Serial transmission vs parallel transmission
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fundamentals of networking connectors and transmission types. It explains the difference between series and parallel circuits, then delves into serial and parallel data transmission, highlighting their reliability, speed, distance, and implementation differences. Serial transmission is reliable and ideal for long distances, while parallel transmission is faster but suited for shorter distances. The video also covers the types of connectors and ports used, including serial (DB-9), parallel (DB-25), and the evolution to USB standards like USB 2.0, Mini, Micro, Lightning, and USB-C, emphasizing their roles in connecting modern devices for data transfer and charging.
Takeaways
- 😀 Networking keyboards (interfaces) are used to connect different devices and depend on topology, hardware, software, and network size.
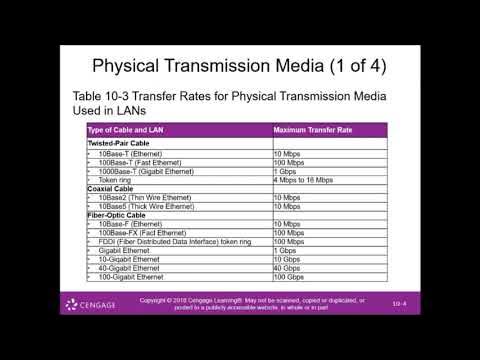
- 😀 Common network cables include coaxial cables, twisted pair, optical fiber, and serial or parallel keyboards.
- 😀 Series circuits have components in a single loop; failure of one component breaks the whole circuit.
- 😀 Parallel circuits have components in separate loops; failure of one component does not affect others.
- 😀 Serial transmission sends data one bit at a time and can be asynchronous or synchronous.
- 😀 Parallel transmission sends multiple bits simultaneously but requires synchronization and is faster for short distances.
- 😀 Serial transmission is reliable, simpler, cheaper, and suitable for long-distance communication.
- 😀 Parallel transmission is faster but less reliable, more complex, and mainly used for short distances.
- 😀 Serial keyboards typically use RS-232 communication with 9-pin D-sub connectors, while parallel ports use 25-pin DB connectors.
- 😀 USB technology has largely replaced serial and parallel ports, supporting charging and data transfer with multiple connector types like USB 2.0, Micro USB, Mini USB, Lightning, and USB-C.
- 😀 USB technology is continuously evolving, providing compatibility with a wide range of devices.
Q & A
What are the most common types of cables used in networking?
-The most common network cables include coaxial cable, twisted pair cable, optical fiber, and parallel or serial cables. The choice depends on the network topology, hardware, software, and network size.
To which layer of the OSI model do networking cables and connectors belong?
-Networking cables, connectors, and their specifications belong to the Physical Layer (Layer 1) of the OSI model.
What is the difference between a series circuit and a parallel circuit?
-In a series circuit, components are connected in a single loop, current is the same through all components, and a break in one component breaks the entire circuit. In a parallel circuit, components are connected in separate loops, each has its own voltage, and the failure of one component does not affect the others.
How does serial transmission work and what are its types?
-Serial transmission sends data one bit at a time sequentially over a communication channel. It can be asynchronous, where data is sent at any time without synchronization, or synchronous, where data is sent as a continuous stream with a synchronized clock between sender and receiver.
What are the main characteristics of parallel transmission?
-Parallel transmission sends multiple bits (usually 8) simultaneously over different channels. It is faster than serial transmission but requires synchronization, is more complex, and is generally used for short distances.
Compare serial and parallel transmission in terms of reliability, speed, distance, and implementation.
-Serial transmission is more reliable, slower, suitable for longer distances, and cheaper to implement with thinner cables. Parallel transmission is faster, less reliable, used for shorter distances, and more complex with thicker cables.
What are the common uses and connectors for serial keyboards?
-Serial keyboards are typically used for RS-232 communication and connect to devices like modems, printers, and mice. The most common connector is the 9-pin male D-sub (DB-9) connector.
What devices typically use parallel ports, and what has largely replaced them?
-Parallel ports, commonly 25-pin female D-sub (DB-25), are used to connect printers, scanners, and other peripherals. They have largely been replaced by USB technology.
What is USB and what are its common types and uses?
-USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a standard interface that replaces both serial and parallel connections, used for charging and data transfer. Common types include USB 2.0 for peripherals, Micro USB for mobile devices, Mini USB for cameras, Lightning USB for Apple products, and USB-C as an emerging standard.
Why is serial transmission still widely used despite being slower than parallel transmission?
-Serial transmission is reliable, generates fewer errors, is less prone to noise, can be used over longer distances, and is cheaper and easier to implement, which makes it more popular than parallel transmission in modern applications.
What are the differences between asynchronous and synchronous serial transmission?
-In asynchronous serial transmission, data can be sent at any time without needing synchronization between sender and receiver. In synchronous serial transmission, data is sent as a continuous stream, and both sender and receiver must operate with a synchronized clock.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Animasi : Media Transmisi Jaringan Komputer lengkap UTP, STP, Coaxial, Fiber Optic, Wireless
Module 10 Communicating Digital Content Wired and Wireless Networks and Devices PART5

Network Connectors Explained

Hub, Bridge, Switch, Router - Network Devices - Networking Fundamentals - Lesson 1b

Stage Electricity & Connection

Coaxial cables and common connectors
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
