MANDIBULAR NERVE AND ITS BRANCHES
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the course of the mandibular nerve, the third division of the trigeminal nerve, is explored in detail. The mandibular nerve is a mixed nerve, containing both motor and sensory components. It exits the skull and divides into an anterior and posterior division, each giving off various branches that serve both motor functions for muscles of mastication and sensory functions for regions like the skin, tongue, and lower lip. Key branches include the lingual nerve, inferior alveolar nerve, and the mental nerve, which provide vital sensations to the face and mouth.
Takeaways
- 😀 The mandibular nerve is a mixed nerve, containing both motor and sensory components.
- 😀 It forms at the trigeminal ganglion from the union of the motor root and the third division of the sensory root.
- 😀 The nerve exits the skull through the foramen ovale, where the motor root merges with the sensory root to form the mandibular nerve trunk.
- 😀 The undivided mandibular nerve splits shortly after exiting the skull into an anterior and a posterior division.
- 😀 The two branches from the undivided nerve trunk are the nervus spinosus and the medial pterygoid nerve.
- 😀 The nervus spinosus re-enters the cranium via the foramen spinosum, carrying the middle meningeal artery to supply the dura mater and mastoid air cells.
- 😀 The medial pterygoid nerve provides motor innervation to the medial pterygoid muscle and small branches to the tensor veli palatini and tensor tympani muscles.
- 😀 The anterior division of the mandibular nerve gives off four branches: buccal nerve (sensory), deep temporal nerve, nerve to the masseter, and nerve to the lateral pterygoid muscle.
- 😀 The posterior division of the mandibular nerve gives off three branches: auriculotemporal nerve, lingual nerve, and inferior alveolar nerve.
- 😀 The inferior alveolar nerve provides sensory innervation to the mandibular teeth and branches into the incisive and mental nerves for sensory input to the chin and lower lip.
Q & A
What is the mandibular nerve and why is it called a mixed nerve?
-The mandibular nerve is the third division of the trigeminal nerve and is called a mixed nerve because it contains both sensory and motor components. The motor root is responsible for motor functions, while the sensory root carries sensory information.
How does the motor root of the mandibular nerve relate to the sensory root?
-The motor root and the sensory root of the mandibular nerve are connected at the trigeminal ganglion. The motor root joins the third division of the sensory root to form the mandibular nerve, which exits the skull through the foramen ovale.
What is the significance of the undivided mandibular nerve trunk?
-The undivided mandibular nerve trunk is short-lived, lasting only 2 to 3 mm before splitting into the anterior and posterior divisions. During this brief period, it gives off two branches: the nervous spinosus and the medial pterygoid nerve.
What are the two branches that arise from the undivided mandibular nerve trunk?
-The two branches from the undivided mandibular nerve trunk are the nervous spinosus and the medial pterygoid nerve.
What is the function of the nervous spinosus branch?
-The nervous spinosus branch re-enters the cranium through the foramen spinosum, accompanying the middle meningeal artery. It supplies the dura mater and mastoid air cells.
What muscles are innervated by the medial pterygoid nerve?
-The medial pterygoid nerve is motor to the medial pterygoid muscle, and it also sends small branches to the tensor veli palatini and tensor tympani muscles.
What is the function of the buccal nerve (also known as the buxin nerve)?
-The buccal nerve, arising from the anterior division of the mandibular nerve, provides sensory innervation to the skin of the cheek, the buccal gingiva of the mandibular molars, and the mucosal fold in that region. It does not innervate the buccinator muscle, which is innervated by the facial nerve.
What are the branches of the anterior division of the mandibular nerve?
-The anterior division of the mandibular nerve gives off four branches: the nerve to the lateral pterygoid muscle, the nerve to the masseter muscle, the deep temporal nerve, and the buccal nerve.
What is the role of the lingual nerve?
-The lingual nerve, a branch of the posterior division of the mandibular nerve, provides general sensation and taste sensation (via the chorda tympani branch of the facial nerve) to the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. It also innervates the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth and the gingiva on the lingual side of the mandible.
What is the significance of the inferior alveolar nerve and its branches?
