THE NATURE OF THE ROOTS OF A QUADRATIC EQUATION USING THE DISCRIMINANT || GRADE 9 MATHEMATICS Q1
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how to evaluate the expression b² - 4ac, known as the discriminant, in quadratic equations. The discriminant helps determine the nature of the roots. If the discriminant is zero, the roots are real and equal. A positive discriminant, whether a perfect square or not, indicates rational or irrational roots, respectively, and if negative, the equation has no real solutions. Several examples illustrate how to substitute values for a, b, and c to calculate the discriminant and determine the type of roots for quadratic equations.
Takeaways
- 😀 The discriminant (b² - 4ac) is used to determine the nature of the roots of a quadratic equation.
- 😀 The quadratic formula is x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / 2a, where the discriminant is b² - 4ac.
- 😀 The discriminant helps determine whether the roots are real, rational, irrational, or nonexistent.
- 😀 If the discriminant equals 0, the roots of the quadratic equation are real and equal.
- 😀 If the discriminant is positive and a perfect square, the roots are real, rational, and unequal.
- 😀 If the discriminant is positive but not a perfect square, the roots are real, irrational, and unequal.
- 😀 If the discriminant is negative, the quadratic equation has no real roots.
- 😀 Example 1: For the equation x² - 4x + 4 = 0, the discriminant is 0, meaning the roots are real and equal.
- 😀 Example 2: For the equation x² + 7x + 10 = 0, the discriminant is 9 (a perfect square), indicating rational, unequal roots.
- 😀 Example 3: For the equation x² + 6x + 3 = 0, the discriminant is positive but not a perfect square, resulting in irrational, unequal roots.
- 😀 Example 4: For the equation x² + 2x + 5 = 0, the discriminant is negative, so the equation has no real roots.
Q & A
What is the discriminant in the quadratic formula?
-The discriminant is the part of the quadratic formula under the square root, represented as b² - 4ac. It helps determine the nature of the roots of the quadratic equation.
How is the quadratic formula structured?
-The quadratic formula is structured as x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / 2a, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are the coefficients of the quadratic equation ax² + bx + c = 0.
What does it mean if the discriminant is zero?
-If the discriminant is zero, it indicates that the quadratic equation has real and equal roots.
How do you evaluate the discriminant for the values a = 1, b = 5, and c = 4?
-For a = 1, b = 5, and c = 4, substitute into the discriminant formula: b² - 4ac = 5² - 4(1)(4) = 25 - 16 = 9. The result is 9, which is a positive perfect square.
What is the result if the discriminant is a positive perfect square?
-If the discriminant is a positive perfect square, the roots of the quadratic equation are rational numbers, but not equal.
What does a negative discriminant imply for the roots of a quadratic equation?
-A negative discriminant implies that the quadratic equation has no real roots or solutions, meaning the roots are complex.
How do you determine if the roots of a quadratic equation are irrational?
-If the discriminant is positive but not a perfect square, the roots of the quadratic equation are irrational and not equal.
What does the discriminant tell us about the equation x² - 4x + 4 = 0?
-For the equation x² - 4x + 4 = 0, the discriminant is 0 (since (-4)² - 4(1)(4) = 16 - 16 = 0), indicating that the roots are real and equal.
What is the significance of the equation x² + 7x + 10 = 0 in terms of the roots?
-For x² + 7x + 10 = 0, the discriminant is 9 (a positive perfect square), meaning the roots are rational and unequal.
Why does the quadratic equation x² + 6x + 3 = 0 result in irrational roots?
-The discriminant for x² + 6x + 3 = 0 is 24, which is positive but not a perfect square. This means the roots are irrational and not equal.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
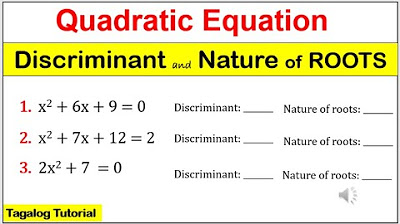
MATH9 DISCRIMINANT and NATURE OF ROOTS of quadratic equation #math9 #discriminant #natureofroots

Nature of Roots of Quadratic Equations

Nature of Roots - Examples | Quadratic Equations | Don't Memorise

Jenis-jenis akar persamaan kuadrat || akar real berbeda, akar real sama, akar tidal real (IMAJINER)

Solving Quadratic Equations by Quadratic Formula | Not A Perfect Square | Part 2 |
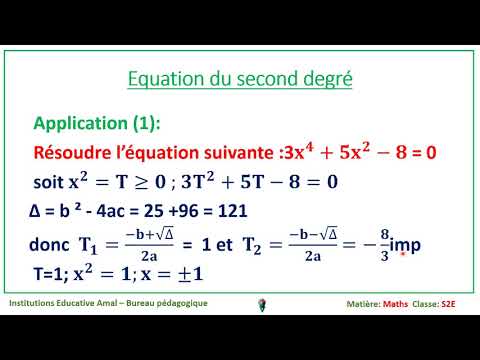
Maths - EB11 - S - chap2 - v1 - polynomes et equation du second degre
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
