Hukum hukum Dasar Kimia bag 1, XMIPA
Summary
TLDRThis educational video covers fundamental chemistry laws, starting with the Law of Conservation of Mass by Lavoisier, emphasizing how mass remains constant before and after a reaction. It also explores the Law of Definite Proportions by Proust, demonstrating fixed mass ratios in compounds, and the Law of Multiple Proportions by Dalton, showing how elements combine in simple whole number ratios. The video includes practical examples, such as the formation of compounds like sodium chloride, water, and copper sulfide, along with calculation examples of mass ratios in different chemical reactions.
Takeaways
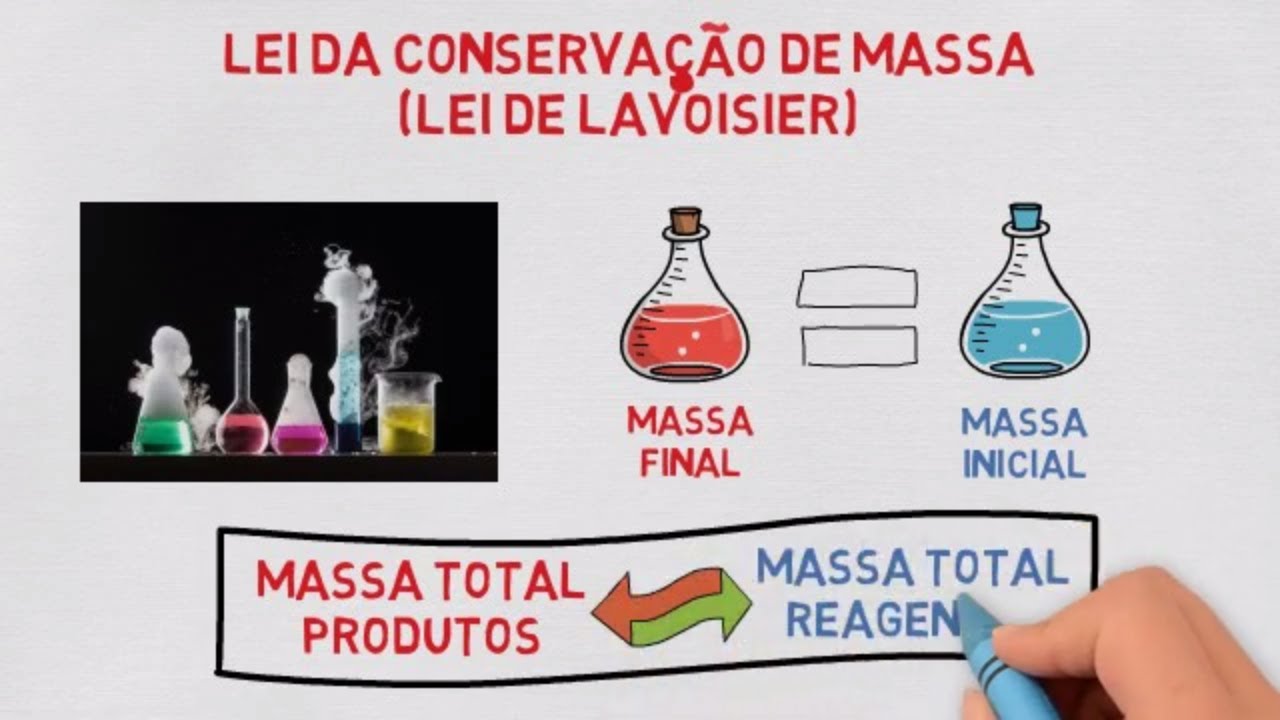
- 😀 The concept of the Law of Conservation of Mass by Lavoisier is introduced, stating that mass before and after a reaction remains the same.
- 😀 An example is given using a reaction in a closed container where the mass before and after remains the same.
- 😀 It is explained that it's difficult to calculate mass in reactions occurring in open environments, like a bonfire or rusting of iron.
- 😀 The Law of Definite Proportions by Proust is explained, showing that the ratio of elements in a compound is always fixed and consistent.
- 😀 An example of the formation of sodium chloride from sodium and chlorine is used to demonstrate the law of definite proportions.
- 😀 A case study involving hydrogen and oxygen reacting to form water shows how mass ratios in chemical reactions remain consistent.
- 😀 The Law of Multiple Proportions by John Dalton is introduced, explaining how elements can form different compounds, with mass ratios being simple whole numbers.
- 😀 The concept is further explained using nitrogen and oxygen forming multiple compounds like NO, N2O, and NO2, with their mass ratios forming simple whole numbers.
- 😀 A practical problem is provided where the mass ratio of iron and oxygen in forming iron oxide compounds (FeO and Fe2O3) is calculated, showing the application of the law of multiple proportions.
- 😀 A second problem demonstrates how the mass ratio of nitrogen and oxygen in forming nitrogen monoxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and nitrous oxide (N2O) follows the law of multiple proportions with simple integer ratios.
Q & A
What is the Law of Conservation of Mass as explained in the script?
-The Law of Conservation of Mass, as explained in the script, states that the mass before a chemical reaction is equal to the mass after the reaction, provided that the system is closed. This was demonstrated through an experiment where sodium sulfate and calcium carbide reacted to form calcium sulfate and sodium chloride, with no mass loss.
Why is it difficult to apply the Law of Conservation of Mass to reactions in open environments?
-It is difficult to apply the Law of Conservation of Mass in open environments because some mass may escape in the form of gases or vapor, as seen in examples like a campfire or the rusting of iron. In these cases, the mass of products cannot be accurately measured without considering the loss of substances to the surroundings.
What does the Law of Definite Proportions state?
-The Law of Definite Proportions, explained in the script, states that a chemical compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions by mass, regardless of the amount of the compound or its source. For example, sodium chloride (NaCl) always contains 39% sodium and 61% chlorine by mass.
How is the Law of Definite Proportions demonstrated in the formation of water (H2O)?