-The inferior alveolar nerve, the largest branch of the mandibular nerve, enters the mandibular canal and provides sensory innervation to the mandibular posterior teeth. It also gives off the mylohyoid nerve, which is motor to the mylohyoid muscle and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle, as well as sensory innervation to the mandibular incisors. At the mental foramen, the inferior alveolar nerve divides into the incisive and mental nerves.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
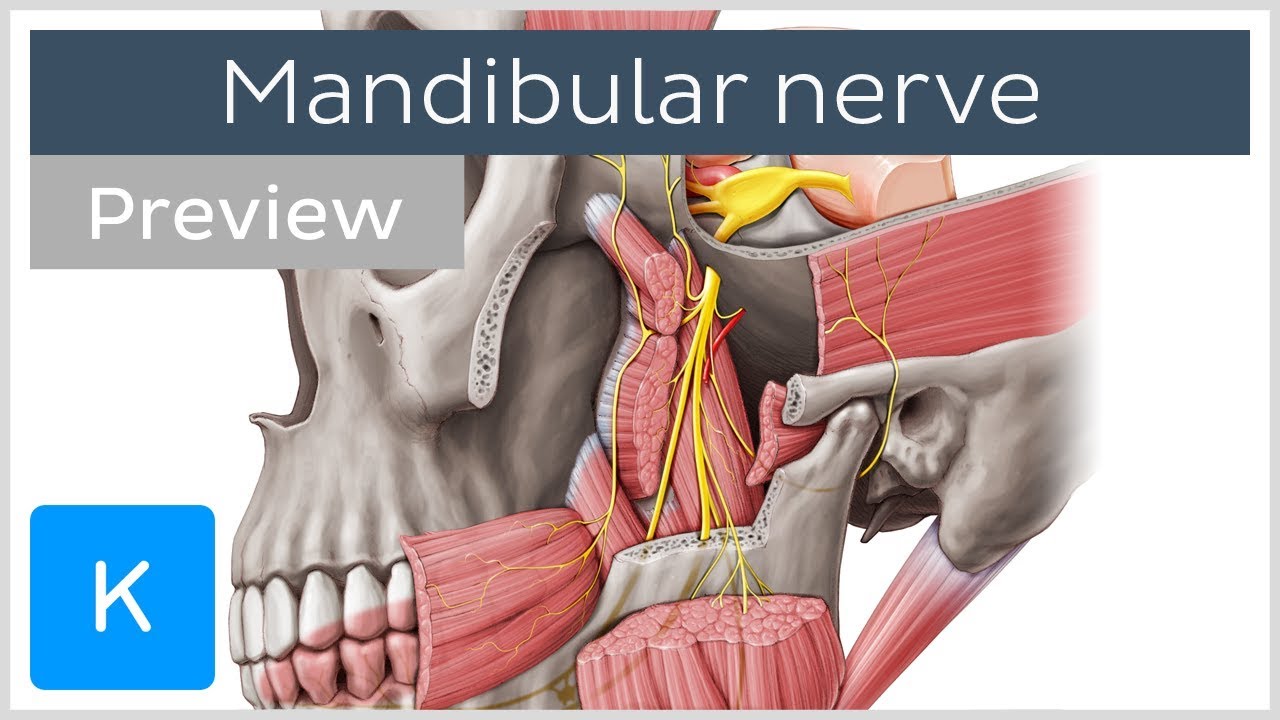
