How Your Brain Processes Information
Summary
TLDRThis video explores how the brain processes information during learning. It explains the importance of minimizing distractions and focusing attention on meaningful signals to enhance memory retention. Key concepts include working memory's limited capacity, the importance of rehearsal strategies like mnemonics and self-testing, and how encoding information into long-term memory relies on meaningful connections. The video emphasizes that learning alters the brain's neural structure, improving speed and accuracy in recall. To maximize learning, the brain needs regular 'workouts' through focused practice, retrieval, and effective study techniques.
Takeaways
- 😀 Minimize distractions while studying, as the brain can't process all stimuli at once, and you will only remember what you focus on.
- 😀 Multitasking is ineffective for learning, as paying attention to other activities (like Instagram) will reduce your ability to retain class material.
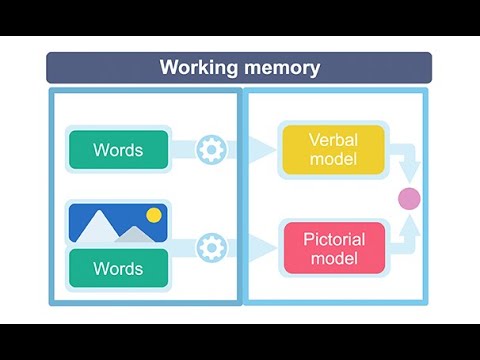
- 😀 Working memory is the first place new information goes, but it has limited capacity and duration, typically holding 7-9 items for just 5-15 seconds.
- 😀 Cramming might work short-term, but it's unlikely you'll retain information in the long run without rehearsal and review.
- 😀 Break material into small chunks and use varied rehearsal strategies (mnemonics, visuals, color-coding) to improve retention.
- 😀 To encode information into long-term memory, make the material meaningful by connecting it to what you already know or care about.
- 😀 Retrieval practice is key for reinforcing learning; regularly test yourself or reflect on the material to strengthen your memory.
- 😀 Learning alters the brain's neural structure by strengthening the myelin around neurons, allowing for faster and more accurate recall.
- 😀 To improve learning, adopt a strategy that includes minimizing distractions, breaking information into small bits, and practicing retrieval.
- 😀 Real learning occurs when information can be retrieved from long-term memory when needed, so focus on both encoding and retrieval practices.
- 😀 For academic success, regularly review notes, test yourself, and use effective rehearsal strategies to ensure lasting learning.
Q & A
Why is it important to minimize distractions while studying or in class?
-Minimizing distractions is crucial because your brain can only focus on a limited number of signals at once. Distractions compete for attention, and you will only remember the signals you actively focus on. Therefore, staying focused improves retention and understanding of the material.
What role does sensory input play in the learning process?
-Sensory input, such as sights, sounds, and smells, constantly bombard our brain. However, the brain cannot process all stimuli simultaneously. It shifts attention to the most relevant or unique signals, which influences what we remember and how we learn.
Why is multitasking ineffective for learning?
-Multitasking is ineffective for learning because it divides attention between multiple activities, making it difficult to retain or understand any one thing fully. For example, if you’re distracted by social media during a lecture, you will only remember the distractions instead of the actual content.
What is working memory, and why is it important in learning?
-Working memory is the part of the brain where new information is temporarily stored while we process it. It has limited capacity (about 7-9 items) and a short duration (5-15 seconds). Understanding working memory is important because it influences how much and how long we can hold onto new information before encoding it into long-term memory.
Why doesn’t cramming work for long-term retention?
-Cramming doesn’t work for long-term retention because working memory can only hold a limited amount of information for a short time. Without proper rehearsal or spaced review, the information is likely to be forgotten once the pressure of the exam is over.
What are some effective strategies to maximize learning?
-To maximize learning, break the material into smaller chunks, use rehearsal techniques (such as mnemonics, acronyms, or self-testing), and make the information meaningful by connecting it to prior knowledge or personal interests. These strategies help encode information more effectively into long-term memory.
How do rehearsal strategies help with memory retention?
-Rehearsal strategies, like creating mnemonic devices or reviewing notes regularly, help to reinforce the information in your working memory. By actively engaging with the material in different ways, you increase the chances of transferring it to long-term memory, where it can be retained for a longer period.
What is the process of encoding, and how does it affect learning?
-Encoding is the process by which information moves from working memory to long-term memory. For encoding to be successful, the information must be meaningful and connected to previously learned content or personal interests, which enhances recall and retention.
Why is retrieval practice essential in learning?
-Retrieval practice is essential because it strengthens the ability to pull information from long-term memory. By practicing retrieving information through self-testing or reflection, you reinforce neural connections and improve your capacity to recall the information when needed.
How does learning change the structure of the brain?
-Learning physically changes the structure of the brain by strengthening the myelin on neurons, which helps the signals travel faster and more accurately. This neural adaptation allows for easier and quicker recall of information over time, making learning more efficient.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)