The Periodic Table Explained
Summary
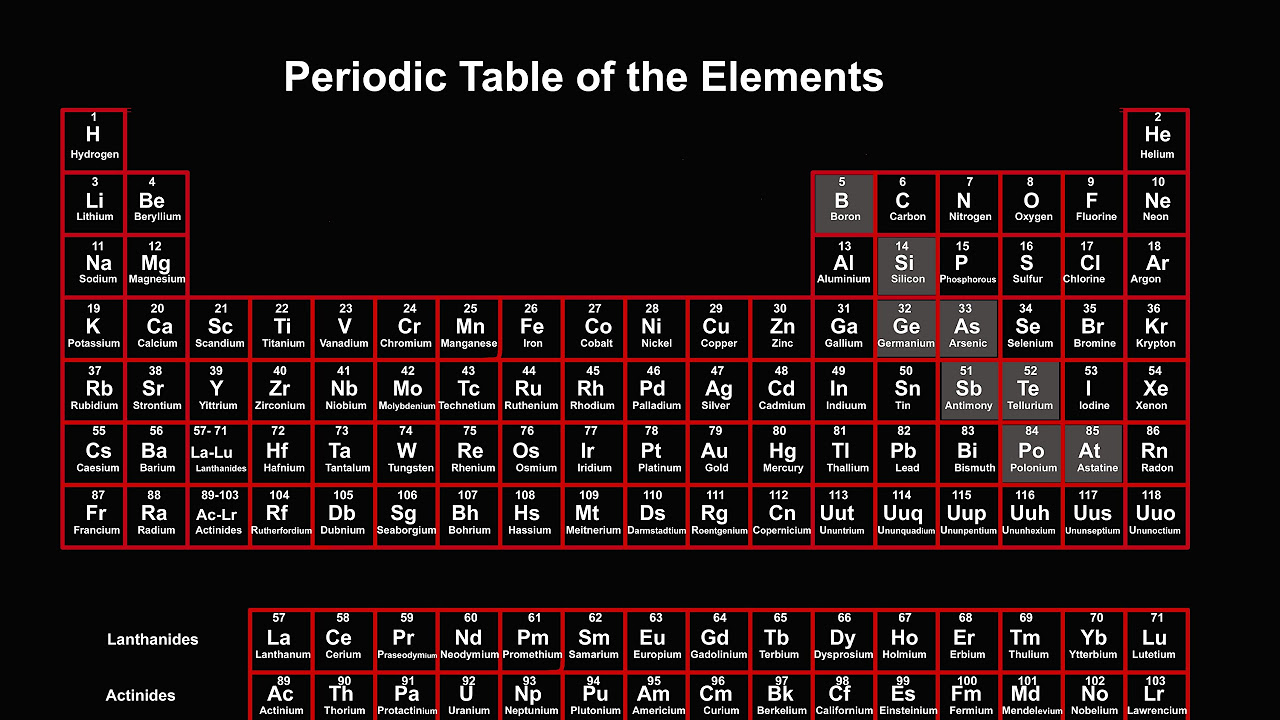
TLDRThe periodic table is a systematic arrangement of elements, each represented by a symbol and defined by its atomic number, which indicates the number of protons in the nucleus. Elements are categorized as metals or nonmetals, and their position reveals patterns in atomic size and ionization energy. The table is structured into rows (periods) and columns (groups), with groups sharing similar properties such as valence electrons. Understanding these trends helps predict element behavior and is essential for scientific experiments and studies.
Takeaways
- 😀 The periodic table represents elements, each made up of atoms with a specific number of protons in the nucleus.
- 😀 Elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, which indicates how many protons are in the atom's nucleus.
- 😀 Each element has a unique symbol (e.g., H for Hydrogen, He for Helium) that represents the atom's name.
- 😀 The periodic table is color-coded to show whether an element is a metal or nonmetal, and to indicate its specific type.
- 😀 Elements are grouped into columns called 'groups,' with similar characteristics shared by all elements within the same group.
- 😀 The rows in the periodic table are called 'periods,' and they correspond to the number of electron shells in an atom.
- 😀 The number of valence electrons (electrons in the outer shell) helps determine how elements bond.
- 😀 As you move down the periods, the atomic size (atomic radius) increases, while moving from left to right across the groups causes the atomic size to decrease.
- 😀 Ionization energy, or how easily an electron can be removed from an atom, decreases as you move down a period but increases as you move from left to right across a group.
- 😀 Understanding the periodic table is crucial for predicting an element's behavior and its application in scientific experiments.
- 😀 Mastering the periodic table is essential for students and scientists to determine atomic structure and understand how elements interact.
Q & A
What does each box on the periodic table represent?
-Each box on the periodic table represents an element, which is made up of atoms with a specific number of protons in the nucleus.
How is the periodic table organized?
-The periodic table is organized by increasing atomic number, which corresponds to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
What is the significance of the atomic number?
-The atomic number indicates how many protons are present in the nucleus of an atom. It also determines the element's position on the periodic table.
What information is typically found within each element's box on the periodic table?
-Each element's box includes the atomic number, atomic mass, element name, and element symbol.
What are groups and periods in the periodic table?
-Groups are the vertical columns in the table, and periods are the horizontal rows. Elements in the same group have similar characteristics, while periods show the number of electron shells.
What do the colors on the periodic table indicate?
-The colors on the periodic table are used to indicate whether an element is a metal or a nonmetal, helping to distinguish between different types of elements.
What do the valence electrons determine?
-Valence electrons, which are found in the outermost electron shell of an atom, determine how the element will bond with other elements.
How do the number of electron shells change as you move down through the periods?
-As you move down through the periods on the periodic table, the number of electron shells in the atom increases.
How does the atomic radius change as you move across the periodic table?
-As you move from left to right across the groups, the atomic radius decreases, meaning the atoms become smaller.
What happens to ionization energy as you move down the periods and across the groups?
-As you move down the periods, ionization energy decreases, while it increases as you move from left to right across the groups. This refers to how easily an electron can be removed from an atom.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
Periodic Table Explained: Introduction

Atom Explained in Simple Terms

How to Read the Periodic Table

Atomic Number & Mass Number | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool

Why Does the Periodic Table Look the Way It Does?

Electron Configuration of First 20 Elements | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