What is the Mandibular Nerve? (preview) - Human Anatomy | Kenhub
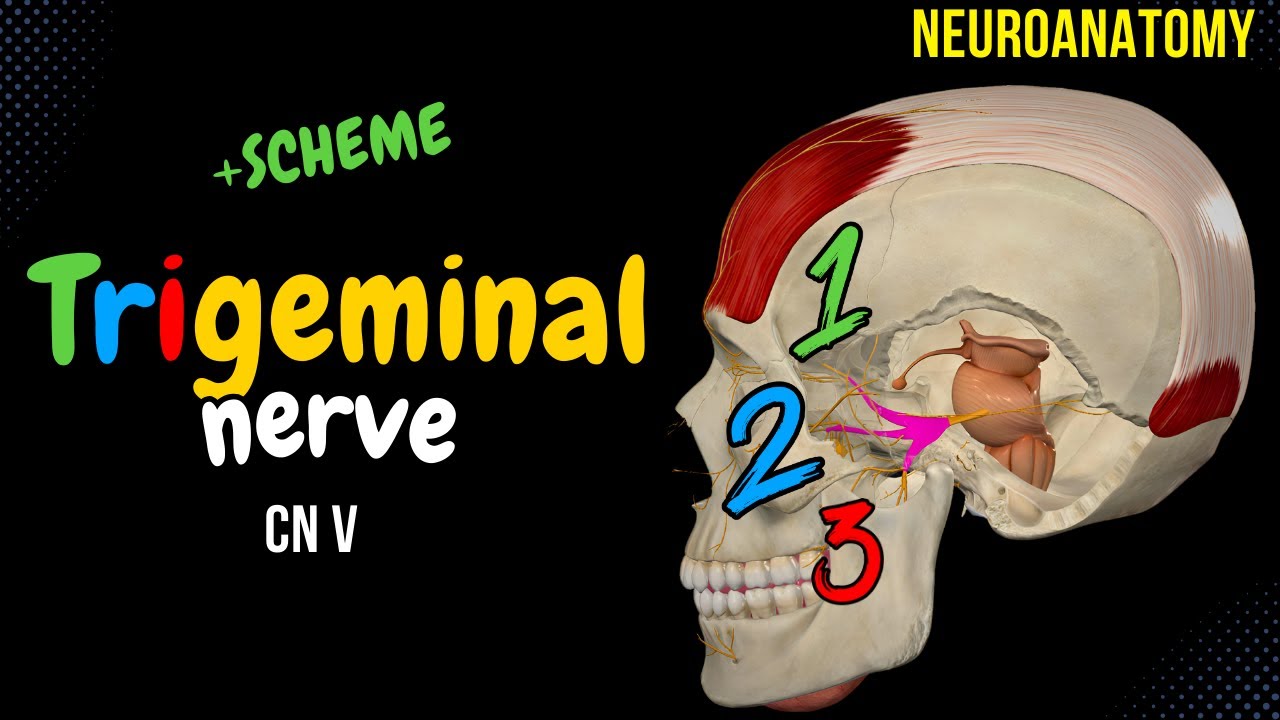
CN 5: Trigeminal Nerve (Scheme, Divisions, Pathway) | Neuroanatomy
2-Minute Neuroscience: Trigeminal Nerve (Cranial Nerve V)

Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy - Cranial Nerve 5 Course and Distribution
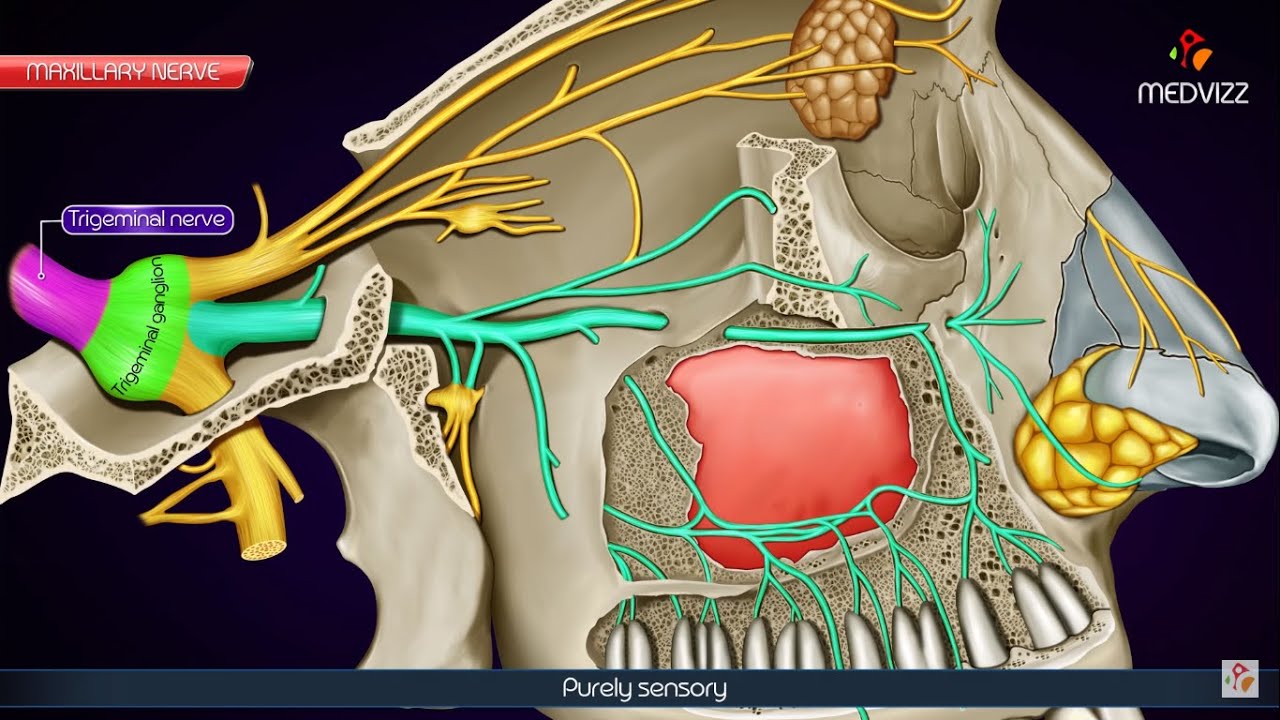
Maxillary division of Trigeminal nerve (V2 or Vb) / Maxillary nerve - Anatomy Animation

NERVE SUPPLY / INNERVATION OF MAXILLA AND MANDIBLE
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
