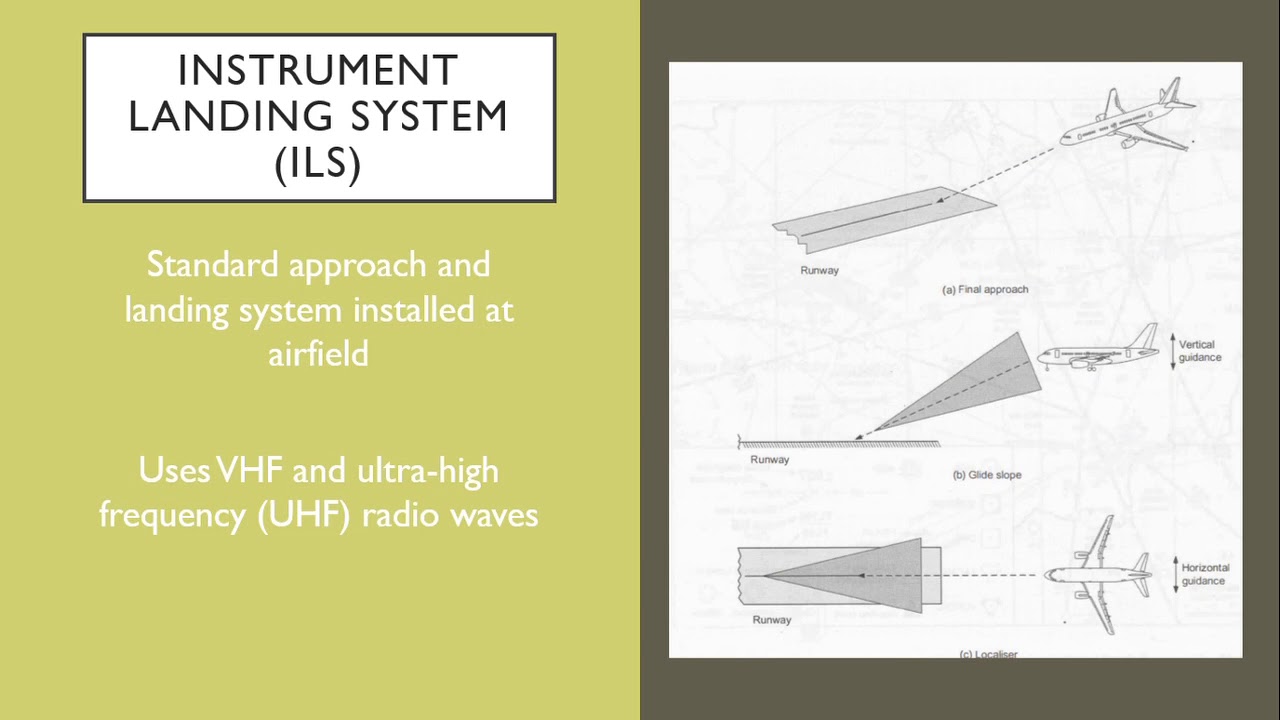
ATPL Radio Navigation - Class 8: MLS.
Summary
TLDRThe Microwave Landing System (MLS) was designed as a more advanced alternative to traditional ILS systems, offering improved navigation capabilities with its precise vertical and horizontal beams. However, due to its high cost and competition from GPS systems, which provide similar or better accuracy without requiring costly ground infrastructure, MLS became largely obsolete. Despite this, MLS remains part of aviation exam syllabi. The system's unique ability to adjust for obstacles, like mountains, made it a promising technology, but its timing was ultimately outpaced by more reliable and cost-effective GPS navigation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Microwave Landing Systems (MLS) were designed to replace older Instrument Landing Systems (ILS).
- 😀 MLS uses microwave signals in the super high-frequency range (5.031 to 5.090 GHz) for vertical and horizontal guidance.
- 😀 The system operates with two beams: one for vertical (elev) and one for horizontal (azimuth) positioning.
- 😀 MLS allows for more complex and flexible approach procedures, including curved flight paths around obstacles like mountains.
- 😀 GPS technology has made MLS obsolete, as GPS can achieve similar results at a lower cost and without ground infrastructure.
- 😀 MLS uses a more accurate Precision DME for determining the distance to the runway compared to traditional DME systems.
- 😀 The horizontal guidance beam sweeps back and forth, allowing aircraft to measure gaps and determine their position.
- 😀 The vertical guidance works similarly, using a fan-shaped beam that sweeps up and down to calculate vertical position.
- 😀 One unique advantage of MLS is the ability to temporarily turn off sweeping beams to prevent interference from terrain.
- 😀 Despite its potential advantages, MLS is rarely used at airports today, with GPS being the dominant navigation system.
- 😀 Although MLS remains in some aviation training syllabi, its practical use is almost non-existent in the modern aviation world.
Q & A
What is the Microwave Landing System (MLS)?
-The Microwave Landing System (MLS) is an advanced navigation technology designed to replace the traditional Instrument Landing Systems (ILS) at airports. It uses microwave signals for both vertical and horizontal guidance during aircraft approach procedures.
Why is the Microwave Landing System not widely used today?
-MLS is not widely used today because GPS technology has become more accurate, reliable, and cost-effective. GPS offers similar capabilities without the need for extensive ground-based infrastructure like MLS.
How does the Microwave Landing System work?
-MLS uses two beams: one for vertical guidance (elevation) and one for horizontal guidance (azimuth). Both beams operate at the same frequency but are distinguished through multiplexing, and a Precision DME provides accurate distance information to the runway.
What is multiplexing in the context of MLS?
-Multiplexing is a technique used in MLS where multiple signals are transmitted simultaneously but given unique identifiers, allowing the system to distinguish between different signals and accurately guide the aircraft.
What is the coverage range for the horizontal beam in the Microwave Landing System?
-The horizontal beam in MLS covers a 40° range on either side of the centerline, extending up to 20 nautical miles.
How does the Microwave Landing System determine the horizontal position of an aircraft?
-The system uses the timing of the sweeping horizontal beam's hits on the aircraft. The gap between the hits helps determine the aircraft's position in azimuth or horizontal direction.
What is the role of the Precision DME in MLS?
-The Precision Distance Measuring Equipment (DME) in MLS provides highly accurate distance measurements to the runway, with an accuracy of plus or minus 100 feet. This enhances approach precision and allows for curved or multiple-waypoint approaches.
Why is the Microwave Landing System considered more flexible than traditional ILS?
-MLS offers greater flexibility because it allows for 3D approach procedures, including curved paths and the ability to avoid obstacles like mountains or valleys, unlike the fixed, linear approach of ILS.
What are the main disadvantages of the Microwave Landing System?
-The main disadvantages of MLS include its high installation and upgrade costs, the susceptibility to signal reflection and interference, and the rise of GPS technology, which offers similar benefits at a lower cost.
Why did GPS replace MLS as the preferred navigation system?
-GPS replaced MLS because it is cheaper, does not require ground infrastructure, and offers similar or superior accuracy. The widespread adoption of GPS made upgrading to MLS less appealing.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)