#23 Types Of Data In Cluster Analysis |DM|
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the presenter explains the types of data used in cluster analysis, focusing on four main data types: interval scale, binary, categorical, and mixed variables. The video also discusses two primary data structures—data matrices and dissimilarity matrices—used in clustering. Data matrices represent entities and their properties, while dissimilarity matrices help identify the distance between objects. The presenter breaks down the nuances of each data type, including the standardization process for interval data and the difference between symmetric and asymmetric binary variables. The video concludes with an invitation to viewers to ask questions in the comments.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script explains the types of data used in cluster analysis, including data structures and data types.
- 😀 There are two main data structures in cluster analysis: the data matrix and the dissimilarity matrix.
- 😀 A data matrix is a table or rectangular matrix where rows represent entities and columns represent properties of those entities.
- 😀 A dissimilarity matrix is a square matrix (n x n) that shows the dissimilarities between objects, with diagonal elements being zero.
- 😀 The first type of data for cluster analysis is **interval scale data**, which involves continuous intervals and requires data standardization before clustering.
- 😀 **Binary variables** have two values (0 or 1) representing the presence or absence of a variable and can be symmetric or asymmetric.
- 😀 Symmetric binary variables allow swapping of values (e.g., male=0, female=1 or vice versa), while asymmetric binary variables do not allow such swaps.
- 😀 **Categorical variables** are divided into categories (e.g., gender, pass/fail), with two subtypes: nominal (no order) and ordinal (specific order required).
- 😀 **Nominal categorical variables** do not require any particular order (e.g., male/female), while **ordinal categorical variables** must follow a specific order (e.g., low, medium, high).
- 😀 **Mixed variables** combine different types of variables, such as binary, ordinal, nominal, and interval, to form more complex datasets.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video?
-The video explains the types of data used in cluster analysis and the data structures that support them.
What are the two main data structures discussed in the video?
-The two main data structures discussed are the Data Matrix and the Dissimilarity Matrix.
How is data represented in a Data Matrix?
-In a Data Matrix, data is represented as a table or a rectangular matrix (n by p), where rows represent real-world entities, and columns represent their properties.
What is the purpose of a Dissimilarity Matrix?
-A Dissimilarity Matrix is used to measure the dissimilarities between objects. It is represented as a square matrix (n by n), where diagonal elements are zero, and the off-diagonal elements represent the distance or dissimilarity between objects.
What are Interval Scale Variables in the context of clustering?
-Interval Scale Variables are continuous variables divided into intervals, such as 10-20, 20-30, and so on. These variables require standardization to remove units and then are divided into intervals based on their mean absolute deviation.
How does data standardization work for Interval Scale Variables?
-Data standardization involves removing units from the data, making it unitless. After standardization, the data is converted into continuous data and then divided into intervals using mean absolute deviation.
What are Binary Variables, and what types are discussed?
-Binary Variables are variables with only two values (either 0 or 1). The video discusses two types: symmetric binary variables, where the values can be swapped, and asymmetric binary variables, where the values cannot be changed.
Can you change the values of symmetric binary variables? Give an example.
-Yes, symmetric binary variables allow you to swap the values. For example, in a gender classification, male could be represented as 0 and female as 1, or you could swap them, using female as 0 and male as 1.
What is the difference between Nominal and Ordinal variables in categorical data?
-Nominal variables have no specific order between categories (e.g., male, female), while Ordinal variables have a defined order (e.g., low, medium, high). The order matters in ordinal variables but not in nominal variables.
What are Mixed Variables in clustering?
-Mixed Variables are a combination of different types of variables, such as binary, nominal, ordinal, and interval scale variables, used together in clustering.
What is the next topic the video will cover in the series?
-The next video will explain different clustering methods and how each type of data can be used with them.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

CARA MEMBEDAKAN JENIS DATA NOMINAL, ORDINAL, INTERVAL, DAN RASIO | STATISTIKA PENELITIAN
Variables and Types of Variables | Statistics Tutorial | MarinStatsLectures

02 Klasifikasi data statistika

What is Classification? What is a Classifier?

Teori dan Aplikasi Pengukuran Psikologi
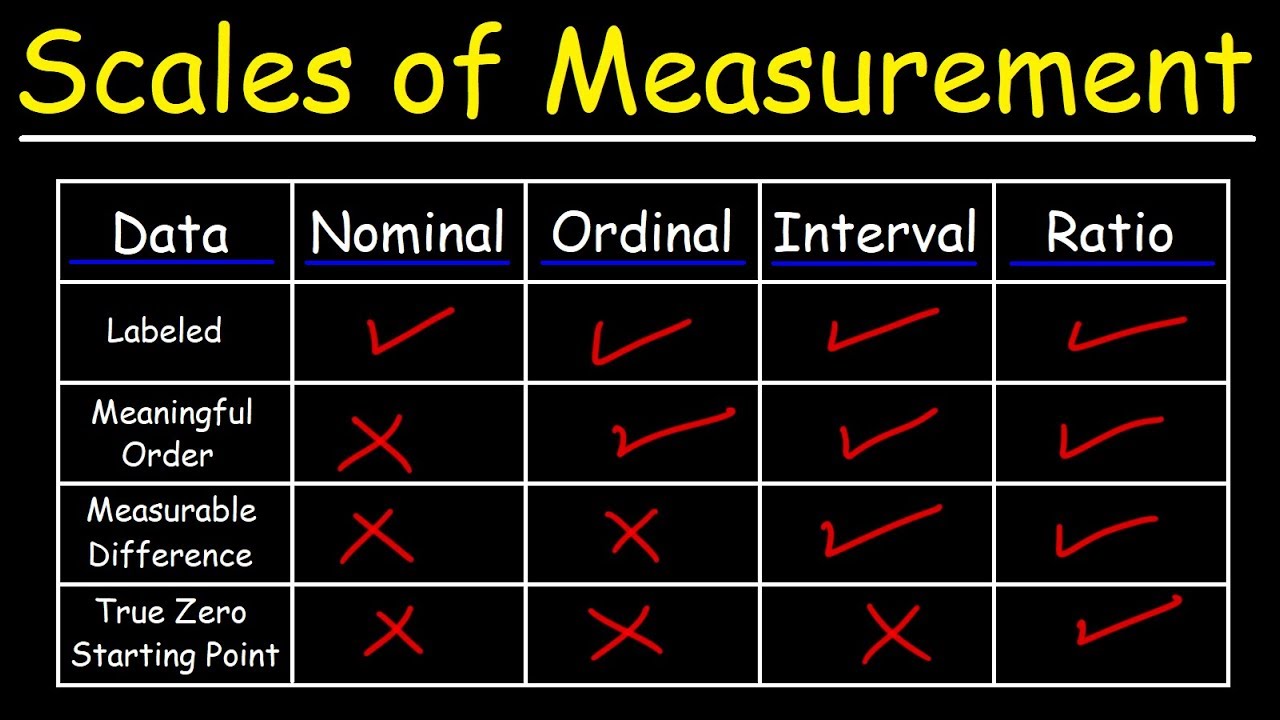
Scales of Measurement - Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, & Ratio Scale Data
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
