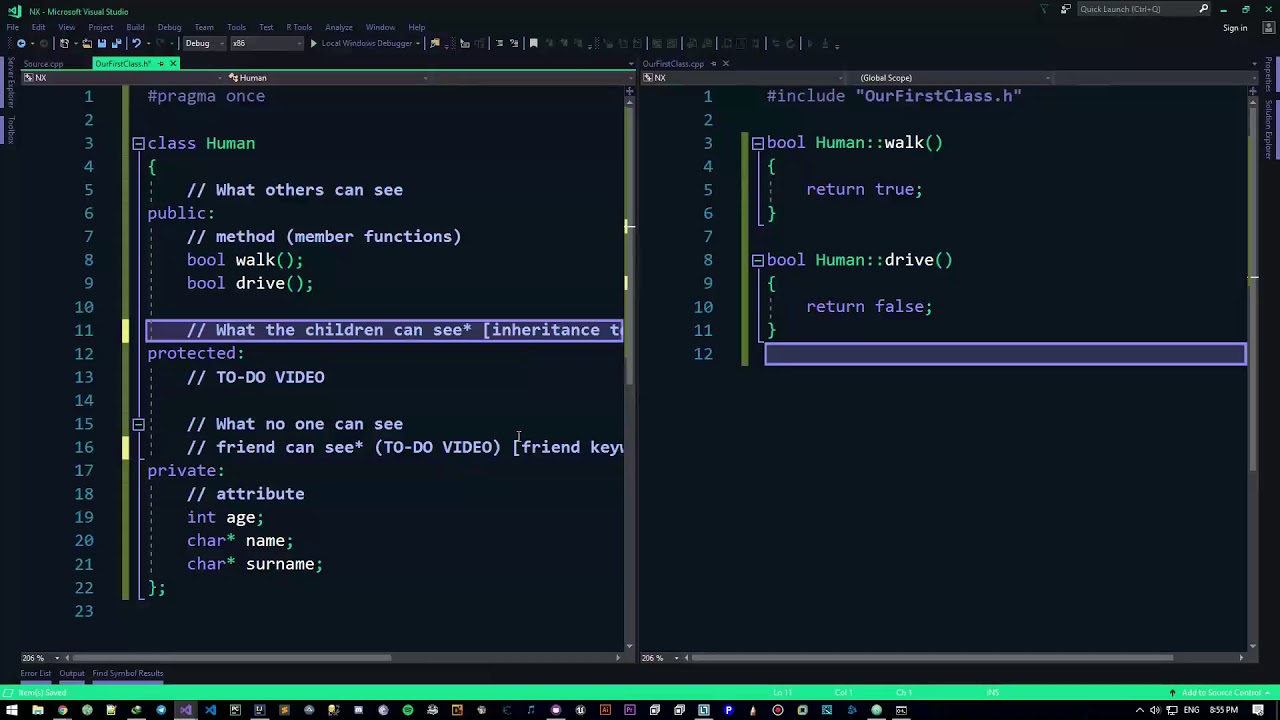
- 😀 Functions defined outside the class need to be declared first within the class, and the actual definition outside the class is done by using the `::` operator.
- 😀 The `Student::showStudent()` function is an example of a member function being defined outside the class after being declared inside it.
- 😀 The `main()` function serves as the entry point to call class methods and create objects. It’s responsible for calling member functions like `readStudent()` and `showStudent()` on the object.
- 😀 The `readStudent()` function takes input from the user (student ID and name) using `cin` and stores it in the private data members of the object.
- 😀 The `showStudent()` function outputs the stored student data to the console using `cout`.
- 😀 When using object-oriented programming, it is important to understand the distinction between function declaration (inside the class) and function definition (either inside or outside the class).
- 😀 The process of calling a member function in C++ requires creating an object of the class, which then allows you to call the member functions like `readStudent()` and `showStudent()`.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of including header files like <iostream.h> and <conio.h> in a C++ program?
-The header file <iostream.h> is required for input/output operations in C++, such as using `cin` and `cout`. The <conio.h> header file is used for console input/output functions, like `getch()`, which pauses the program until a key is pressed.
What is the difference between class declaration and class definition in C++?
-In C++, class declaration refers to specifying the structure of the class, such as the class name and its members, without providing the actual implementation of the member functions. Class definition, on the other hand, includes both the declaration and the full implementation of the functions within the class.
Why are data members like `ID` and `name` declared as private in the `Student` class?
-In C++, private data members are used to encapsulate the data, ensuring that they are not directly accessible from outside the class. This is a core principle of object-oriented programming (OOP) known as encapsulation, which helps maintain data integrity by controlling access through public methods (functions).
What is the purpose of the `void` keyword in the function definitions inside the `Student` class?
-The `void` keyword specifies that the function does not return any value. Both `readStudent()` and `showStudent()` are functions that perform actions (like reading input or displaying output) but do not need to return any data to the caller.
Can you explain the significance of the `Student::` syntax when defining functions outside the class?
-The `Student::` syntax is used to define member functions outside the class. It indicates that the function belongs to the `Student` class. This is necessary to associate the function definition with the correct class when the definition is provided separately from the class declaration.
How does the `readStudent()` function work in the provided example?
-The `readStudent()` function prompts the user to enter a student's ID and name using `cin`. The values entered by the user are then stored in the `ID` and `name` data members of the `Student` object.
What does the `showStudent()` function do in the example code?
-The `showStudent()` function displays the student's ID and name by printing the values stored in the `ID` and `name` data members of the `Student` object using `cout`.
Why is memory allocated for the `Student` object `s` in the `main()` function?
-When the `Student` object `s` is created in the `main()` function, memory is allocated for the data members `ID` and `name`. This allows the program to store and manipulate the student's information during its execution.
What is the role of the `getch()` function in the `main()` function?
-The `getch()` function from the <conio.h> library is used to pause the program and wait for the user to press any key. This prevents the console window from closing immediately after displaying the output.
How does the function calling process work in the provided code example?
-In the `main()` function, the `Student` object `s` calls the `readStudent()` function to get user input for the student's ID and name, followed by calling the `showStudent()` function to display the entered information. This demonstrates how functions can be called on objects to perform specific tasks.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Object Oriented Programming Features Part 4 | C ++ Tutorial | Mr. Kishore
01 - [Classes] C++ Intermediate Programming Tutorial

Programs related to Class in C++

Belajar Java [OOP] - 13 - Static atau Class Attributes

Learn Functions – Understand In 7 Minutes

Video Pembelajaran Animasi PJOK-Teknik Dasar Permainan Sepakbola
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
