Nature of Roots of Quadratic Equations
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Monsieur explains the nature of roots in quadratic equations through the discriminant, \( b^2 - 4ac \). He illustrates that a discriminant of zero results in real, rational, and equal roots, while a positive discriminant indicates real roots that are rational if it's a perfect square or irrational if not. A negative discriminant signifies no real roots. Several examples are provided to demonstrate these concepts, making the lesson clear and engaging.
Takeaways
- 📚 The lesson focuses on characterizing and describing the roots of quadratic equations, specifically identifying whether they are real, rational, irrational, equal, or unequal.
- 🔍 The discriminant, represented by the expression b^2 - 4ac, is a key factor in determining the nature of the roots without explicitly knowing them.
- ✅ If the discriminant equals zero (b^2 - 4ac = 0), the roots are real, rational, and equal.
- 📉 If the discriminant is a positive perfect square (b^2 - 4ac > 0 and is a perfect square), the roots are real, rational, and unequal.
- 📈 If the discriminant is a positive non-perfect square (b^2 - 4ac > 0 and is not a perfect square), the roots are real, irrational, and unequal.
- ❌ If the discriminant is negative (b^2 - 4ac < 0), the equation has no real roots; they are considered unreal and unequal.
- 📝 The quadratic formula, which includes the discriminant, is used to find the roots of a quadratic equation.
- 🔢 Examples are provided to illustrate how to calculate the discriminant and determine the nature of the roots for specific quadratic equations.
- 📐 The process involves identifying the coefficients a, b, and c from the quadratic equation, then substituting them into the discriminant formula.
- 🤓 Understanding the discriminant's value is crucial for classifying the roots of a quadratic equation without solving it.
- 🌐 The concepts are applicable to various quadratic equations, providing a universal method for root analysis.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The main topic of the video script is characterizing and describing the roots of quadratic equations.
What is a discriminant in the context of quadratic equations?
-The discriminant is the value of the expression b^2 - 4ac and is used to describe the nature of the roots of a quadratic equation.
What are the conditions for the roots of a quadratic equation to be real, rational, and equal?
-The roots are real, rational, and equal when the discriminant b^2 - 4ac is equal to 0.
How does the value of the discriminant determine if the roots are real and rational but unequal?
-The roots are real and rational but unequal if the discriminant is greater than zero and a perfect square.
What type of roots does a quadratic equation have if the discriminant is greater than zero but not a perfect square?
-If the discriminant is greater than zero but not a perfect square, the roots are real, irrational, and unequal.
What does a negative discriminant indicate about the roots of a quadratic equation?
-A negative discriminant indicates that the roots are unreal and unequal, as they involve the square root of a negative number.
How can you identify the nature of the roots without knowing them explicitly?
-You can identify the nature of the roots by evaluating the discriminant and its value relative to zero and whether it is a perfect square.
What is the significance of the discriminant being a perfect square in determining the roots of a quadratic equation?
-If the discriminant is a perfect square, it indicates that the roots are rational numbers; otherwise, they are irrational.
Can you provide an example of a quadratic equation with a discriminant of zero?
-An example of a quadratic equation with a discriminant of zero is x^2 - 2x + 1 = 0, which has real, rational, and equal roots.
How does the video script illustrate the process of determining the nature of the roots for different quadratic equations?
-The script provides several examples of quadratic equations, calculates their discriminants, and explains the nature of their roots based on the discriminant's value.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Nature of Roots - Examples | Quadratic Equations | Don't Memorise
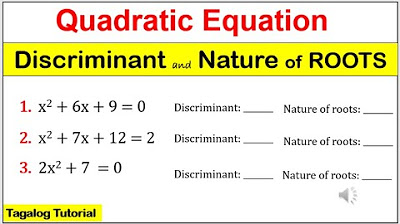
MATH9 DISCRIMINANT and NATURE OF ROOTS of quadratic equation #math9 #discriminant #natureofroots

THE NATURE OF THE ROOTS OF A QUADRATIC EQUATION USING THE DISCRIMINANT || GRADE 9 MATHEMATICS Q1

Jenis-jenis akar persamaan kuadrat || akar real berbeda, akar real sama, akar tidal real (IMAJINER)

Solving Quadratic Equations by Quadratic Formula | Not A Perfect Square | Part 2 |

Solving Quadratic Equations using Quadratic Formula
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)