PROGLIN - Transportasi bagian 2 (VAM/Vogel Aproximation Method)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the Full Approximation method for solving transportation problems in linear programming. It walks through the steps of calculating opportunity costs for each row and column, selecting the largest opportunity cost, and allocating goods based on the smallest costs. The process continues until all supply and demand are met. The method is compared to the North-West and Least Cost methods, showing that it results in a significantly lower total cost. Viewers will learn how to efficiently allocate resources and minimize transportation costs through a clear and structured approach.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video discusses solving transportation problems using the Vogel's Approximation Method (VAM).
- 😀 The method involves calculating opportunity costs for each row and column in a transportation matrix.
- 😀 Opportunity cost for a row is determined by subtracting the smallest cost from the next smallest cost within the row.
- 😀 Similarly, opportunity cost for a column is determined by subtracting the smallest cost from the next smallest cost within the column.
- 😀 The row or column with the largest opportunity cost is selected for allocation.
- 😀 Allocations are made by choosing the box with the minimum transportation cost in the selected row or column.
- 😀 After each allocation, the supply and demand are adjusted accordingly, reflecting the amount allocated.
- 😀 Once a row or column’s supply or demand is fulfilled, it is eliminated from further consideration.
- 😀 The process continues until all supply and demand have been fully met, meaning all allocations are completed.
- 😀 The total transportation cost is calculated by multiplying the allocated quantities by the corresponding transportation costs and summing them up.
- 😀 The Vogel's Approximation Method typically results in a lower total cost compared to other initial solution methods in transportation problems.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the second video in the series?
-The second video focuses on solving transportation problems using the Approximation Method, which is a method used to find the initial solution for such problems.
How does the Approximation Method relate to other methods like the Northwest Corner and Least Cost methods?
-The Approximation Method shares similarities with the Northwest Corner (NWC) and Least Cost (LC) methods, as it also aims to allocate resources while minimizing transportation costs, but it uses a different approach involving opportunity cost calculation.
What is the first step in the Approximation Method for solving transportation problems?
-The first step is to calculate the opportunity cost for each row and each column in the transportation matrix.
How is the opportunity cost for a row calculated?
-To calculate the opportunity cost for a row, subtract the smallest value in the row from the next smallest value in that same row.
What happens if two rows or columns have the same opportunity cost?
-If two rows or columns have the same opportunity cost, only one is selected for further allocation, based on the overall method's rules.
What is the next step after calculating the opportunity cost for rows and columns?
-After calculating the opportunity costs, the next step is to select the row or column with the largest opportunity cost.
How do you allocate the supply in the selected row or column?
-Allocate as much as possible to the box with the minimum cost value in the selected row or column.
What do you do once a row or column's supply or demand has been fully met?
-Once a row or column's supply or demand has been fully met, that row or column is eliminated from the further allocation process.
What is the final goal of the Approximation Method in transportation problems?
-The final goal is to satisfy all supply and demand requirements while minimizing the total transportation cost.
What is the key difference between the Approximation Method and the Northwest Corner method in terms of total cost?
-The Approximation Method often results in a lower total cost compared to the Northwest Corner method, as it carefully selects allocations based on opportunity costs.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Operations Research 06A: Transportation Problem
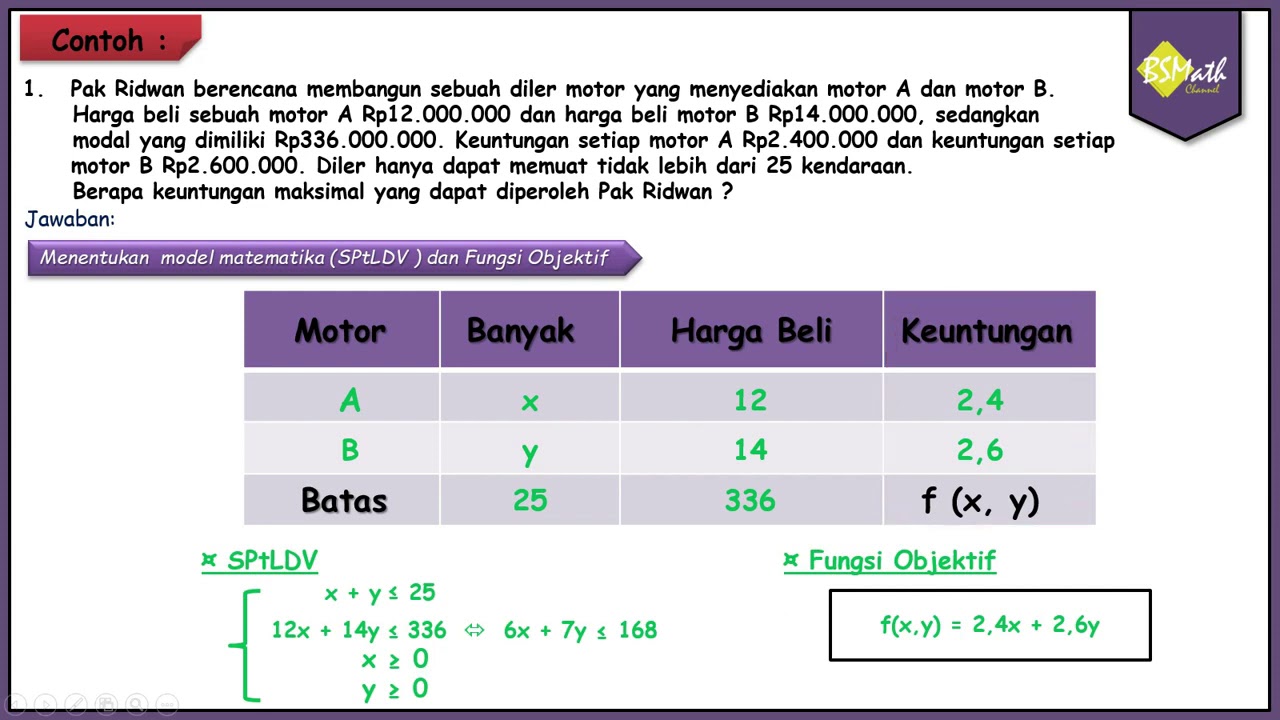
Menyelesaikan Permasalahan Program Linear Menentukan Nilai Optimum dengan Metode Uji Titik Pojok