-The Law of Definite Proportions is demonstrated in the formation of water by showing that hydrogen and oxygen combine in a fixed ratio. In the script, it is explained that 1 gram of hydrogen reacts with 8 grams of oxygen to form 9 grams of water, with no leftovers. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen remains constant.
What does the Law of Multiple Proportions (Dalton's Law) state?
-The Law of Multiple Proportions, as stated by Dalton, explains that when two elements combine to form more than one compound, the masses of the second element in each compound are in simple, whole-number ratios. For example, nitrogen and oxygen can form multiple compounds like N2O, NO, and NO2, where the mass of oxygen in each compound is a simple whole number ratio.
Can you explain the example of nitrogen and oxygen compounds used in the script to demonstrate the Law of Multiple Proportions?
-In the script, nitrogen and oxygen form several compounds, including nitrogen monoxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and dinitrogen monoxide (N2O). When the mass of nitrogen is kept constant in each compound, the mass of oxygen follows a simple whole-number ratio: 1:2:4, demonstrating the Law of Multiple Proportions.
How is the mass of oxygen calculated when comparing two iron oxide compounds (FeO and Fe2O3)?
-In the script, the mass of oxygen in two iron oxide compounds is calculated by first finding the mass of iron in each compound and then determining the corresponding mass of oxygen. For FeO, the ratio of Fe to O is 56:16. For Fe2O3, the ratio is 112:48. When the mass of iron is made the same (112 grams), the mass of oxygen in FeO becomes 32 grams, and in Fe2O3 it remains 48 grams. The ratio of oxygen mass is then 2:3.
What is the significance of keeping the mass of one element constant when comparing multiple compounds?
-The significance of keeping the mass of one element constant is that it allows for the clear comparison of the mass ratios of the second element in each compound. This approach helps to identify simple whole-number ratios between the elements, as required by the Law of Multiple Proportions.
In the script, how is the mass ratio of oxygen determined for the nitrogen compounds N2O, NO, and NO2?
-The mass ratio of oxygen for the nitrogen compounds N2O, NO, and NO2 is determined by first calculating the mass of nitrogen in each compound and then finding the corresponding mass of oxygen. When the mass of nitrogen is made the same (288 grams), the mass of oxygen in N2O is 16 grams, in NO it is 32 grams, and in NO2 it is 64 grams. This gives the simple ratio of 1:2:4 for the oxygen masses.
What is the relationship between the masses of elements in a chemical reaction, as described in the script?
-The script emphasizes that in a chemical reaction, the masses of elements combine in definite ratios according to various laws. The Law of Conservation of Mass ensures no mass is lost, the Law of Definite Proportions shows that elements combine in fixed ratios, and the Law of Multiple Proportions explains that the ratio of masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of another element can form multiple compounds with simple, whole-number ratios.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

HUKUM- HUKUM DASAR KIMIA (PART 1)

Praktikum Konsep Mol (Hukum Kekekalan Massa)

HUKUM KEKEKALAN MASSA ( HUKUM LAVOISIER ) : HUKUM DASAR KIMIA

Hukum Lavoisier (Hukum Kekekalan Massa) | Kimia SMA | Tetty Afianti
Lei de Lavoisier: Lei de Conservação das Massas!

HUKUM DASAR KIMIA | HUKUM KEKEKALAN MASSA (LAVOISER) - BAGIAN 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
