5 Criterio de resistencia Mohr Coulomb
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the Coulomb failure law and its relation to soil mechanics, explaining how shear stress and normal stress interact. It describes the frictional forces acting on a block and the mathematical relationship between these forces. The script further explores the behavior of soils under different stress conditions, including undrained and drained scenarios. Emphasis is placed on understanding the cohesion, friction, and the effect of normal stress on shear strength. The video also discusses the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion, highlighting its application in soil analysis for both short-term and long-term conditions.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script explains the relationship between the ancient Coulomb friction law and shear stress resistance.
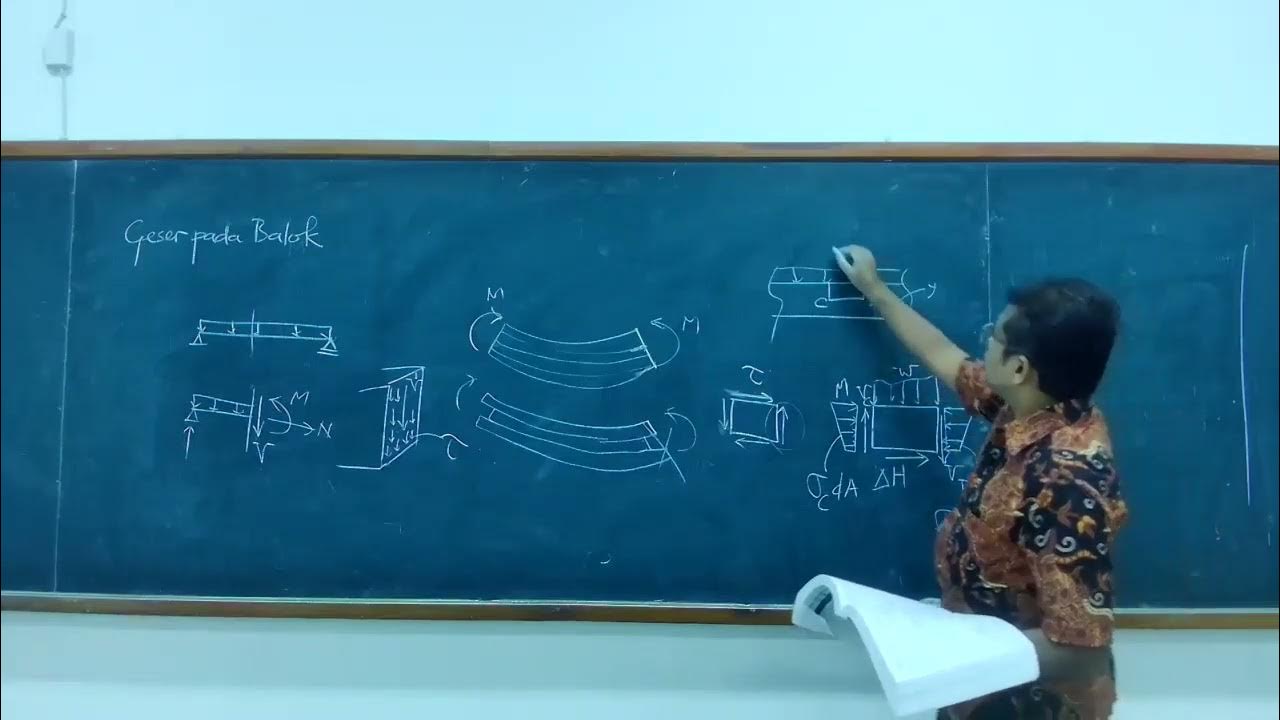
- 😀 Coulomb's friction law involves a block that slides along a surface, where normal and tangential forces create shear stress and resistance.
- 😀 The shear stress of failure is directly proportional to the normal stress, governed by the angle of internal friction (ϕ).
- 😀 When the normal stress increases, the resistance to shear stress also increases, both for soils and blocks.
- 😀 The script describes how shear stress failure in soils is analogous to direct shear tests, where normal and tangential forces interact.
