KOGNITIF, BELAJAR, DAN MEMORI -BIOPSIKOLOGI
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Butiran Gini from the Faculty of Psychology explains the cognitive processes of learning and memory. She discusses the definitions of learning and cognition, and the essential processes of memory, including encoding, storage, and retrieval. The video explores how learning influences memory and how different brain regions contribute to storing and recalling information. Factors that cause forgetting, such as encoding failure and interference, are also covered. Additionally, Gini highlights learning difficulties caused by brain disorders, the physiological role of sensory organs in learning, and the connection between memory and behavior. The presentation concludes with a reflection on how all these processes work together to shape human understanding and action.
Takeaways
- 😀 **Learning** is a process where individuals acquire knowledge and modify their behavior based on what they've learned.
- 😀 **Cognition** refers to the mental processes used to acquire understanding and interpret information.
- 😀 **Repetition** is key to enriching memory by reinforcing information through repeated exposure.
- 😀 **Fundamental Change** in mindset and cognitive processes helps individuals to transform their basic perceptions.
- 😀 **Authentic Infotainment** enhances understanding of the environment, making learning more meaningful.
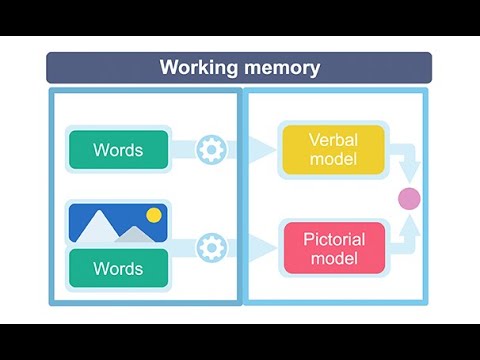
- 😀 Memory involves three main processes: **Encoding** (input), **Storage** (keeping), and **Retrieval** (recalling).
- 😀 Short-term memory holds information temporarily, while long-term memory stores information for extended periods, sometimes indefinitely.
- 😀 **Explicit Memory** can be consciously recalled, while **Implicit Memory** influences behavior unconsciously, including procedural and priming memories.
- 😀 The relationship between learning and memory is inseparable—learning cannot occur without memory to store knowledge, and memory cannot be filled without the learning process.
- 😀 Key brain areas involved in memory include the **hippocampus** (temporary storage), **cortex** (various types of storage), and **amygdala** (emotional memories), among others.
- 😀 Forgetting can be caused by encoding failure, consolidation issues, decay, interference, the tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon, and neural pruning of unused memories.
- 😀 Learning disabilities, such as **aphasia**, **alexia**, **apraxia**, and **agnosia**, are brain-related impairments that affect communication and motor skills, disrupting the learning process.
Q & A
What is the definition of learning as mentioned in the video?
-Learning is defined as a process in which an individual acquires knowledge and then attempts to apply that knowledge to change or improve their behavior.
How is cognition defined in the context of the video?
-Cognition is described as a mental process that involves obtaining understanding or comprehension of information.
What are the main reasons for learning, according to the video?
-The video outlines three main reasons for learning: repetition (to enhance memory), fundamental change (to alter basic mindsets and perceptions), and authentic understanding (to better comprehend the environment).
What are the three main processes involved in memory?
-The three main processes of memory are encoding (inputting information into storage), storage (keeping the information in the brain), and retrieval (accessing and recalling stored information).
What factors affect the encoding process in memory?
-The encoding process is influenced by attention, the depth of processing, elaboration (forming connections with existing knowledge), and mental imagery (visual associations).
What are the two types of memory and how are they different?
-The two types of memory are short-term memory (temporary storage used until the information is either used, consolidated, or forgotten) and long-term memory (information that has undergone consolidation and is stored permanently).
What is the difference between explicit and implicit memory?
-Explicit memory refers to memories that can be consciously recalled, while implicit memory involves memories that are recalled unconsciously, often related to habits or skills.
What are the subdivisions of explicit memory?
-Explicit memory is divided into episodic memory (personal experiences) and semantic memory (facts and general knowledge).
How is memory stored in the brain?
-Memory is stored in various parts of the brain: the hippocampus (temporary storage), cortex (long-term storage), amygdala (emotional memory), prefrontal cortex (rational thinking and working memory), cerebellum (motor skills), and striatum (habits).
What are some common causes of forgetting?
-Forgetting can be caused by encoding failure, consolidation failure, decay, interference, the tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon, and pruning (elimination of unused neural connections).
What are some types of learning difficulties caused by brain disorders?
-Types of learning difficulties include aphasia (language disorders), alexia (reading inability despite normal vision), agraphia (writing impairment), apraxia (difficulty performing purposeful movements), and agnosia (failure to recognize objects despite intact senses).
What role do the senses play in the learning process?
-The senses play an essential role in learning by providing sensory input. Vision helps with understanding visual information, hearing helps with processing sound, and touch and taste help in understanding texture, size, and taste-related information.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)