This Globally Systemic Bank Just Went Into Crisis Mode (Derivatives)
Summary
TLDRThe video script discusses a potential financial crisis triggered by a Japanese bank's derivatives exposure and wrong-way bets on interest rates. It outlines the bank's predicament with inverted yield curves and rising funding costs, leading to a need to sell off assets at a loss. The script further explores the interconnectedness of the global banking system and the systemic risks posed by one bank's failure, drawing parallels to the 2008 financial crisis. It concludes with the bank's risky strategy to mitigate losses by investing in higher-risk assets, suggesting a possible 'Big Short 2.0' scenario and the implications for the broader economy.
Takeaways
- 🏦 A globally systemic bank, Noren Chukin, is in crisis mode due to derivatives exposure and wrong-way bets on interest rates.
- 📉 The bank plans to sell around $63 billion in US and European Sovereign bonds to mitigate losses from its investment strategy.
- 💡 The script raises the question of whether this could be the start of 'The Big Short 2.0', indicating a potential financial crisis.
- 📚 The bank's balance sheet is under scrutiny, with assets and liabilities affected by the inverted yield curve and increased funding costs.
- 🌐 The global monetary system is described as a network of interconnected bank balance sheets, implying systemic risk.
- 🔄 The bank's strategy of borrowing short and lending long has backfired due to rising interest rates, leading to a negative carry.
- 📉 The bank is forced to sell off low-yielding assets at a loss as their funding costs have increased significantly.
- 💸 The sale of treasuries will result in a substantial loss, but it's a temporary solution to a more significant systemic issue.
- 🔗 The interconnectedness of banks means that the failure of one can impact many, creating a domino effect in the financial system.
- 🚀 The bank's potential solution to buy higher-yielding but riskier assets, such as CLOs (Collateralized Loan Obligations), could amplify future risks.
- 📊 Economic indicators are showing signs of weakness, with the PMI rule and unemployment rate suggesting an impending recession.
Q & A
What is the core issue that led to the crisis at Noren Chukin Bank?
-The core issue is that Noren Chukin Bank, like many other global systemic banks, engaged in borrowing short-term at low interest rates and lending long-term at higher rates. However, when the yield curve inverted due to the Federal Reserve raising rates to combat inflation, their funding costs increased significantly, leading to a negative carry and financial losses.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
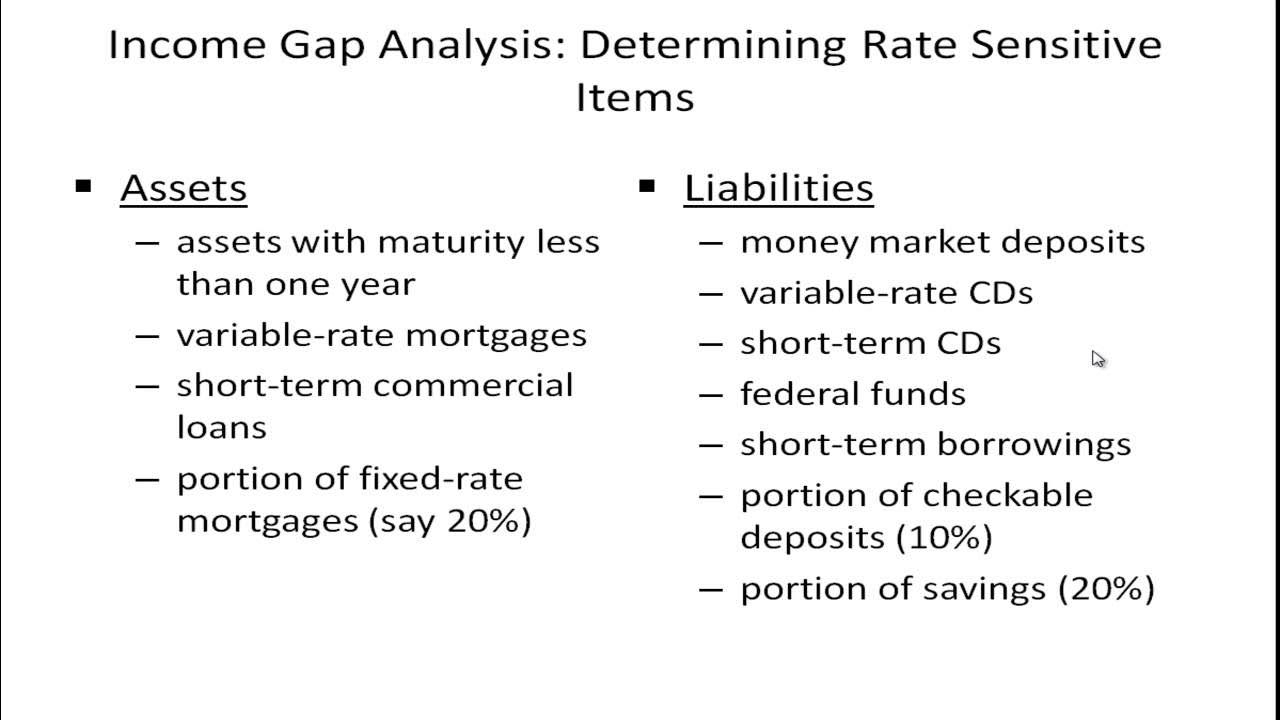
Managing Interest Rate Risk - Income Gap Analysis
Japan’s Banking System Collapsing! HUGE Bank JUST FAILED! $1.1 Trillion at Risk!

JP Morgan Chase and The scandal of London Whale

It Started: Japan Just Broke The US Stock Market

Global Debt: The Coming Financial Crisis?

Unrecoverable Catastrophe Just Hit America's Biggest Banks
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