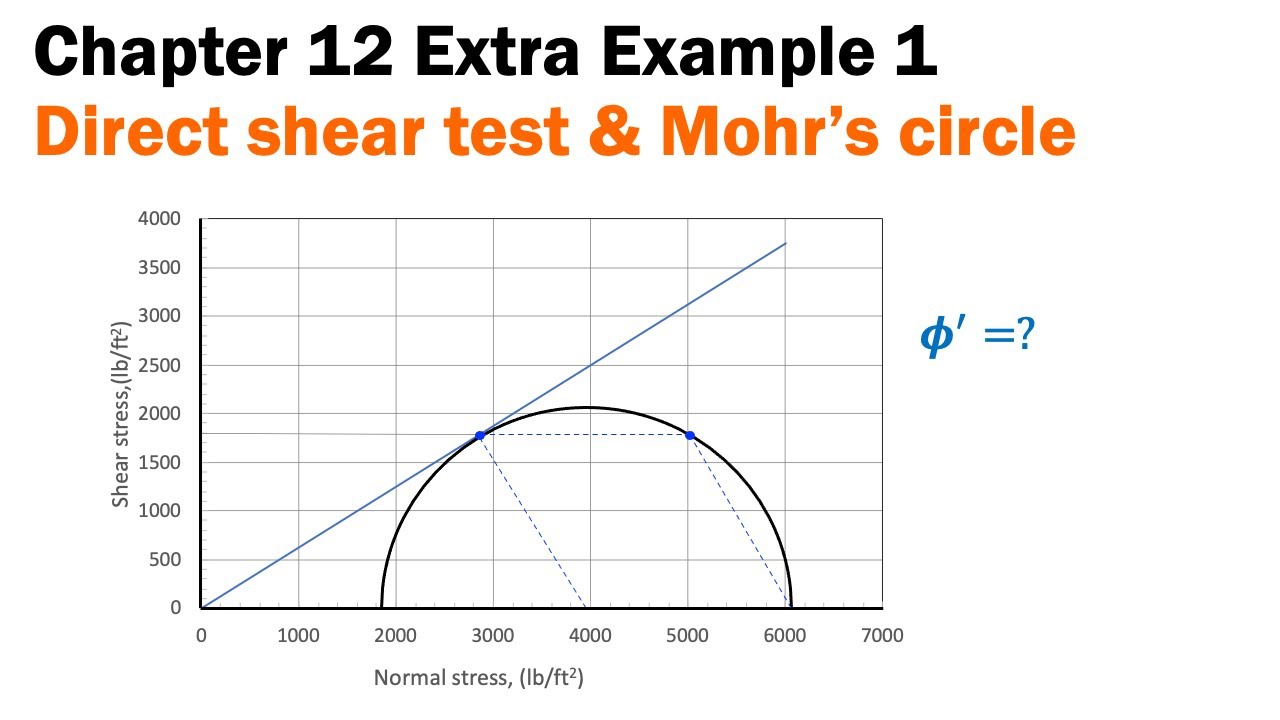
- 😀 The relationship between principal stresses (σ1 and σ3) and the failure angle (ϕ) can be derived using Mohr's circle.
- 😀 A detailed geometric analysis explains how the angle of failure planes and the internal friction angle are connected through trigonometric identities.
- 😀 The script highlights how increasing principal stress, particularly σ3 (the confining stress), directly affects shear strength and failure in soils.
- 😀 Different soil behaviors are explained, including soils with no normal stress but still having resistance to shear stress due to cohesion (c).
- 😀 The law of shear resistance is divided into different types: frictional resistance, cohesion-based resistance, and undrained shear strength based on the water-soil interaction in saturated soils.
Q & A
What is the connection between Coulomb’s friction law and shear strength in soils?
-Coulomb's friction law relates shear strength in soils to the normal stress applied. It states that the shear strength is proportional to the normal stress, with the proportionality constant being the tangent of the internal friction angle. This law explains how a material resists shear stress based on the normal stress and friction.
How is the angle of inclination in Coulomb’s law determined?
-The angle of inclination in Coulomb’s law is determined by considering the relationship between the tangential force (shear force) and the normal force. The tangent of the angle is equal to the ratio of the shear force to the normal force, which gives the internal friction angle of the material.
How does shear stress affect the failure of soils?
-Shear stress causes soils to fail when it exceeds a critical value, which depends on the normal stress applied. The failure plane is inclined at an angle, and the shear stress needed for failure is directly related to the normal stress applied, as described by Coulomb’s law.
What is the significance of principal stresses in soil mechanics?
-Principal stresses are the maximum and minimum normal stresses acting on a soil element. They are important because they define the state of stress at any point and help predict the failure conditions of the soil using concepts like the Mohr circle and failure envelopes.
How does the Mohr circle relate to soil failure?
-The Mohr circle represents the state of stress at a point in the soil. The circle touches the failure envelope when the soil is about to fail. The distance between the Mohr circle and the failure envelope indicates the factor of safety for the soil structure.
What is the relationship between the friction angle (fi) and the failure plane in soils?
-The friction angle (fi) is related to the angle of the failure plane. The inclination of the failure plane is determined by the internal friction angle, and this relationship is used to calculate the shear strength of the soil at failure.
What is the significance of the equation τf = σn * tan(φ)?
-This equation describes the relationship between shear strength (τf) and normal stress (σn). It states that the shear strength at failure is equal to the normal stress multiplied by the tangent of the internal friction angle (φ). This equation is essential in soil mechanics for determining when soil will fail under shear stress.
What is the effect of cohesion (c) on soil shear strength?
-Cohesion (c) is an additional factor that contributes to shear strength, especially in soils with low friction. The shear strength equation for such soils becomes τf = c + σn * tan(φ), where c represents the cohesive strength of the soil, allowing the material to resist shear stress even when normal stress is zero.
What happens when the normal stress is zero in a soil?
-When the normal stress is zero, soils can still exhibit shear strength due to cohesion (c). This scenario occurs in cohesive soils, which have inherent bonding between particles that provides resistance to shear stress, even without any applied normal stress.
What is the difference between drained and undrained shear strength?
-Drained shear strength occurs when pore water pressure dissipates over time, and the soil's shear strength is governed by the friction between soil particles. Undrained shear strength occurs when pore water pressure does not dissipate, and the soil behaves as if it has no effective stress. The analysis of these strengths depends on the time scale of loading and water migration in the soil.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)