ART TEACHES MATHEMATICS IN THE MODERN WORLD-LESSON 1: INTRO TO LINEAR PROGRAMMING

Riset Operasi #4 - Linear Programming dengan Metode Simpleks | Tutor Manajemen by Gusstiawan Raimanu

Ch04 Linear Programming
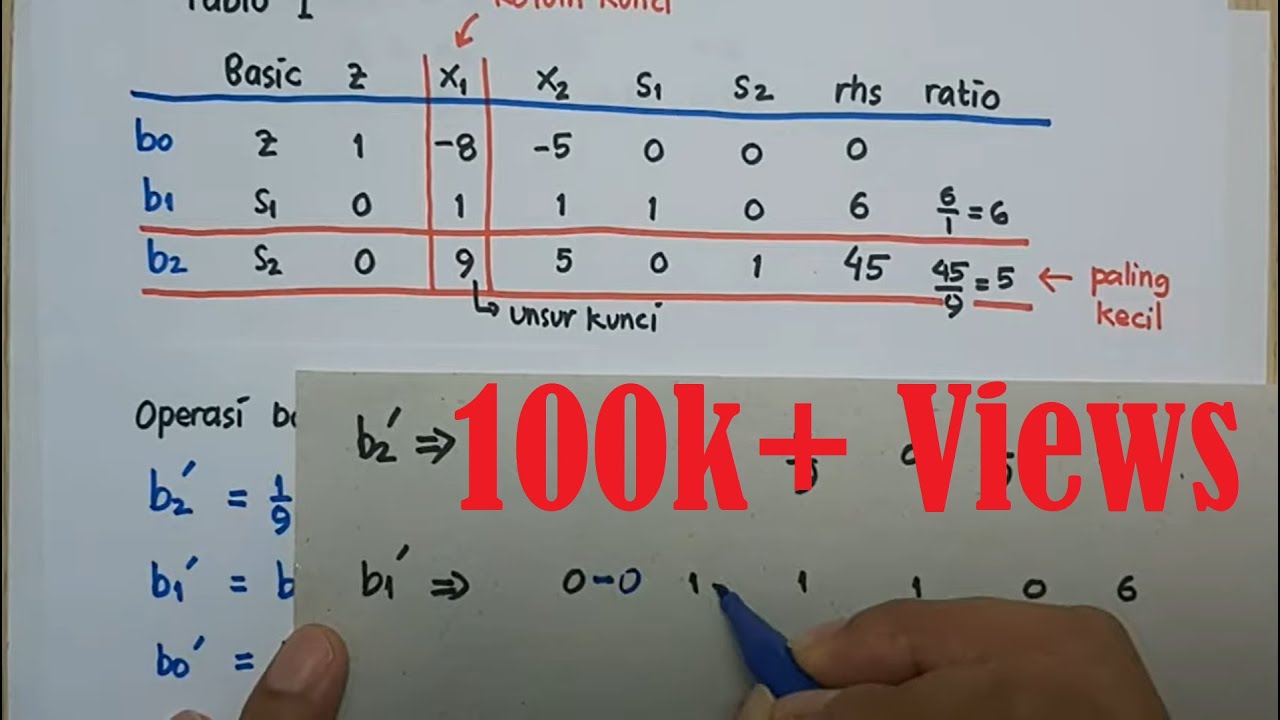
Metode Simpleks (Contoh soal untuk kasus maksimisasi)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
